Description
Harvesting rainwater and separating the first dirty rainwaters, washing the roofs, from the clean following ones. Here is a simple and efficient method based on a T-shaped pipe and a floating ball!
Introduction
Rainwater is fresh water that we can almost drink (depending on regions and local pollution). It is interesting to harvest rainwater for various domestic uses : sanitation facilities (shower, toilets), watering gardens, ... When filtered, it can also be used for drinking.
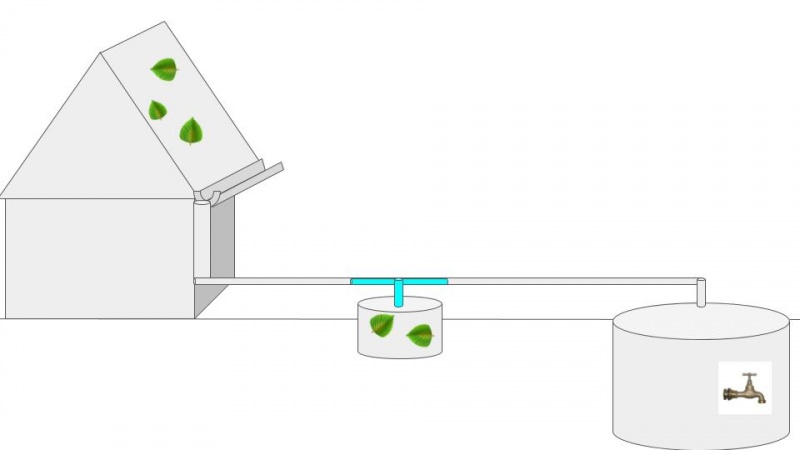
An ingenious system of rainwater harvest has been implemented in Desde Oriente, at Punte de Lobos in Chile. In this place, there is a house where a bunch of inventions are tested in order to become self-sufficient and reduce one's environmental impact. There, all roofs are fitted with a gutter that allows to collect rainwater and direct it to a tank where it will be stored.
The issue lies in the fact that the first liters of rainwater wash the roofs from its accumulated dust, dead leaves and dirt. The simple and efficient tip is to separate these first dirty liters from the next thanks to a T-shaped pipe and a floating ball. This methods prevents the leaves, dirt and particles to clog the smaller piping and filters for clean water.Youtube
Matériaux
PVC pipes of different diameters, bends, junctions, T-shaped pipe
a 50 liters container
A ping-pong ball
Outils
Drill, drill bits
Saw or angle grinder
Personal protective equipment
Étape 1 - Installing the rainwater harvesting system
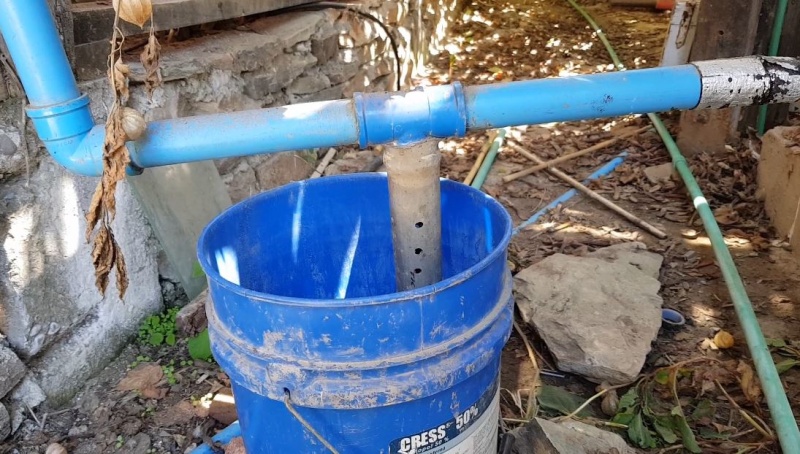
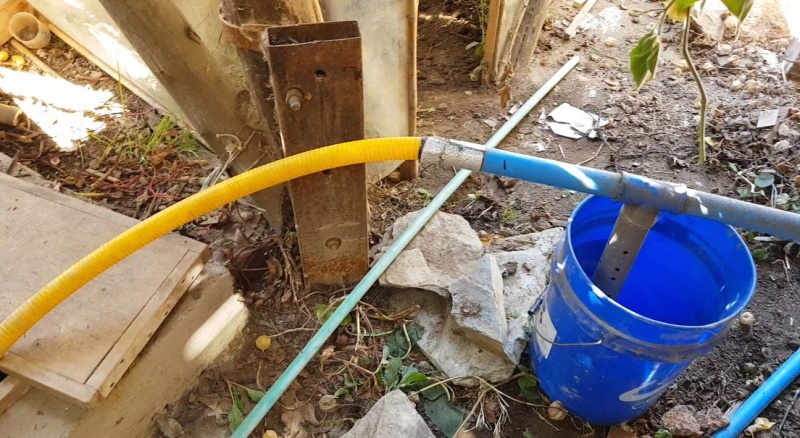
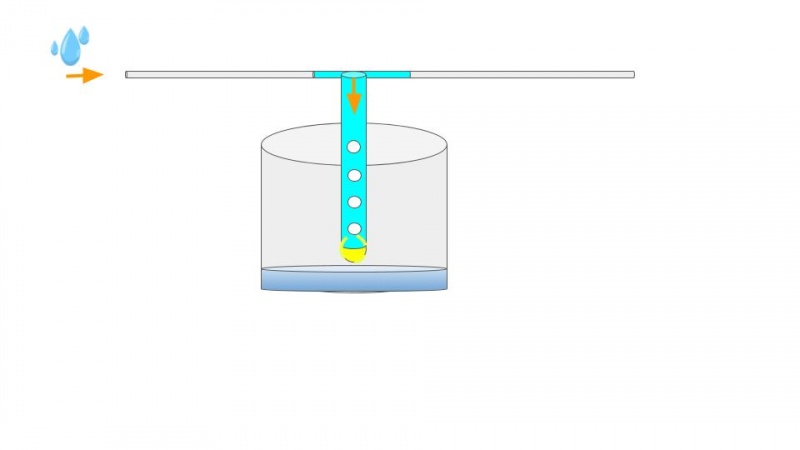
The pipe leading rain waters to the tank (1) comes horizontally and splits in a T :
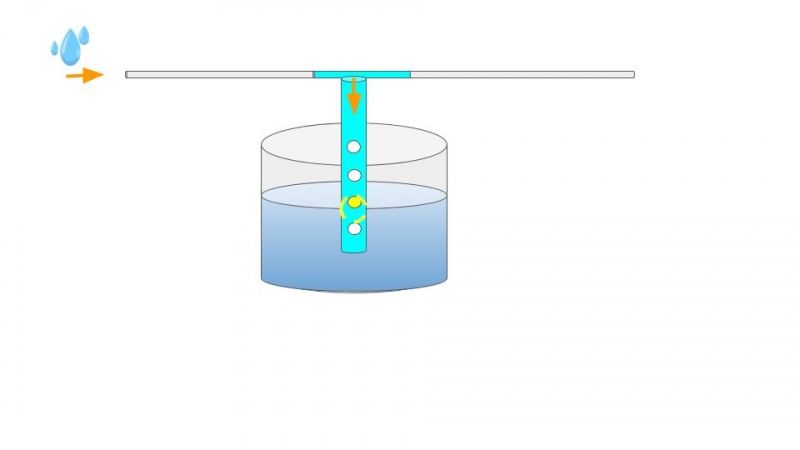
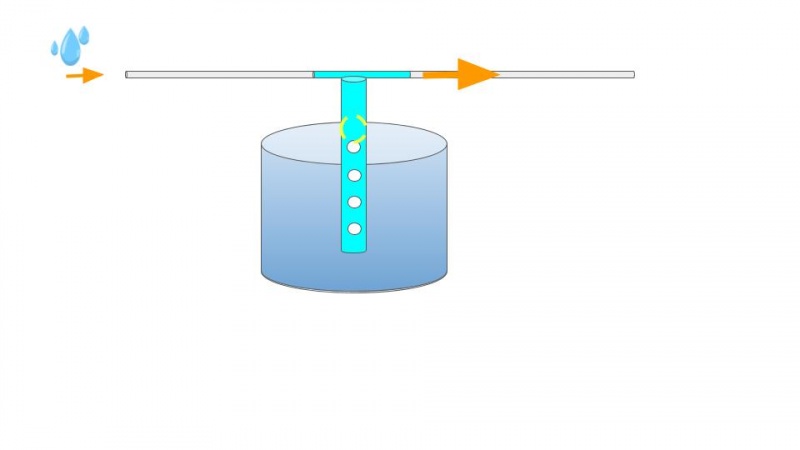
- At first, the water preferentially goes into the 50 centimeters long vertical tube, connected to a 50 liter container (2) (You should adapt the volume based on the roof's surface area). This tube is drilled with holes, allowing the water to fall into the container (2). Inside this tube, there is a floating ball that rises while the water level in the container (2) increase. The ball rises until it is over the holes. The vertical tube is then blocked allowing the water to flow through the horizontal part of the T-shaped pipe.
- This horizontal tube will drive the following clean water directly into the tank (1) of drinking water.
The first 50 liters that washed the roof, collected in the container (2) can be used to water the garden.
Notes et références
Thanks to Jorge, Rodrigo and Sean for welcoming us at DesdeOriente!
Follow Jorge's project at DesdeOrient, in Punta de Lobos, Chile on Instagram "desdeorientepuntadelobos" or desdeoriente.cl.
The next step is to also create a self-sufficient place in water and energy in the center of Santiago in order to prove it is also possible in a town! Stay tuned!
Hydraulic system : http://lowtechlab.org/wiki/Système_hydraulique_global_d%27une_habitation
Electrical system :
http://lowtechlab.org/wiki/Système_électrique_global_d%27une_habitation
We are two French students exploring low technologies in South America. Do not hesitate to follow our adventure here : https://www.facebook.com/LAtelierLowTech/
Published


 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português