(Mise à jour pour être en accord avec la nouvelle version de la source de la page) |
(Mise à jour pour être en accord avec la nouvelle version de la source de la page) |
||
| Ligne 2 : | Ligne 2 : | ||
|Main_Picture=Chauffage_solaire_version_ardoise_47949921956_479ae5b9ec_kk.jpg | |Main_Picture=Chauffage_solaire_version_ardoise_47949921956_479ae5b9ec_kk.jpg | ||
|Licences=Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-SA) | |Licences=Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-SA) | ||
| − | |Description=Solar air heater, adaptable to any type of house, by Guy Isabel. | + | |Description=<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
| + | Solar air heater, adaptable to any type of house, by Guy Isabel. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
|Area=Habitat, Energy | |Area=Habitat, Energy | ||
|Type=Tutorial | |Type=Tutorial | ||
Version du 27 avril 2021 à 10:06
Description
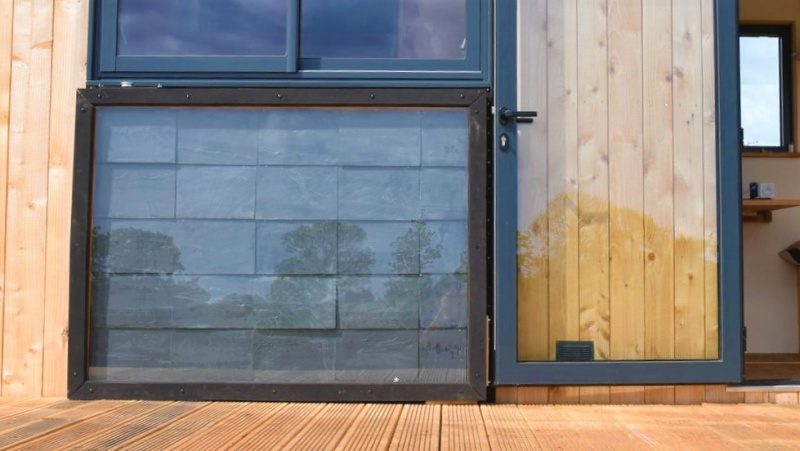
Solar air heater, adaptable to any type of house, by Guy Isabel.
Solar air heater, adaptable to any type of house, by Guy Isabel.
Sommaire
Sommaire
- 1 Description
- 2 Sommaire
- 3 Introduction
- 4 Video d'introduction
- 5 Étape 1 - Téléchager les plans CAO
- 6 Étape 2 - Frame
- 7 Étape 3 - Background and insulation of the frame
- 8 Étape 4 - Opening the sensor input and output
- 9 Étape 5 - Optional: Rain protection
- 10 Étape 6 - Summer hatch
- 11 Étape 7 - Reflective surface
- 12 Étape 8 - Glass weatherstrip
- 13 Étape 9 - Baffle circuit
- 14 Étape 10 - Slate laying
- 15 Étape 11 - Oiling and varnishing
- 16 Étape 12 - Installing the glass
- 17 Étape 13 - Valve system, fixed part
- 18 Étape 14 - Valve system, moving part
- 19 Étape 15 - Valve system, Assembly
- 20 Étape 16 - Installation
- 21 Étape 17 - use
- 22 Étape 18 -
- 23 Étape 19 - Contenu pédagogique à télécharger
- 24 Notes et références
- 25 Commentaires
Introduction
The design of this solar heating was strongly inspired by Guy Isabel, on the plans he describes in his book Les capteurs solaires à air, Eyrolles edition.
The sun transmits energy to the earth by radiation. At the equator, the radiation reaches the power of 1000 W / m², it is by comparison, the power of a small electric heater.
Solar energy is a free and intermittent energy, which is relatively simple to transform efficiently as heat, (yield easily above 60%).
This website allows to know according to the season and the geographical position, many parameters such as the maximum power per m², the angle of the sun compared to the place.
This other website makes it possible to calculate these values almost everywhere on earth by taking into account the horizon line, the orientation of the panels and other parameters. The values displayed by default correspond to the photovoltaic energy generated, but it is possible to display the radiation in kwh/m².
Solar air heater
Concretely, it is a question of transforming the solar radiation into heat thanks to what is called a black body (for example the very hot tar in the summer or the dashboard of a car parked in full sun).
For housing, the most common systems on this principle are solar water heaters, often installed on the slopes of roofs to make domestic hot water supplements of conventional systems.
Less known, the air sensor allows to heat the air of a room.
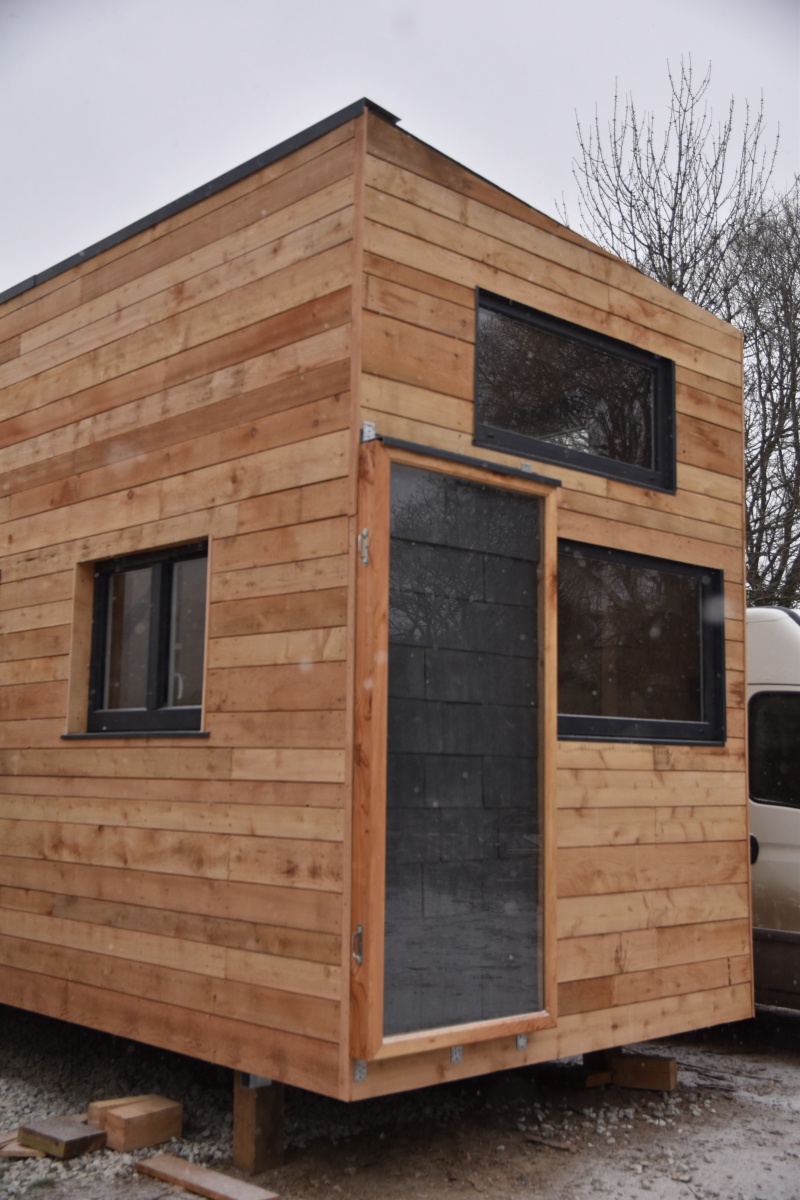
This tutorial presents the manufacture of an air sensor of 2 m² designed for the heating of the air of a room of 10 to 15 m² of 5 to 7 ° C winter on average, for France. It is a complement to the conventional heating system, which allows appreciable financial and ecological savings. At a cost of around € 200, it is quickly amortized.
Principle
In winter, the sensor sucks in the air from below, heats it thanks to the shaving sun, then restores it to the habitat through the high outlet, at a temperature of up to 70 ° C locally instantly diluted in the ambient atmosphere.
In summer, an external hatch allows to reject the hot air of the sensor outside while aspiring at the same time the air of the habitat, thus creating a natural ventilation.
A valve connected to a thermostatic jack, allows to manage automatically and without electricity, the opening of the air circulation, only when it has reached more than 25 ° C in the sensor.
Retrouvez dans ce rapport une analyse à l'usage de ce chauffage solaire, ainsi que des 11 autres low-techs expérimentées lors du projet En Quête d'un Habitat Durable.Youtube
Matériaux
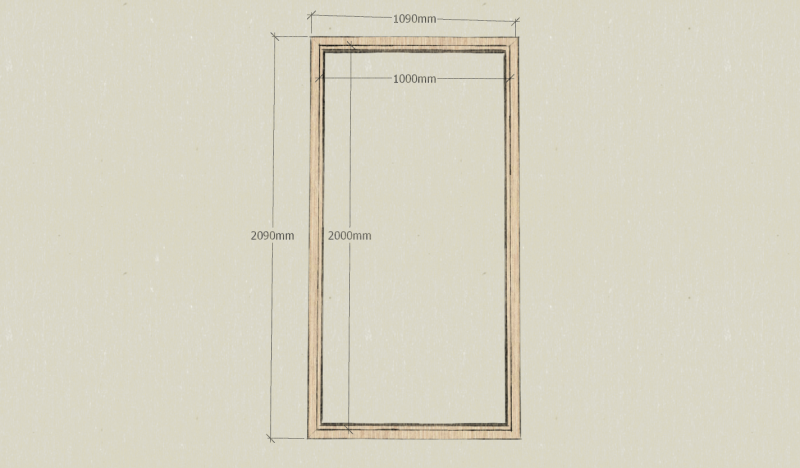
The tutorial presented here is 2.09m x 1.09m overall
Sensor:
- Chevron Douglas (here the final section is 95mm x 45mm)
- 2 of 2m10
- 2 of 1m10
- 15 m of douglas sheets (20mm x 53mm)
- Rigid plate (here plywood filmed, 10mm)
- Rigid insulation (here Steico plate, 22mm)
- Sika cartridge
- Silicone cartridge
- PU glue for outdoor wood gluing
- Wood glue
- Nails
- Wood screws, from 30mm to 150mm
- Comprehensive seal
- Linseed oil
- Wood varnish
- 15 m of douglas sheets (30mm x 16 mm)
- Aluminum adhesive
- Tempered glass or polycarbonate plate (1m x 2m)
- Expanded metal grid (300mm x 50mm)
- 4 screw legs (example)
- 1m of aluminum drip 100mm width (example)
- Double-sided adhesive
- Thin insulation (here parquet insulation)
- 30 to 35 slates 320mm x 220mm, thickness 3,5mm
- 8 reinforced squares, mini width 40mm
- 1 tube diameter 100mm length of the housing wall, pvc / aluminum / stainless steel for the low entrance
Valve system:
- 1 Thermostatic cylinder Vernet EL 0769
- 100mm of brass tube diameter 4mm
- compression spring length 70mm
- 1 washer
- 1 small screw
- 2 rivets
- 5 cm of copper wire diameter 2mm
- 1 domino electrician diameter 4mm
- Plumbing / gas equipment:
- 100mm of threaded brass tube 15/21
- 2 brass blind nuts 15/21
- 1 brass through nut 15/21
- 1 copper sleeve diameter 12mm
- 1 copper sleeve diameter 14mm
- 1 brass nipple 15/21
- 1 ventilation valve, here diameter 100mm
- 1 ball catch
- 1 aluminum or stainless steel tube along the wall of the house wall, diameter of the valve
optional:
- Rain barrier
- Sealant
Outils
- Wood saw
- Screwdriver / drill and wood / metal drills
- Wall stapler
- Paint brushes
- Hammer
- Cutter
- Grinder and diamond / metal discs
Étape 1 - Téléchager les plans CAO
Des plans détaillés et CAO ont été réalisée par Enerlog. Ils sont disponibles en open-source ici: https://cloud.ecutsa.fr/index.php/s/apRoi395xdQb52T#pdfviewer
Ces plans ont servi à la réalisation d’une première version construite en atelier. Ces plans sont ici partagés afin de répondre à un des objectifs d’Enerlog: soutenir la réappropriation des savoirs par les citoyens en partageant la connaissance et en favorisant sa transmission.
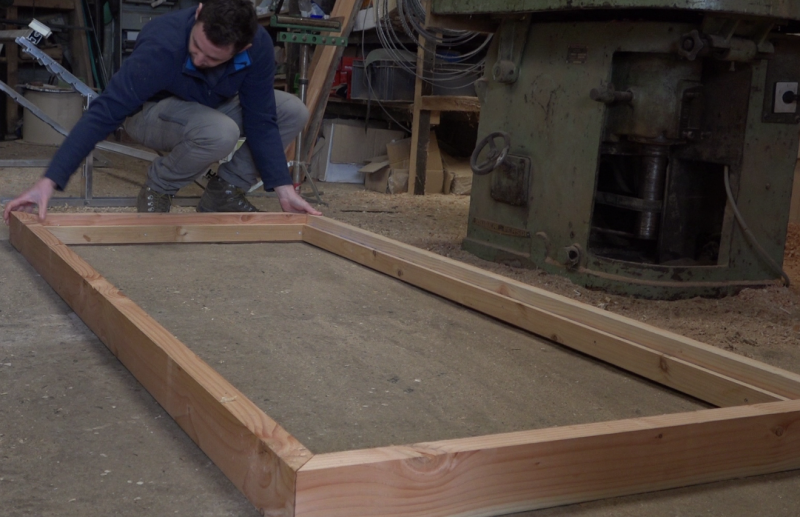
Étape 2 - Frame
Note: Here, the frame is sized to accommodate a glass 1m x 2m by 6mm thick, a 10mm film plywood bottom and a 22mm insulating layer in STEICO. The dimensions will therefore be adapted according to the availability of each.
- Prepare 2 rafters of section 93mm x 45mm and 209 cm in length.
- Prepare 2 rafters of section 93mm x 45mm and 109 cm in length.
- Prepare 2 battens of section 20mm x 53mm and 209 cm long.
- Prepare 2 battens of section 20mm x 53mm and 109 cm long.
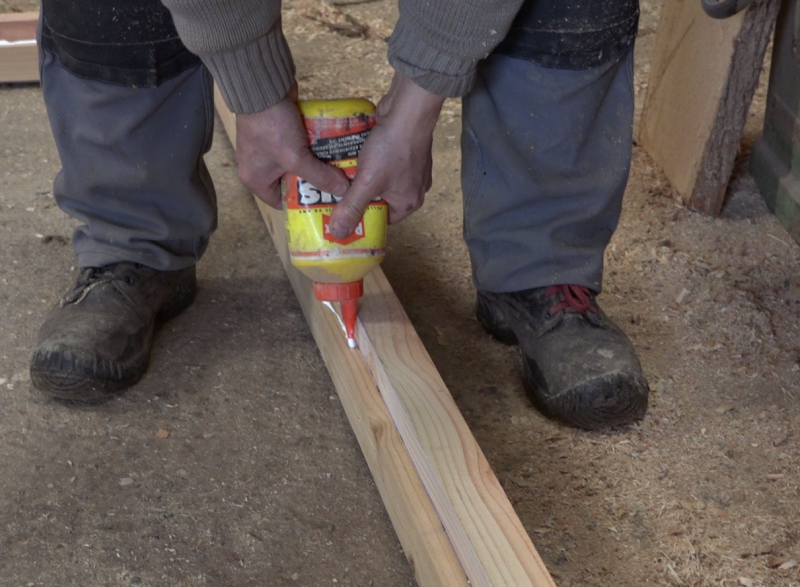
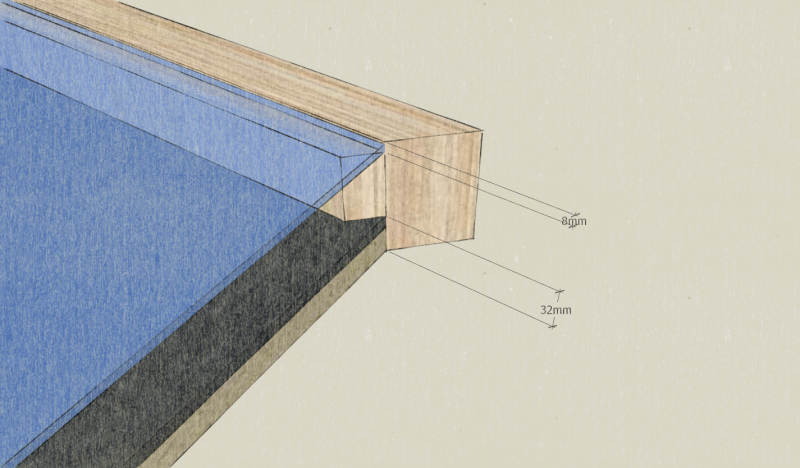
- Glue PU glue and screw the battens on the rafters associated a face of 93mm thick, 32mm from one of the edges.
Note: These 32mm correspond to the insulating thickness + filmed plywood. There is 8mm remaining on the other edge to accommodate the thickness of the glass and a seal comribande.
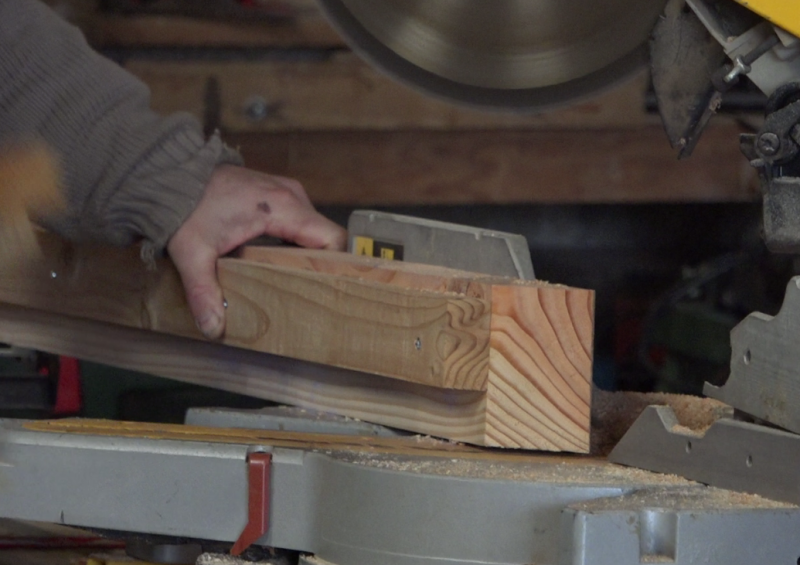
- Cut the corners of each wood profile thus obtained at 45 °, paying careful attention to the direction of the cut. The cut is made on the length of 93mm.
Note: This cut allows to find the dimension 1m x 2m of the window inside the frame.
- Assemble the frame using PU glue and long wood screws in each of the 4 corners.
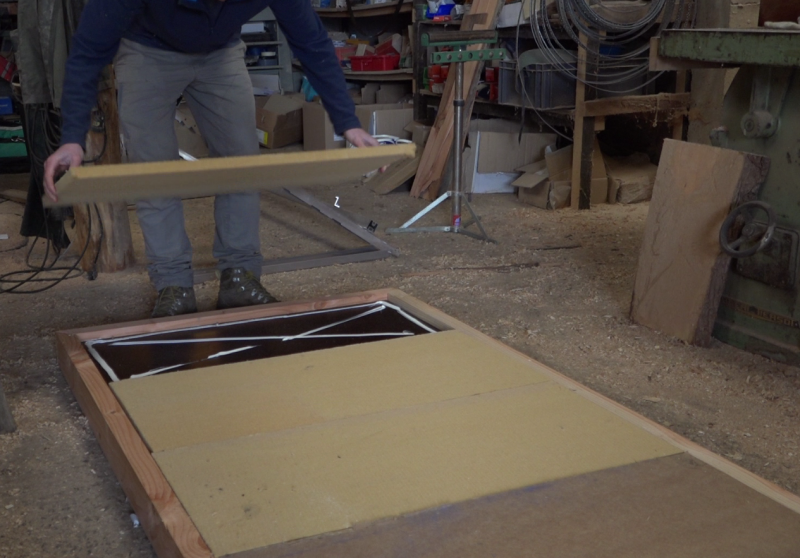
Étape 3 - Background and insulation of the frame
- Prepare an area of 1m x 2m for the chosen background (here a 10mm thick film plywood).
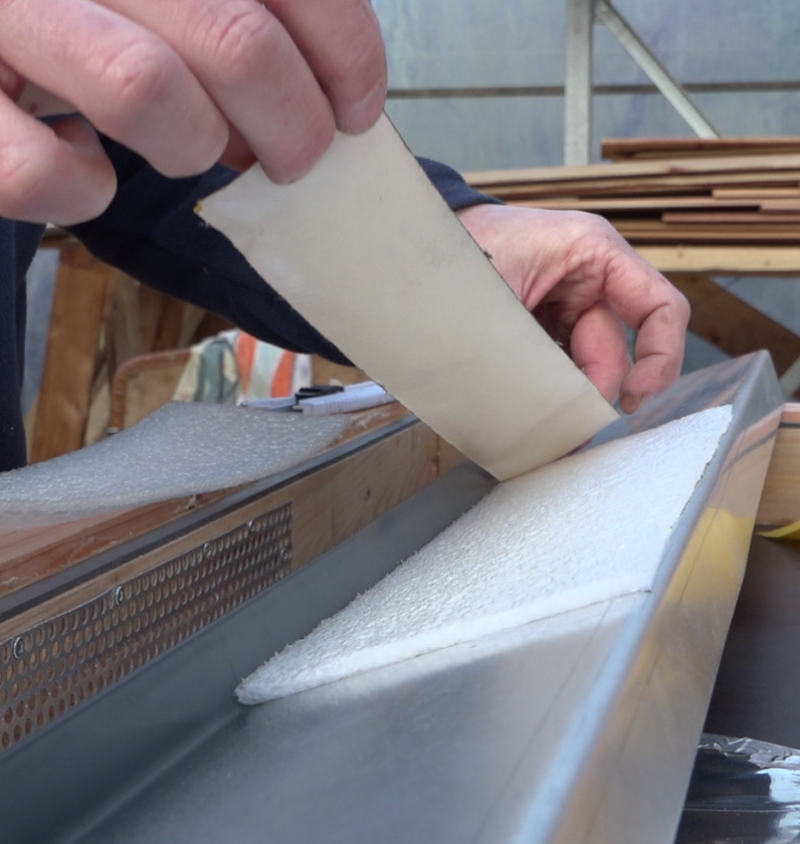
- Prepare a surface of 1m x 2m for the chosen insulation (here STEICO plates of 22mm thickness).
- Pull a wood glue seal on the frame battens, 32mm thick side.
- Deposit 'the bottom first' then ensure the plating with regular studding.
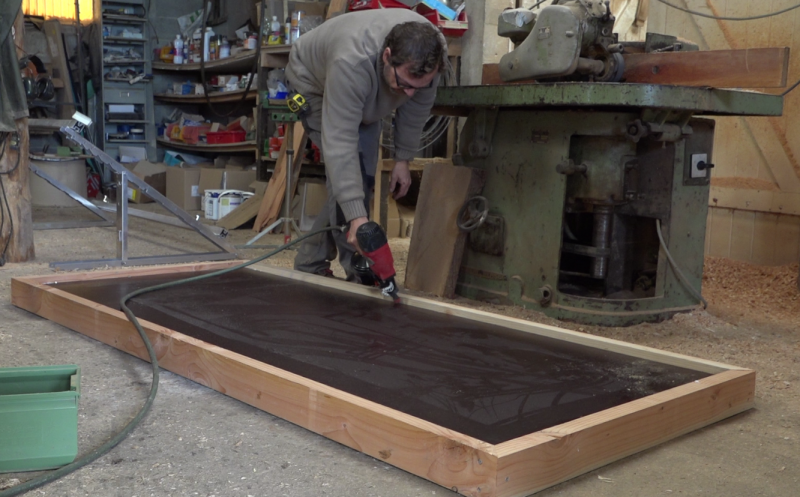
- Draw sika cords on the bottom then lay the insulation. This is the outermost layer of the frame.
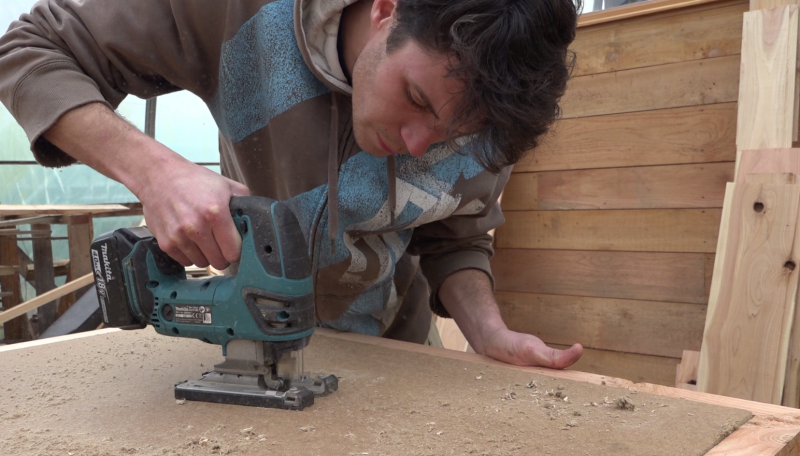
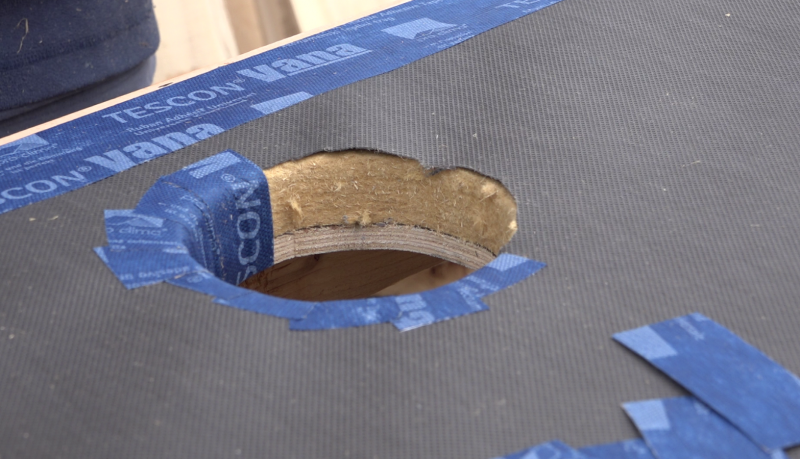
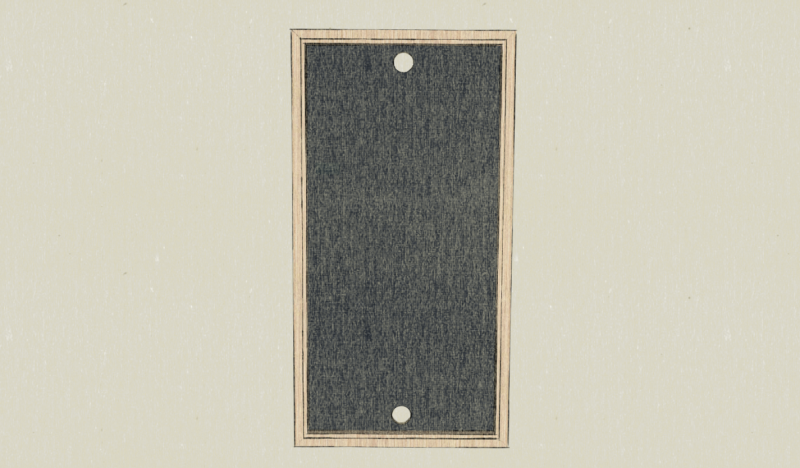
Étape 4 - Opening the sensor input and output
Note: Here, the chosen ventilation flap is 100mm in diameter, so it is at this diameter that the inlet and the outlet will be made.
- On the central axis of the sensor, trace and cut the air inlet hole, 30mm from the batten, at the bottom of the frame.
- On the central axis of the sensor, trace and cut the air outlet hole, 30mm from the batten, at the top of the frame.
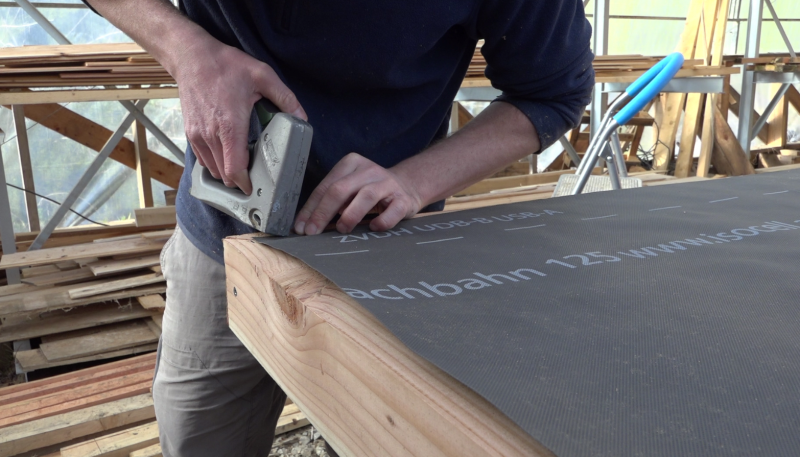
Étape 5 - Optional: Rain protection
Note: Depending on the chosen insulation, the installation of a rain screen at the back is not necessarily necessary if it is well waterproof.
- Remove the rain cover on the insulation layer leaving a 2cm overhang on the Douglas frame.
- Staple the rain cover.
- Open the rain shield at the inlet and outlet.
- Glue a waterproof adhesive between the frame and the rain screen.
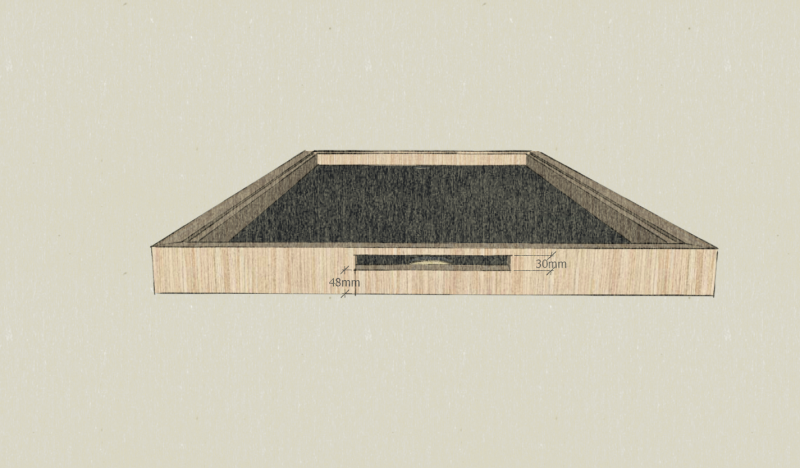
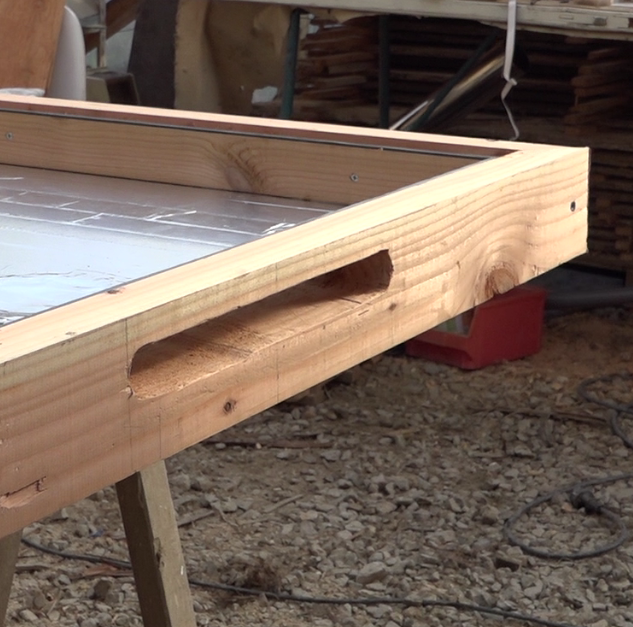
Étape 6 - Summer hatch
- On the upper part of the frame, open a hatch of 300mm long by 30mm wide. It is at the bottom of the water.
- Fix inside the anti-rodant grill
- Using double-sided tape, center and glue a rectangle of parquet insulation on the underside of the dripstone, which serves as a cover.
- Position 4 screws around the hatch taking care to check that the parquet insulation can be placed in the rectangle formed by the screw legs.
- Drill the drip so that it can fit on the screw legs.
- Put it aside, it will be added at the end of editing.
Étape 7 - Reflective surface
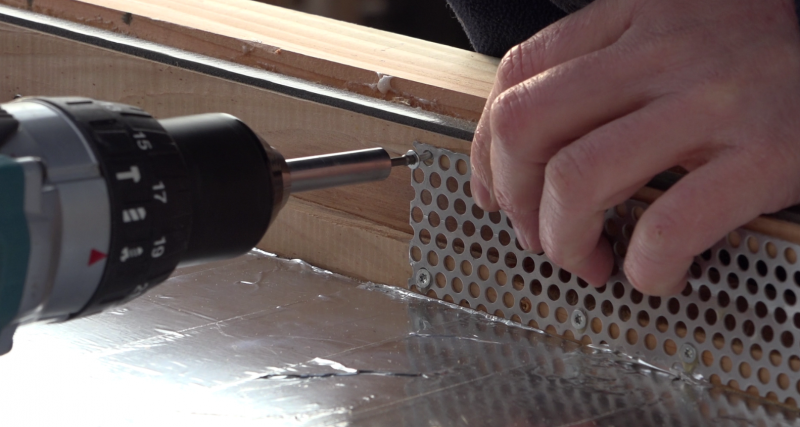
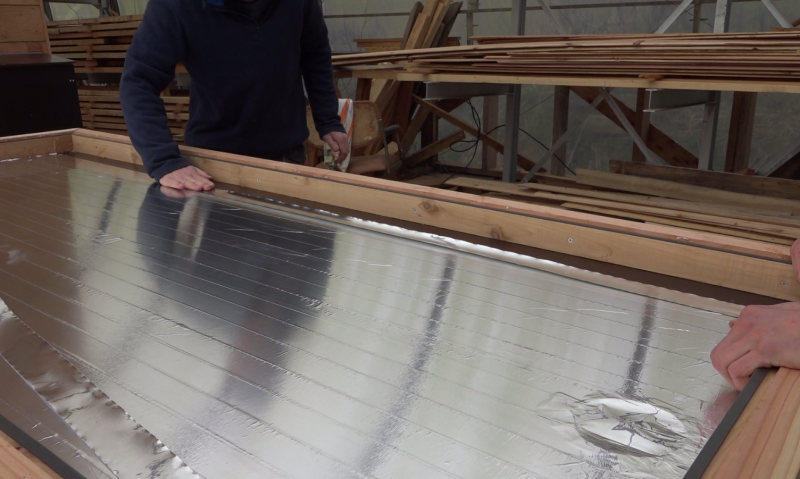
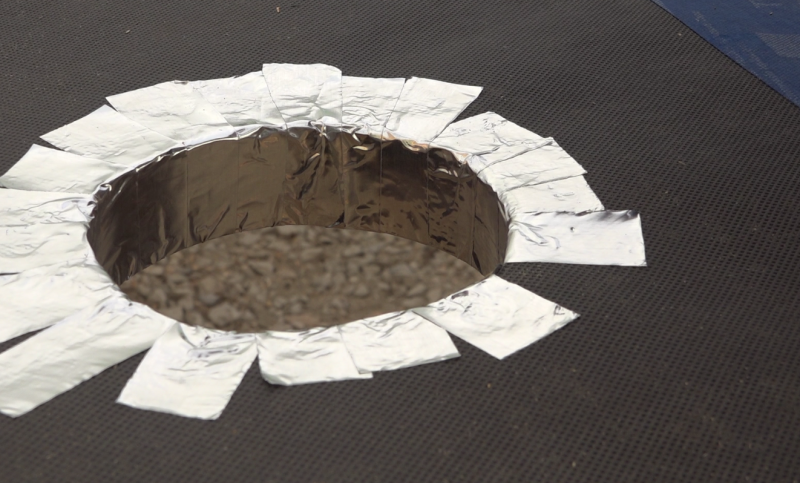
Note: In order to reduce the energy loss in the sensor, the film plywood bottom is covered with an aluminum layer to reflect the infrared radiation in the sensor.
- Line the bottom of the aluminum adhesive sensor.
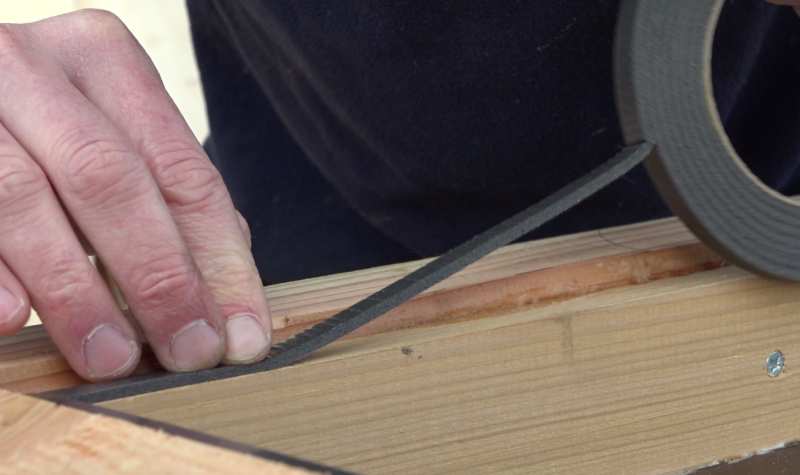
Étape 8 - Glass weatherstrip
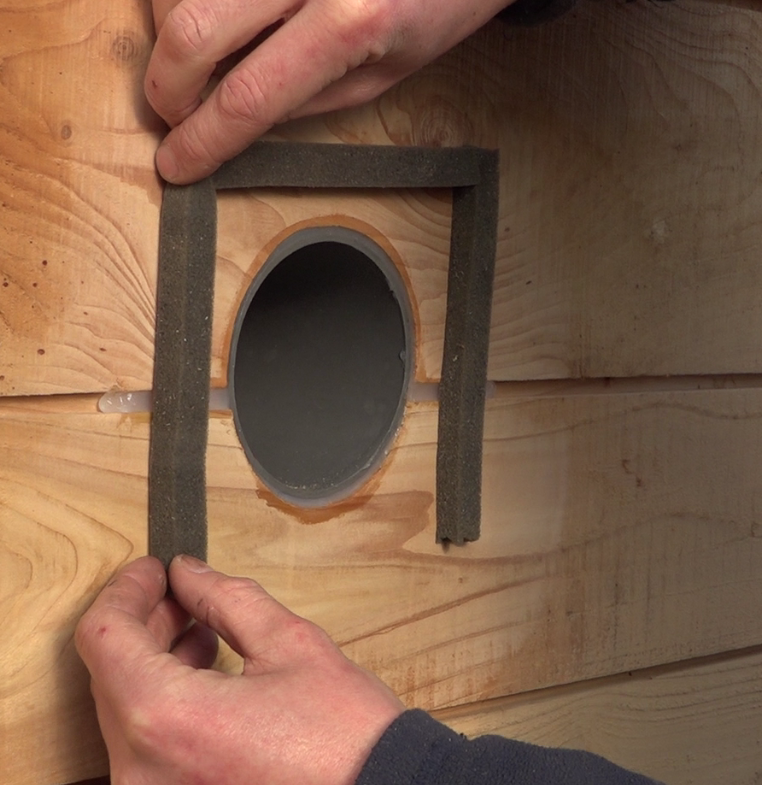
- Place an adhesive joint on the battens of the frame 1mm from the edge, all along the frame. It will serve to welcome the glass.
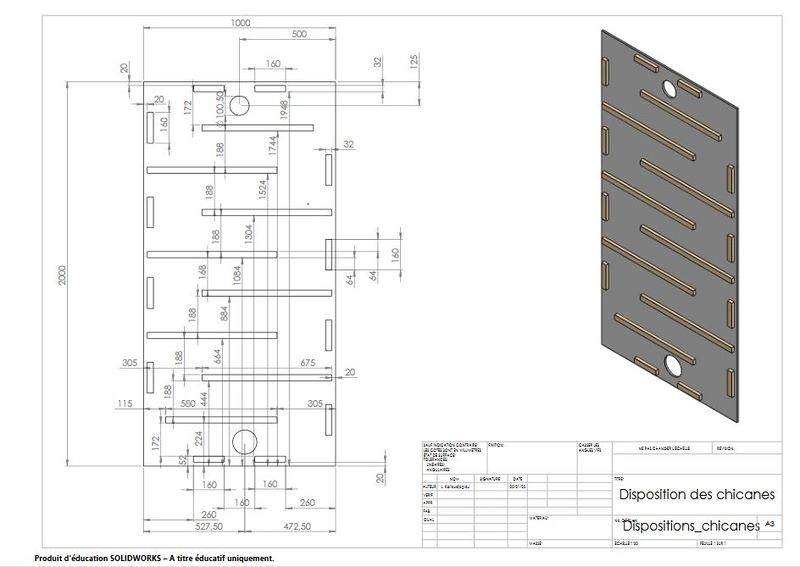
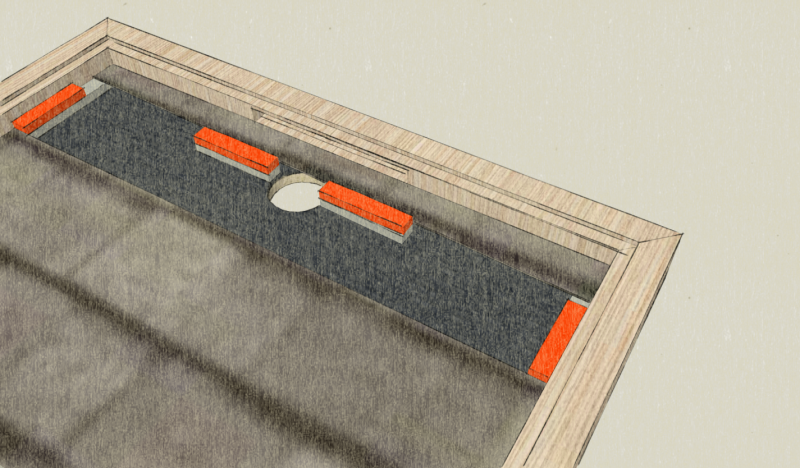
Étape 9 - Baffle circuit
- Screw the 30mm x 16mm battens to the reflective part in a baffle pattern.
- The baffles, by 675mm, cover 3/4 of the width of the panel.
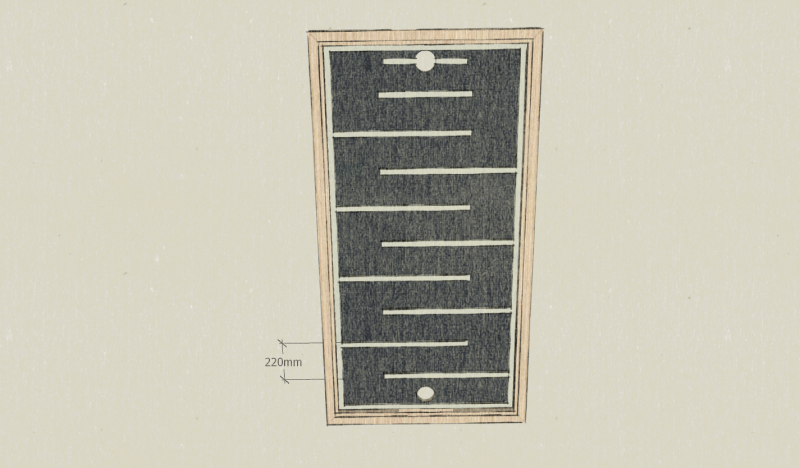
Note: Here, the gap including 2 cleats is 220mm, this is the width of the slates used later. This spacing will allow a slight recovery of each slate.
'Note' : Here, the gap including 2 cleats is 220 mm, this is the width of the slates used later. This spacing will allow a slight recovery of each slate.
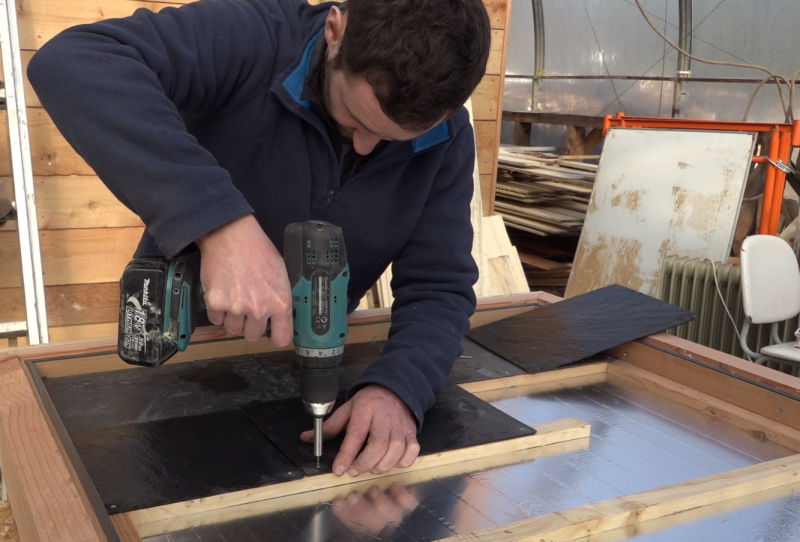
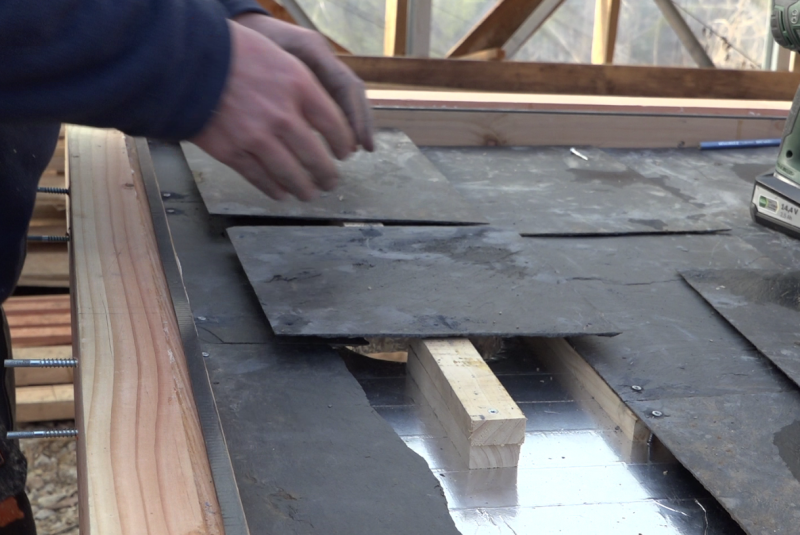
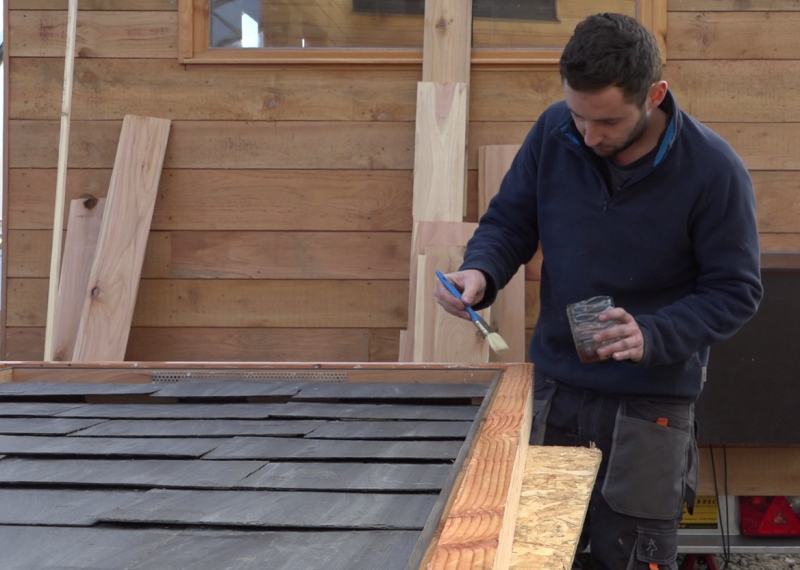
Étape 10 - Slate laying
- Position the first slate rack on the lowest level of baffle.
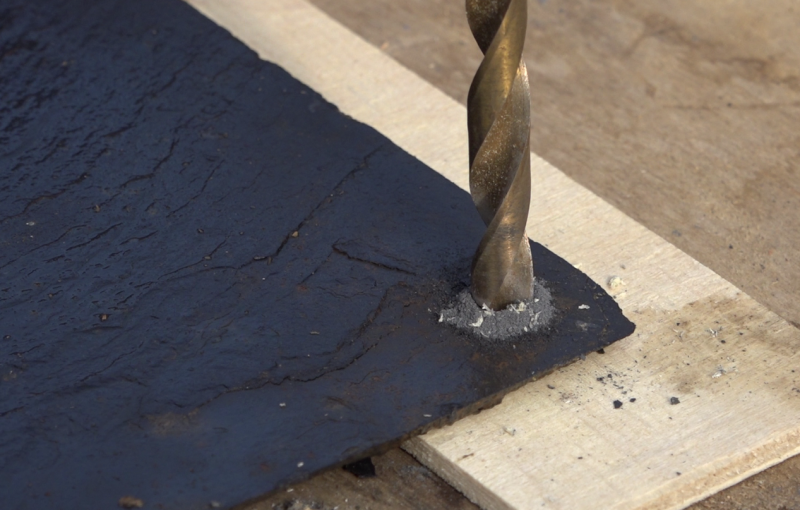
- Mark 2 holes and drill with a 4mm drill. It is possible to slightly mill the holes with a wider drill so that the screw head is integrated in the thickness of the slate.
- If necessary, cut the slates with the diamond disc grinder, a hacksaw can possibly do the trick.
- Complete the slate frame, taking care to raise the slates on the baffles closest to the exit (see photo).
Note: The row of slate is raised near the exit so that the air in front of and behind the slates can be evacuated, both in winter and in summer by the "summer hatch".
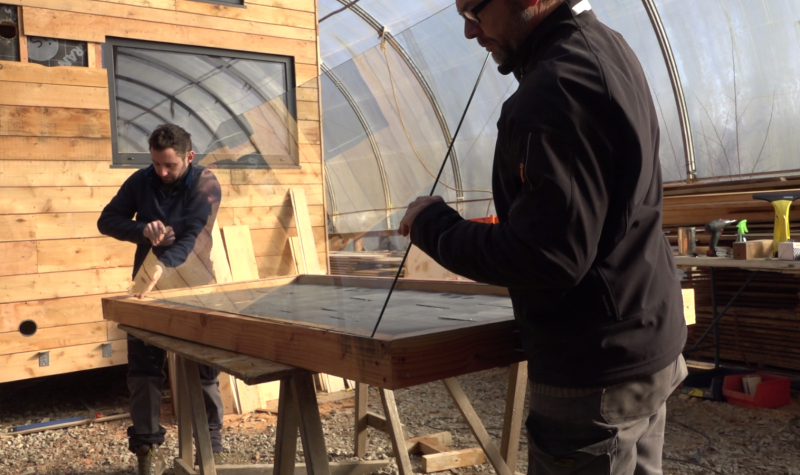
Étape 12 - Installing the glass
Note: Here, a tempered glass 6mm thick is used. It is also possible to use polycarbonate.
- Clean the glass.
- Prepare the beading in the rest of battens of 53mm x 20mm. A chamfer is made for a good water evacuation and a 45 ° cut as for the frame. Oil and varnish the screens.
'Note:' The baffles are used to hold the glass in its housing by compressing the compression joint. They must both cover the edge of the glass and rest on the frame.
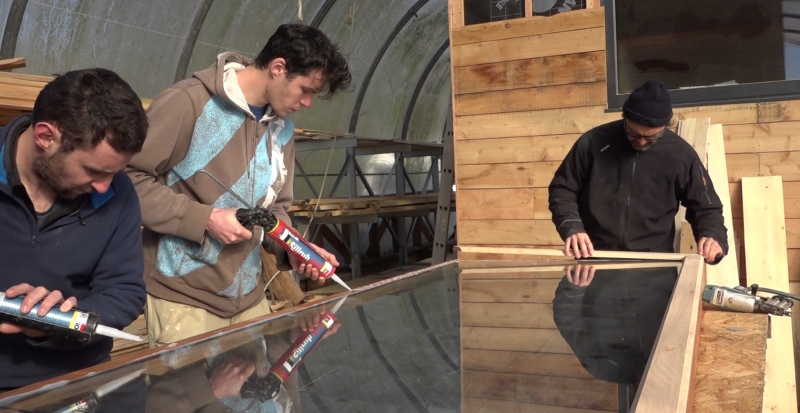
- Pull a silicone gasket between the compression seal and the frame.
- Position the glass.
- Pull a silicone seal again on the edge of the glass as well as on the frame.
- Position and screw the baffles.
- Pull a silicone bead on the glass edge / beading
.
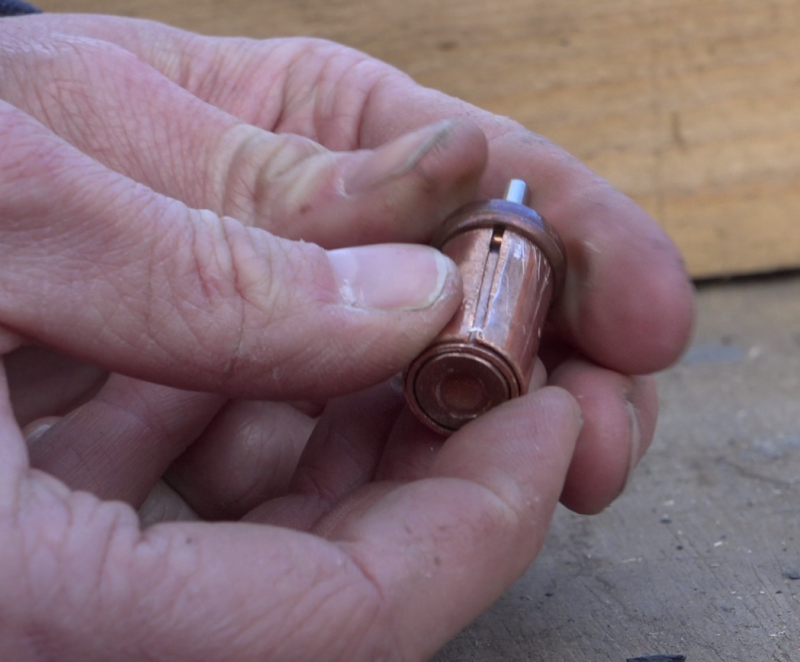
Étape 13 - Valve system, fixed part
Note: The thermostatic cylinder works without electricity. It contains a calibrated material that expands from 25 ° C and retracts below.
- Limer the internal pointing of 12mm and 14mm copper sleeves
- Split the length of the 14mm sleeve.
- Insert the cylinder into the 12 mm sleeve and all into the 14 mm sleeve.
- Insert this assembly into the brass nipple 15/21.
- Close the bottom side of the cylinder by aiming a blind nut on the nipple.
- Screw the open nut onto the other side of the nipple.
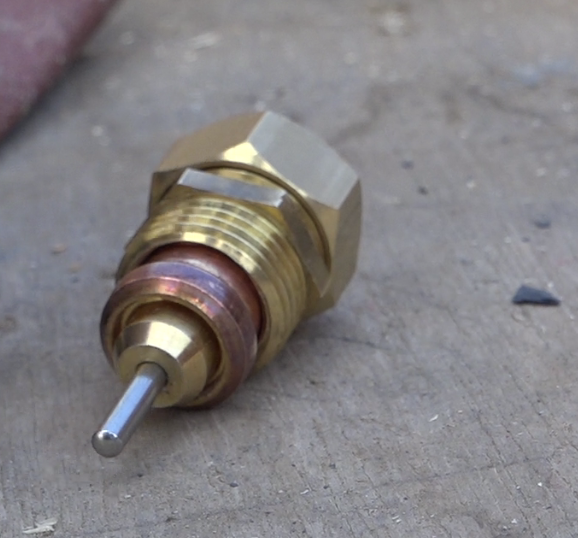
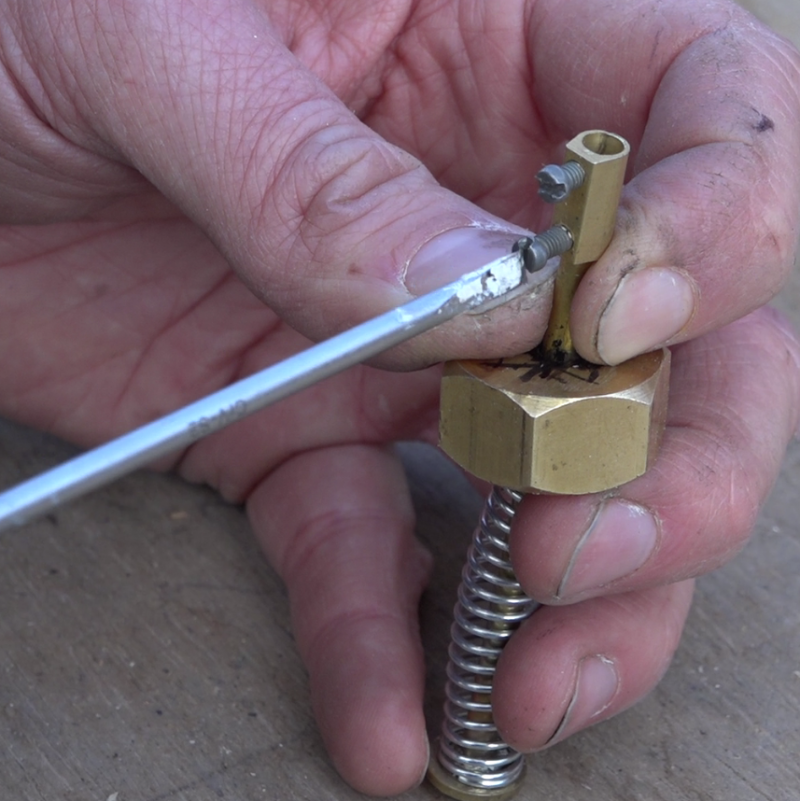
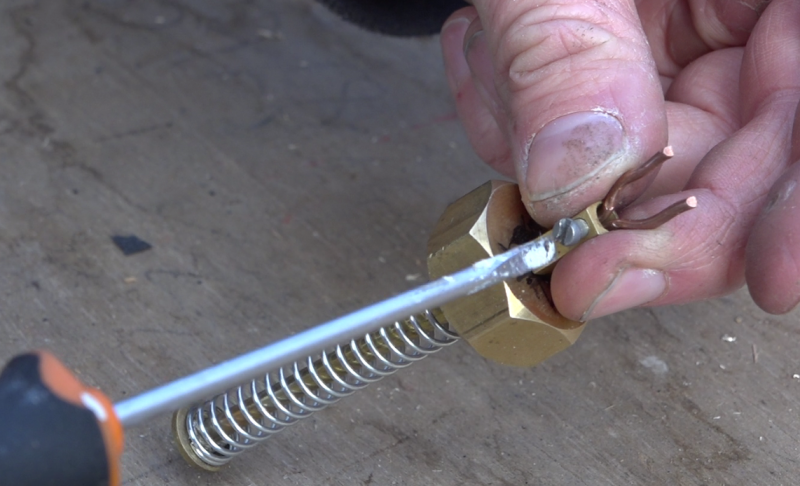
Étape 14 - Valve system, moving part
- Cut 100mm of brass tube diameter 4mm.
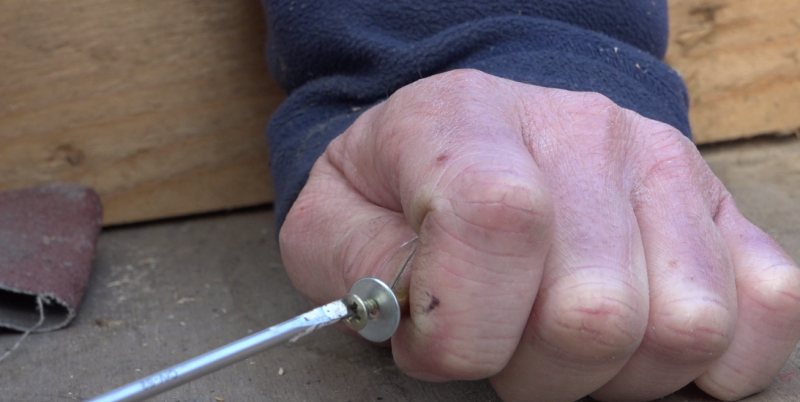
- Insert a screw and a washer at one end.
- Drill a 15/21 brass nut in the center with a 4mm drill bit.
- Insert the spring and the drilled nut on the tube.
- Remove the plastic part of a domino diameter 4mm and screw it on the free end of the brass tube.
- Prepare a small fork in thick copper wire and place it on the domino.
- A brass threaded tube 15/21 is used to hold the moving part thus created. Cut this tube so that once screwed into the fixed part, the spring is slightly compressed when the cylinder is retracted (cold).
- Assemble everything without forgetting to pass 2 nuts around the threaded tube.
- Glue the fixed part of the ball catch onto the flat of the 2 nuts of the threaded tube.
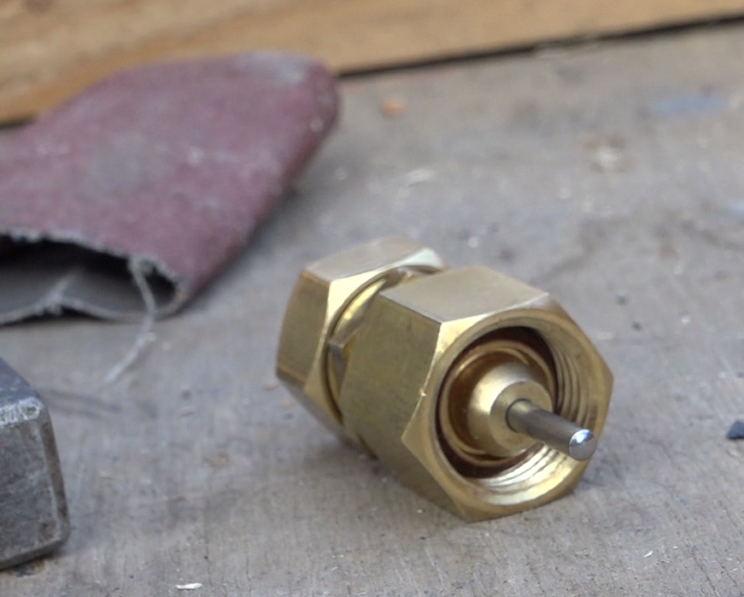
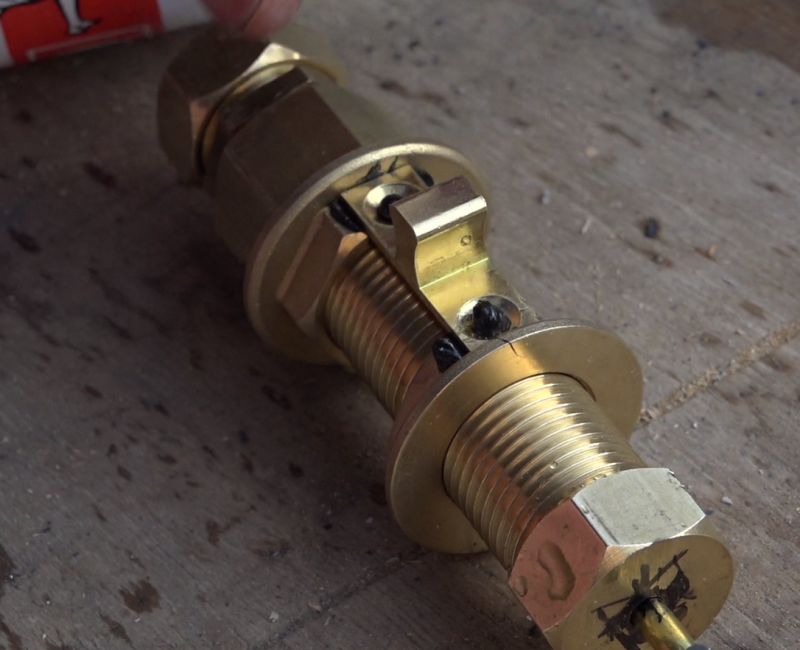
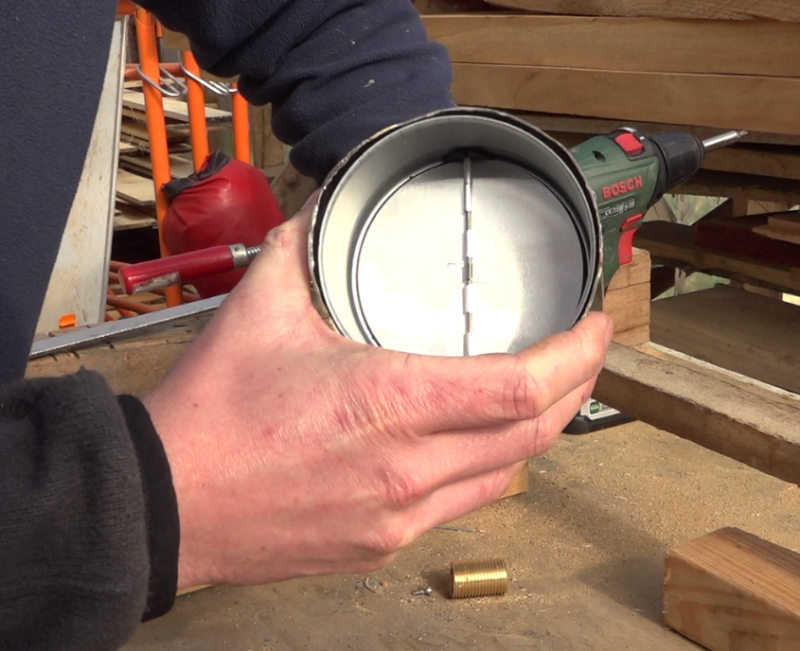
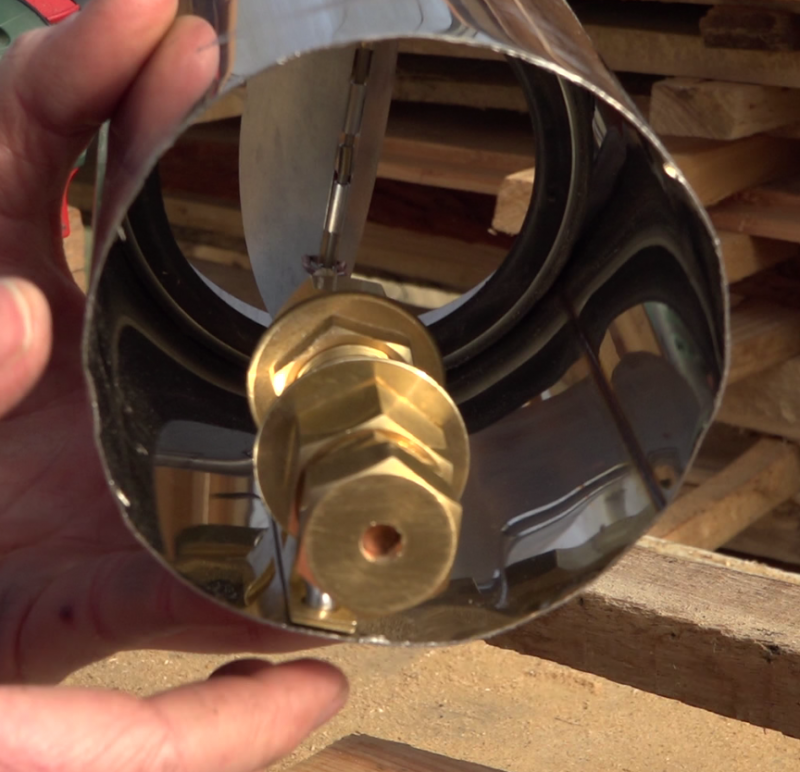
Étape 15 - Valve system, Assembly
- Prepare a stainless steel tube of the width of the wall where the sensor will be installed. (here, a 100mm diameter tube is used)
- Position the valve at one end of the tube, the opening to the outside
- Mark the positioning of the cylinder assembly, hot and completely out , so that the copper fork pushes the fins in maximum opening.
- Rivet the ball portion of the latch to this position.
- Place the tube in the wall, at the air outlet of the sensor, the flap towards the habitat.
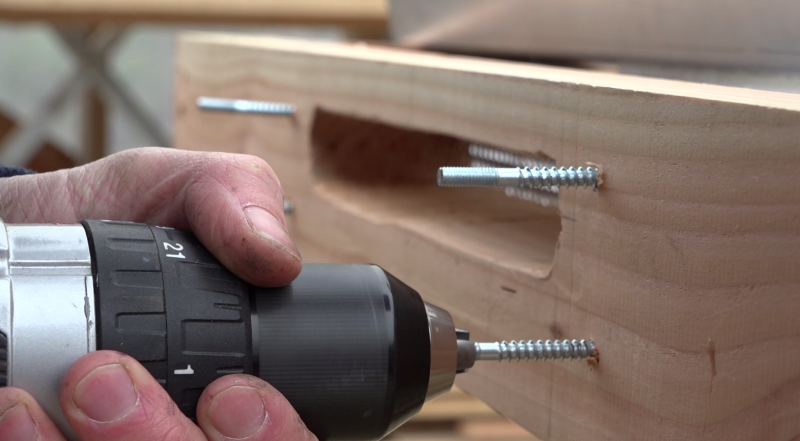
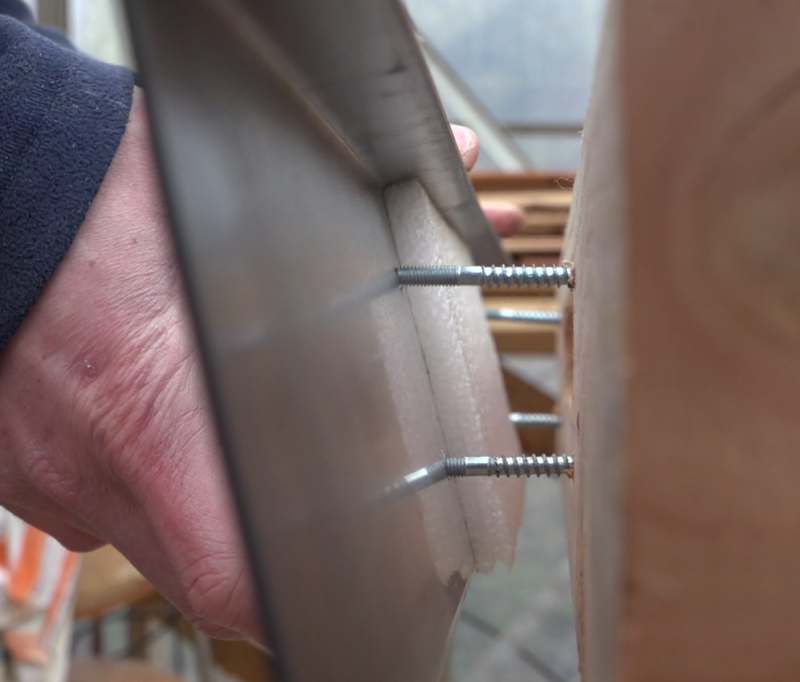
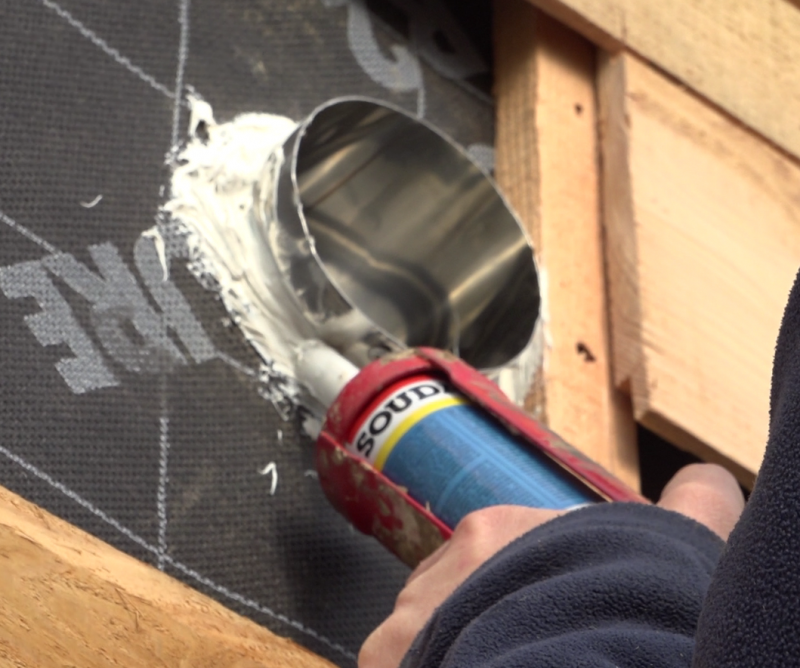
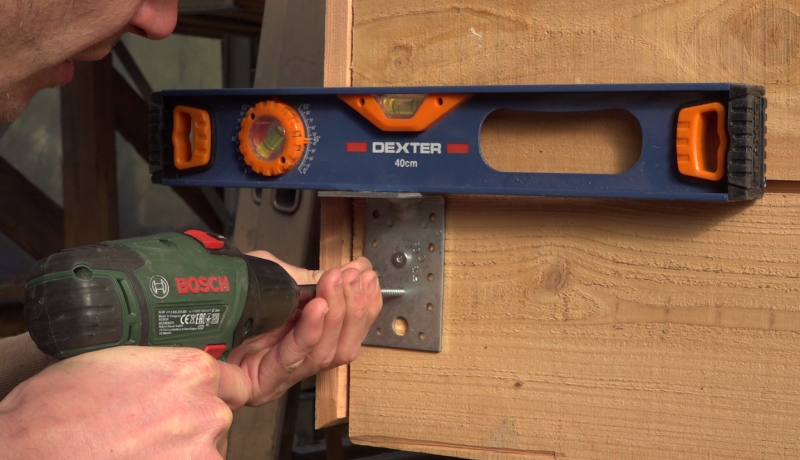
Étape 16 - Installation
- Glue a compound seal around the entrance and exit holes on the habitat.
- Position the sensor support brackets on the wall, at the bottom and at the top, then screw the sensor tightly to the wall so that the compression joints are stressed.
Étape 17 - use
Winter :
- Leave the hatch closed.
- The grazing winter sun shines on the slates that will heat the sensor enclosure.
- By "thermosyphon" effect, the warm air will naturally rise, creating a draw sucking the air of the habitat from the bottom of the sensor.
- Circulation will only be allowed by the valve when the temperature in the sensor will exceed 25 ° C.
Summer:
- Open the summer hatch
- The sun shines on the slates that will heat the system.
- The air will naturally go up and escape out through the summer hatch.
- A suction through the bottom hole of the sensor will allow to evacuate the air of the habitat thus creating a natural summer ventilation.
Étape 18 -
Vous avez une minute ? Que vous souhaitiez ou non réaliser cette low-tech, votre réponse à ce formulaire nous aiderait à améliorer nos tutos. Merci d'avance pour votre aide !
Comme tout le travail du Low-tech Lab, ce tutoriel est participatif, n'hésitez pas à ajouter les modifications qui vous semblent importantes, et à partager vos réalisations en commentaires.
Étape 19 - Contenu pédagogique à télécharger
Vous pouvez télécharger une fiche pédagogique créée par le Low-tech Lab à l'occasion de l'exposition "En Quête d'un Habitat Durable" dans la partie "Fichiers" du tutoriel (onglet au niveau de la section "Outils-Matériaux")
Notes et références
- Guy Isabel, Solar air collectors, Eyrolles edition.
- Tutorial directed by Camille Duband and Pierre-Alain Lévêque as part of the, February 2018.
- Thanks to Jean Daniel Blanchet for the experimentation on one of these tiny houses, penty cozy in Langolen, Brittany.
- Thanks to Benjamin and Mickaël for their help.
- Black Body, wikipedia.
Published









































 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português