(Page créée avec « Unzip the obtained archive ») |
(Page créée avec « text previously copied <blockquote> ») |
||
| (288 révisions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 152 : | Ligne 152 : | ||
Unzip the obtained archive | Unzip the obtained archive | ||
| − | + | Use balena etcher to create a bootable usb stick to install dietpi on your single board computer (orange pi 5 in the present case but it works the same on other single board computers) | |
https://etcher.balena.io/#download-etcher | https://etcher.balena.io/#download-etcher | ||
| − | Double | + | Double click on the downloaded file |
| − | + | Select the dietpi downloaded image, select your usb stick, click on flash. | |
| − | + | You only need to plug the usb stick on the orangepi and it will boot automatically on the usb stick. | |
| − | + | For a raspberry pi, we use a sd card but we can configure the usb boot as well (see here:https://makerhelp.fr/booter-un-raspberry-pi-4-sur-un-disque-dur-ou-un-ssd-en-usb ) | |
| − | + | Install nextcloud | |
| − | + | Power your orangepi/raspberrypi with the usb stick plugged. | |
| − | + | The default login at boot is root and the password is dietpi. | |
| − | + | Follow the menus at first boot to install the nextcloud service. It is very easy, it is in english and everything is automated. I have put the images of the menus you have to select. to install nextcloud: see in this stage and on stages 3 to 6 | |
| − | + | You can move the menus with the keyboard and the arrows and the tab key | |
| − | + | Select with space and validate with enter | |
| − | + | See images at stages 3 to 6 for the installation process and select the entries | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Ligne 187 : | Ligne 187 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Install nextcloud 2/4 |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=see images |
|Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_05.jpg | |Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_05.jpg | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_06.jpg | |Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_06.jpg | ||
| Ligne 197 : | Ligne 197 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Install nextcloud 3/4 |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=see images |
|Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_11.jpg | |Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_11.jpg | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_12.jpg | |Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_12.jpg | ||
| Ligne 207 : | Ligne 207 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Install nextcloud 4/4 |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=see images |
|Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_17.jpg | |Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_17.jpg | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_18.jpg | |Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_18.jpg | ||
| Ligne 216 : | Ligne 216 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Configure local ethernet or wifi network |
| − | |Step_Content=<u>' | + | |Step_Content=<u>If you don't have a box and you have a orange pi or raspberry pi and you want connext to a wifi (for example wifi of a shared connection smartphone) </u> |
| − | Dietpi | + | Dietpi gives a utility to configure automatically the wifi which works on raspberry. At my place it works only if the network is wpa2. If you want to activate wpa3 or if |
| + | you want to configure your wifi manually, here are the steps to follow. | ||
| − | Linux | + | <div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
| + | Linux is a bit complicated for network management. A lot of programs exist allowing to manage networks (networking, network interfaces, ifup, wpa_supplicant, network_manager, ifconfig, ip...) | ||
| + | network_manager, ifconfig, ip...). | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| − | + | If you know well, do what you think is best suited for you. | |
| − | + | Otherwise, we will use the default programs installed with dietpi for managing wifi interfaces: wpa_supplicant and dhclient. | |
| − | + | Begin with plugging a wifi usb adapter to your orangepi or verify your wifi adapter on your raspberry pi is well detected. | |
| − | wifi | ||
| − | + | On a orangepi: verify the adapter is well detected entering: <pre>lsusb</pre> | |
| − | <pre>lsusb</pre> | ||
| − | + | This command will list the usb devices and you should see your wifi usb stick in the list. Then verify that the drivers of your usb stick have been loaded entering: <pre>dmesg</pre> | |
| − | |||
| − | <pre>dmesg | ||
|Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_change-ubuntu-ip-address-step-7.jpg | |Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_change-ubuntu-ip-address-step-7.jpg | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=configuring a wireguard vpn to make your server more accessible from a 4g box or a 4g modem |
| − | |Step_Content=<nowiki>[ | + | |Step_Content=<nowiki>[Watch out, this section puts into question the vpn market!!]</nowiki> |
| − | + | This section is useful for 4G connections or in wifi on a smartphone (4G or 5G) | |
| − | + | The 4g has the advantage to be mobile with a very low power consumption of the modem, around 5W, and you can find 4g modems without wifi to limit the attack surface of your server (example netgear lm1200 around 150€) | |
| − | + | what is a vpn? | |
| − | + | The vpn are mainly known to be vpn "clients". Ie you use it on your computer to become "anonymous". | |
| − | + | The vpn is in fact a tunnel between your computer and another distant computer, from which your requests go on to the internet. Your traffic in direction of the internet goes through this tunnel. | |
| − | Internet | + | Internet then thinks your requests come from this distant computer. That is to say your public ip becomes distant computer one. |
| − | + | Your internet provided doesnt see the traffic between your computer and this distant computer, which makes you "anonymous" | |
| − | + | In reality, you are anonymous for your internet provider, but you only move the trust you had in your internet provider to your vpn provider who can see your traffic. | |
| − | + | The vpn has also other uses like giving you access to websites being filtered on a geographic basis (information that can be deducted from your public ip) | |
| − | + | You can very well create your own vpn server, and in our case, this vpn server will redirect the internet requests made on this server to your orangepi/raspberry pi going through the tunnel (in the other direction than when you use it as a client to access the internet) | |
| − | + | An wee will see how. | |
| − | + | Create a server on gandi.net | |
| − | + | Create an account on gandi.net, then create a server on gandicloud vps. See images for the 3clicks server creation that costs 5€/month. | |
| − | + | To create a ssh key and log in see: | |
| − | <nowiki>https://docs.gandi.net/fr/ | + | <nowiki>https://docs.gandi.net/fr/cloud/operations_courantes/connexion_serveur.html</nowiki> |
<nowiki>https://docs.gandi.net/fr/cloud/operations_courantes/connexion_serveur.html</nowiki> | <nowiki>https://docs.gandi.net/fr/cloud/operations_courantes/connexion_serveur.html</nowiki> | ||
| − | + | Once logged onto the server | |
| − | + | launch the command to install wireguard and the necessary dependencies | |
<blockquote>sudo apt update && sudo apt install wireguard resolvconf iptables nano -y</blockquote> | <blockquote>sudo apt update && sudo apt install wireguard resolvconf iptables nano -y</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | Launch the same command on your orangepi/raspberry pi | |
| − | + | then launch the commands on your orangepi/raspberry pi server to create the private and public wireguard keys <blockquote>sudo mkdir -p /etc/wireguard <br><br> | |
| − | + | sudo sh -c 'wg genkey <span>|</span> (umask 0077 && tee /etc/wireguard/private_key) <span>|</span> wg pubkey > /etc/wireguard/public_key' </blockquote> | |
| − | <blockquote>sudo mkdir -p /etc/wireguard | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | sudo sh -c 'wg genkey <span>|</span> (umask 0077 && tee /etc/wireguard/private_key) <span>|</span> wg pubkey > /etc/wireguard/public_key' | ||
| − | </blockquote> | ||
| − | Afficher la clé publique sur votre orange pi/raspberry pi en tapant | + | Afficher la clé publique sur votre orange pi/raspberry pi en tapant <blockquote>sudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key</blockquote> Afficher egalement la clé publique sur votre serveur en tapant <blockquote>sudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key</blockquote> |
| − | <blockquote>sudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key</blockquote> | + | Display the public key on your orangepi/raspberry pi typing <blockquote>sudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key</blockquote> Afficher egalement la clé publique sur votre serveur en tapant <blockquote>sudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key</blockquote> |
| − | Afficher egalement la clé publique sur votre serveur en tapant | ||
| − | <blockquote>sudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | Then enter the following commands to create a configuration file /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf on your server: | |
| − | + | Type the following lines (replace cle_publique_du_orange_pi_ou_raspberry_pi) by the one previously displayed | |
| − | <blockquote>echo "[Interface]" <span>|</span> sudo tee /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | + | <blockquote>echo "[Interface]" <span>|</span> sudo tee /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "Address=10.10.0.1/24" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "PrivateKey=$(sudo cat /etc/wireguard/private_key)" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "ListenPort=12345" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "[Peer]" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "PublicKey=cle_publique_du_orange_pi_ou_raspberry_pi" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "AllowedIPs=10.10.0.2/32" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf</blockquote> |
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "Address=10.10.0.1/24" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "PrivateKey=$(sudo cat /etc/wireguard/private_key)" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "ListenPort=12345" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "[Peer]" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "PublicKey=cle_publique_du_orange_pi_ou_raspberry_pi" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "AllowedIPs=10.10.0.2/32" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | Then enter the following command on the server to launch and activate the vpn service <blockquote>sudo systemctl start wg-quick@wg0 <br><br> sudo systemctl enable wg-quick@wg0</blockquote> | |
| − | <blockquote>sudo systemctl start wg-quick@wg0 | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | sudo systemctl enable wg-quick@wg0</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | then enter <blockquote>curl ifconfig.me</blockquote> to obtain the public ip of your server | |
| − | + | Type the following lines (replace cle_publique_du_serveur by the one previously displayed and ip_publique_du_serveur by the one previously displayed) : | |
| − | <blockquote>echo "[Interface]" <span>|</span> sudo tee /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | + | <blockquote>echo "[Interface]" <span>|</span> sudo tee /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "Address=10.10.0.2/24" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "PrivateKey=$(sudo cat /etc/wireguard/private_key)" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "[Peer]" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "PublicKey=cle_publique_du_serveur" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "AllowedIPs=10.10.0.1/32" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf <br><br> echo "Endpoint=ip_publique_du_serveur:12345" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf</blockquote> |
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "Address=10.10.0.2/24" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "PrivateKey=$(sudo cat /etc/wireguard/private_key)" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "[Peer]" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "PublicKey=cle_publique_du_serveur" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "AllowedIPs=10.10.0.1/32" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | echo "Endpoint=ip_publique_du_serveur:12345" <span>|</span> sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | The line AllowedIPS defines the destination ips (outgoing) that will go through the tunnel and will be encrypted but also the ips authorized to enter. If you want to configure your "client" (orange pi or raspberry pi) to use the vpn to access the internet, replace AllowedIPs=10.10.0.1/32 with AllowedIPs=0.0.0.0/0 Defining 0.0.0.0/0 we indicate that all the traffic of the orangepi/raspberry pi will go through the wireguard tunnel and that all the entering ips will be allowed. It is then important to configure well a firewall for the server! | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | To verify wireguard works, launch the following command on the vpn server: <blockquote>ping 10.10.10.2 -c 4</blockquote> The ping must work | |
| − | <blockquote>ping 10.10.10.2 -c 4</blockquote> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | This doesnt work systematically on my computer, but i am sure that if you try, your digitla weather forecast being better than mine, it will work on your computer ;) | |
|Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_gandi_1.png | |Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_gandi_1.png | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_gandi_2.png | |Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_gandi_2.png | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=vpn openvpn configuration to make your server accessible from a 4g box or a 4g modem |
| − | |Step_Content=<nowiki> | + | |Step_Content=<nowiki>In the case where it would not work with wireguard, you could user openvpn, (which is configurable with the mouse!) </nowiki> |
| − | + | <u>Gandi.net proxy server configuration:</u><br /> For that, follow the stages on https://openvpn.net/vpn-server-resources/installing-openvpn-access-server-on-a-linux-system : | |
| − | |||
| − | + | 27/11/23 update: there is no bookworm version of openvpn-as available for debian. Think about installing bullseye debian version | |
| − | <blockquote>apt update && apt -y install ca-certificates wget net-tools gnupg | + | <blockquote>apt update && apt -y install ca-certificates wget net-tools gnupg <br> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> wget https://as-repository.openvpn.net/as-repo-public.asc -qO /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/as-repository.asc <br> |
| − | wget https://as-repository.openvpn.net/as-repo-public.asc -qO /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/as-repository.asc | ||
| − | <br> | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/as-repository.asc] http://as-repository.openvpn.net/as/debian bullseye main" <span>|</span> sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/openvpn-as-repo.list <br> |
| − | echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/as-repository.asc] http://as-repository.openvpn.net/as/debian bullseye main" <span>|</span> sudo tee | ||
| − | <br> | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> apt update && apt -y install openvpn-as <br> |
| − | apt update && apt -y install openvpn-as | ||
| − | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Ligne 376 : | Ligne 331 : | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| − | + | If the commands above dont owrk, it is possible openvpn has updated elements. Thanks to see https://openvpn.net/access-server/, sign up and follow the installation instructions | |
| − | + | Then go on the server configuration adress: https://<adresse_ip_du_serveur> | |
| − | login | + | login openvpn |
password: indiqué dans le log de l'installation | password: indiqué dans le log de l'installation | ||
| − | <br><br> | + | <br><br> screen 1: go to admin panel enter your login/password |
| − | screen 1: | ||
| − | go to admin panel | ||
| − | |||
| − | screen2: | + | screen2: Network settings: Activate UDP only and port 1194 then save settings |
| − | Network settings: | ||
| − | screen3: | + | screen3: VPN Settings: enter the fields as in the screenshot and then save settings |
| − | VPN Settings: | ||
| − | screen 4 et 5: | + | screen 4 et 5: User Management/User permission : change the password in local password and enter the fixed ip adress on the screenshot and then save. Then update running server.. <br> |
| − | User Management/User permission : | + | To reconnect to the configuration interface : https://adresse_ip_du_serveur:943 |
| − | |||
| − | <br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | https://adresse_ip_du_serveur:943 | ||
| − | screen 6: | + | screen 6: User Management/User profile: click on new profile then click on create profile. <br><br> Rename the downloaded configuration file as openvpn.conf Open the configuration file and find the line auth-user-pass and replace it with the following line: <blockquote>auth-user-pass auth.txt</blockquote> |
| − | User Management/User profile: | ||
| − | |||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <blockquote>auth-user-pass auth.txt</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | <u>Configuration of orangepi/raspberrypi</u> <br><br><br> Then launch on the orange pi and raspberry pi : <blockquote>sudo apt update && sudo apt install openvpn</blockquote> | |
| − | <br><br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | <blockquote>sudo apt update && sudo apt install openvpn</blockquote> | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> Copy the downloaded configuration file to /etc/openvpn/client/openvpn.conf on your orangepi/raspberry pi <br><br> create a file auth.txt in /etc/openvpn/client/ in which you copy the two following lines replacing password with your password <br><br> <blockquote> openvpn<br> password </blockquote> <br><br> Lancer ensuite le client vpn: |
| − | + | <blockquote>sudo systemctl start openvpn-client@openvpn</blockquote> If you want the client to connect automatically at the start of your machine type <br><br> <blockquote>sudo systemctl enable openvpn-client@openvpn</blockquote> | |
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | <blockquote> | ||
| − | openvpn<br> | ||
| − | password | ||
| − | </blockquote> | ||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | Lancer ensuite le client vpn: | ||
| − | <blockquote>sudo systemctl start openvpn-client@openvpn</blockquote> | ||
| − | |||
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | <blockquote>sudo systemctl enable openvpn-client@openvpn</blockquote> | ||
|Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_ovpnscreen1.png | |Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_ovpnscreen1.png | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_ovpnscreen2.png | |Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_ovpnscreen2.png | ||
| Ligne 438 : | Ligne 362 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Redirect all requests of the vpn server to the orangepi-raspberrypi |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=To redirect the requests on the server to the orangepi/raspberry pi, we put in place a http nginx server |
<blockquote>sudo apt install nginx -y</blockquote> | <blockquote>sudo apt install nginx -y</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | We then open the configuration file of this http server: | |
<blockquote>sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default</blockquote> | <blockquote>sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | Replace the content of this file with what follows | |
<blockquote>server { | <blockquote>server { | ||
| Ligne 493 : | Ligne 417 : | ||
}</blockquote> | }</blockquote> | ||
| − | Nginx | + | Nginx will redirect all requests made on the public ip of your server to your orangepi/raspberry pi nextcloud (line proxy_pass <nowiki>http://10.10.0.2</nowiki>;) |
| − | + | you can test if this works when going on the page: | |
| − | http://ip_publique_de_votre_serveur_gandi/nextcloud | + | http://ip_publique_de_votre_serveur_gandi/nextcloud |
| − | ( | + | (note it's http and not https) |
| − | + | Watch out, many navigators dont accept very well the http redirections, see https section to configure https (it will need a domain name) | |
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=domain name and fixed adress |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=the domain name is the adress in your navigator: for example lowtechlab.org |
| − | + | It will allow you to have your server reachable more easily with an adress you can remember. It only associates the domain name and the ip adress of your vpn server or | |
| + | the ip adress of your box. | ||
| − | + | Wether you register a domain name to redirect to your ip adress or not (it's necessary to get the https however), we must note that by default, the internet providers give you | |
| + | a different ip adress on each connection. | ||
| − | + | If you want a fixed ip adress, you will have to ask your internet provider. It is unfortunately not very well spread in the mainstream internet packages. Orange offers instead a "Dyndns" that allows to have a correspondance in letters to your ip but with which you can not attach easily a domain name. A few domain name registrar like infomaniak, offer however to register a domain name for the dyndns which is easily reachable without extra cost on most operators. | |
| − | + | If you have a 4G internet connection, it is not possible to get a fixed ip and your public ip is usually a"pool" ip. That is to say that the operator gives you a public ip adress which is shared among several clients, and doesnt allow you to use the NAT/Port Forwarding technique to have your dietpi available on the internet. | |
| − | + | You will then have to take a domain for your vpn server that redirects the requests to your dietpi. | |
| − | + | See image attached for the recording of a domain: it is the line "@" type A you have to fill with the public ip adress of your box or your vpn proxy server. | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Ligne 523 : | Ligne 449 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title=Configuration | + | |Step_Title=Https Configuration on the vpn proxy gandi server |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=If you have a proxy server |
| − | + | On your gandi server, do the following : | |
| − | + | Create a file /etc/nginx/conf.d/dietpi.conf and paste the following lines: | |
<blockquote>server { | <blockquote>server { | ||
| Ligne 564 : | Ligne 490 : | ||
}</blockquote> | }</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | Then launch the following commands: | |
<blockquote>sudo apt install letsencrypt | <blockquote>sudo apt install letsencrypt | ||
| Ligne 582 : | Ligne 508 : | ||
sudo apt install python3-certbot-nginx</blockquote> | sudo apt install python3-certbot-nginx</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | obtain the certificates (replace __domain__ with your domain) | |
<blockquote>sudo certbot certonly --nginx -d __domain__</blockquote> | <blockquote>sudo certbot certonly --nginx -d __domain__</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | then copy the following lines in your file /etc/nginx/conf.d/dietpi.conf | |
| − | + | replacing __domain__ by your domain | |
<blockquote>server { | <blockquote>server { | ||
| Ligne 676 : | Ligne 602 : | ||
}</blockquote> | }</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | restart nginx | |
<blockquote>sudo systemctl restart nginx</blockquote> | <blockquote>sudo systemctl restart nginx</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | Once you have completed these steps, your server is reachable online in https typing in your browser https://votre_domaine/nextcloud | |
| − | https://votre_domaine/nextcloud | ||
Vous pouvez alors configurer nextcloud en ligne par le compte administrateur | Vous pouvez alors configurer nextcloud en ligne par le compte administrateur | ||
| Ligne 689 : | Ligne 614 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=configuration https on dietpi if you are on a box |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=I dont have a box, i will update when it will be the case and prooftested! :) |
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Make your nomad server offgrid with photovoltaics |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=Wether it be for ecology reasons, or any other reasons, it is interesting to have a energy offgrid server, |
| − | + | that will not rely on the grid hazards | |
| − | NB: | + | NB: for a slightly modified version of the photovoltaics sizing (mean production/range based with jrc model in december instead of minimum sunlight hours) see my other tutorial here: |
[[Dimensionner une installation photovoltaïque autonome]] | [[Dimensionner une installation photovoltaïque autonome]] | ||
| Ligne 704 : | Ligne 629 : | ||
videos: | videos: | ||
| − | + | beginner basis (pannels, regulator, inverter, consumption/production): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Ft4XQj9lQ4 | |
| − | + | simple myshop solaire kit assembly for 230V: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SvmPEhPq_S8 | |
| − | + | ready for use kits (if you have subsidies and colleagues who cooperate well): | |
https://allo.solar/kit-solaire-1650w-230v-autoconsommation-aps.html?gclid=EAIaIQobChMIkY_fxvu-gAMVyLfVCh014gadEAYYASABEgJd8_D_BwE | https://allo.solar/kit-solaire-1650w-230v-autoconsommation-aps.html?gclid=EAIaIQobChMIkY_fxvu-gAMVyLfVCh014gadEAYYASABEgJd8_D_BwE | ||
| − | + | integrated energy storage (expensive and not very lowtech) | |
| − | + | Portable energy station : 230V BLUETTI AC200MAX | |
EcoFlow River 2 pro | EcoFlow River 2 pro | ||
| − | + | semi lowtech kits (the one used in this guide): | |
| − | + | 120W photovoltaics pannels and lead acid car battery. | |
| − | kit | + | really lowtech kit: |
| − | + | build lithium battery from waste: see barnabé chaillot on youtube | |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_hwj7Ds50lU | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_hwj7Ds50lU | ||
| − | + | basis recall: plugging in serie (+ on + and - on -) we add voltage and we keep same amperage, plugging in paralell (+ on +, - on -) we add amperage and we keep same | |
| − | + | same for batteries: keep in paralell to keep the same voltage | |
| − | + | the first problematic in lowtech photovoltaics offgrid is sizing (see other tutorial | |
[[Dimensionner une installation photovoltaïque autonome]]) | [[Dimensionner une installation photovoltaïque autonome]]) | ||
| − | + | To do so you will find a lot of information on the web. | |
| − | + | You can use the libreoffice calc sheet attached to this tutorial for a diy sizing | |
| − | + | Sizing-daily need: | |
| − | + | Orangepi consumes approx. 20W | |
| − | + | An additional usb hard drive consumes approx. 5W | |
| − | + | A 4G modem consumes approx. 5W | |
| − | + | So a constant need of approx 35W taking 16% of error margin | |
| − | + | The daily need for a 24h powered server is approx: 35W*24=840Wh | |
| − | + | The daily need for a server working by day only is : | |
| − | + | in summer: 35W*14h=490Wh | |
| − | + | in winter: 35W*8h=280Wh | |
| − | + | Note this is a mean daily need and if you want to size | |
| − | + | for varying needs, it is recommeded to proceed more precisely | |
| − | + | calculating real time needs | |
| − | + | Battery sizing based on autonomy time: | |
| − | + | Estimate loss to 20% and increase the needs in consequence: | |
| − | + | need 24h=840/0,8=1050Wh | |
| − | + | Estimate wanted autonomy time: | |
| − | + | example 24h | |
| − | + | We will size batteries to hold 24h | |
| − | + | For 12V batteries: 1050Wh/12V=87,5Ah | |
| − | + | Considered we want to limit battery discharge to 50% we will get: | |
| − | 87,5Ah/ | + | 87,5Ah/05=175Ah |
| − | + | So 2100Wh in 12V | |
| − | + | Based on the pannel characteristics (see calc sheet), we can estimate battery charging when the sunlight is minimal (in december) | |
| − | + | Sizing with "full charge in x day" method: | |
| − | + | If we want to be able to charge the batteries in one day in winter, we must consider the power produced by your pannels a day in winter with the less sunlight | |
| − | + | If we take 3,5h for the minimum, the number of necessary pannels of X Watt will be: | |
| − | + | C_battery: battery capacity in Wh | |
| − | + | In our example 2100Wh | |
| − | + | T_winter: minimum daily need in winter (in h) | |
| − | + | In our example 3,5h | |
| − | + | B_winter: daily need outside of sunlight time in winter (Wh) | |
| − | + | in our example: (24h-3,5h)*35W=897Wh | |
| − | + | n_wanted: number of wanted days to fully charge the batteries | |
| − | + | in our example 1 | |
| − | I:amperage | + | I: output amperage of a pannel |
| − | + | in our example 7A | |
| − | U: | + | U: output voltage of a pannel |
| − | + | in our example 12V | |
| − | + | Nb_pannels=C_battery+B_winter*n_wanted/T_wanted*I*U*n_wanted | |
| − | + | In the example: | |
| − | + | nb_pannel=(2100+897*1)/(3,5*12*7*1) | |
| − | + | We will therefore need 10 pannels of 84W 7A in 12V | |
| − | + | Notice the cardinal value here is at line 42 of the attached file, it is | |
| − | + | daily minimal sunlight in december at nominal production. Reference values can be found at | |
<nowiki>https://re.jrc.ec.europa.eu/api/v5_2/seriescalc?lat=44.203142&lon=0.616363&loss=14&angle=45&aspect=0&startyear=2005&endyear=2005&pvcalculation=1&peakpower=1&pvtechchoice=crystSi&browser=0&outputformat=csv</nowiki> | <nowiki>https://re.jrc.ec.europa.eu/api/v5_2/seriescalc?lat=44.203142&lon=0.616363&loss=14&angle=45&aspect=0&startyear=2005&endyear=2005&pvcalculation=1&peakpower=1&pvtechchoice=crystSi&browser=0&outputformat=csv</nowiki> | ||
| − | + | But nothing compares to an empirical measurement to verify all that. | |
| − | + | The graph in illustrationg comes from monitoring two 400km away installations from an entreprise who install and monitors photovoltaics since 2018. I'm waiting to measure all that with a reliable voltmeter on different second hand pannels to update this tutorial in december! :) | |
| − | + | Any comment and feedback is welcome on this matter at the bottom of this page! | |
| − | + | Sizing with try and errors method | |
| − | + | The calc sheet offers at lines 41 and 42 to adjust the number of pannels and the mean sunlight time in december and gives the daily need outside of sunlight time in winter (Wh) and the maximum battery charge in winter (Ah and Wh). Doing try and errors on these two parameters, we can get the minimum number of pannels so the battery | |
| + | get charged positively in winter. | ||
| − | + | The main problematic of lowtech photovoltaics offgrid is how to store the energy. | |
| − | + | You can read the pannel characteristics : | |
| − | - | + | -peak power: they add up to obtain the necessary power found when sizing |
| − | - | + | -voltage: 12V,24V or 48V. see serie/paralell rules to add up |
| − | - | + | -amperage: varying among the models but often below 10A. see serie/paralell rules to add up |
| − | + | To charge batteries, in principle, if you connect the pannels directly on a battery, you only need the output pannel voltage is the same as the battery so it gets charged | |
| − | + | There is one important component you have to think about to charge correctly your batteries: | |
| − | + | the regulator or charging controler | |
| − | + | Three types exist: the tor (everything or nothing), the mppt (maximum power point tracking) and the pwm (pulse width modulation) | |
| − | + | They are built with a DC/DC adapter (direct current to dirrect current) and a circuit breaker. The mppt also has an impedance adapter (it has a resistance to adapt amperag injected in the battery). the mppt accept higher nominal power, ie higher tensions and intensity | |
| − | + | The regulator or charging controler mainly allows to break the circuit when the battery is fully charged surveilling voltage and amperage charge levels. It breas the circuit if their values get higher than the reference range (so the charging regulator stops the charge temporarily and measures the voltage at the battery) | |
| − | + | The mppt has an integrated "electronic algorithm" that seeks the optimal power point thanks to its impedance adapter. | |
| − | + | If you connect several pannels and several batteries, it is recommended to have a regulator to break the charging circuit correctly when the battery is fully charged. | |
| − | + | The charging reference voltage is 12V,24V and 48V. | |
| − | + | However, the model prices get higher with the nominal power (that will depend on amperage) they accept | |
| − | + | To limit amperage and photovoltaics production, it is better to use higher power pannels which generally have higher voltage output | |
| − | + | recall: P=U*I | |
| − | + | recall E=P*t and is kept equal in a closed system). | |
| − | + | notice: if the storage system with batteries or the device connected to your pannels doesnt absorb all the produced power, and if the charging regulator doesnt cut the circuit, the rest will be outputed as heat. | |
| − | + | Amperage will also depend on the battery capacity, sized so as to cover your needs for a period defined at sizing. | |
| − | + | The charge amperage is calculated dividing by 4 or 5 the nominal capacity of the battery expressed in Ah that should then discharge in 4 or 5h. However a battery will also charge with a charge amperage calculated as nominal battery capacity divided by 20 but more slowly (in 20h). | |
| − | + | Sizing and/or arranging your pannels in consequence. | |
| − | + | Pannel arrangements can allow to adjust voltage and amperage | |
| − | + | There is finally a last point on which i would like to bring attention to: the trigger of the battery charging by the charging regulator (that triggers if the voltage of the battery | |
| + | goes below a treshold). | ||
| − | + | Indeed, if the power taken from the battery is too low, it is possible the necessary time to discharge the battery with your daily consumption to trigger the charge in the | |
| + | regulator goes longer than the daily sunlight time. Then the battery won't charge during the day. | ||
| − | + | In that case, the battery will charge every other day (depending on the charging regulator treshold) | |
| − | + | It is a parameter to take into account in the sizing (not included in the calc sheet) | |
| − | + | The regulator has 3 phases: | |
| − | 1.bulk: | + | 1.bulk: the regulator let the current pass |
| − | 2.floating: | + | 2.floating: the regulator switches open and closed at a given frequency to maintain the battery charged |
| − | + | In addition some precautions must be taken because charging batteries can be risky | |
| − | 3.absorption ( | + | 3.absorption (for mppt): the charging voltage raises a bit to create enough potential difference to continue charging the battery which is almost full. |
| − | + | In theory, the charging current goes low when the battery is almost fully charged (queue current etc.) | |
| − | + | Charging the batteries in paralell or in serie on old batteries that do not have the same amperage or voltage is theoretically risky. Indeed, you can read a bit everywhere on the web that the wire resistance to link them | |
| − | + | creates potential differences between the batteries producing discharges from one battery to another, etc. | |
| − | + | creating risks of explosion, degassing for lead batteries, etc. | |
| − | + | We have to remember batteries are assemblies of unit components of weak voltage put in series and in paralell to obtain a generator of a given amperage and tension and therefore doing the same with entire batteries is not really risky... | |
| − | + | We often talk of battery management system (bms) "integrated" for lithium ion batteries. | |
| − | + | In reality the charging regulator is already a "bms". In theory, the integrated bms makes sure the intensity and voltage of each unit of the battery is the same and balances them at need | |
| − | + | We can of course wonder if all this is not a way to make energy storage more expensive with bms components artificially expensive and if this is not a way to avoid to reuse old batteries. | |
| − | + | It is amazing no bms exist to balance automatically old lead acid batteries, which would make reusable all old car batteries of the car industry to store energy without risks | |
| − | + | In any case, if you reuse old lead acide batteries, use a charging regulator to avoid continuing charging your already charged batteries (hydrogen production risk) -or if you dont use a regulator, size with a lot of precaution-, avoid profound discharges, and maintain the batteries at a constant temperature as much as possible. | |
|Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_2.6kWc.png | |Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_2.6kWc.png | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_9kWc.png | |Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_9kWc.png | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Assembly and test |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=We begin sizing on 1/10 of the peak power of the pannels and 1/4 of the storage capacity given by the theoretical calculations to be offgrid 24h/24h and able to charge in one day in winter, so a pannel of 120W and an old car battery of 45Ah in 12V. |
| − | + | It's ok with a lowtech thinking to have the server only run when it's daylight, and for computers respecting human temporality. | |
| − | + | To be ok in winter (hypothesis : a mean of 3,5h of sunlight), we would need a battery of more than 58Ah, but for budget reasons, we do with what we have! :) | |
| − | + | The charging regulator doesnt accept 40V pannels so we did not use the second hand 180W pannel at 20€ found on leboncoin, but i will update this tutorial with assembly of pannels and batteries as soon as i will have the material and with the winter production digits if i manage to! | |
| − | + | <u>Assembly stages</u> | |
| − | <br /> | + | <br/> |
| − | + | Plug an electric cable to the + of the battery and to the + of the pwm regulator (battery output). Plug an electric cable to the - of the battery and to the - of the pwm regulator (battery ouput) | |
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| − | + | Plug the pannels to the mc4 cables. Plug the nude cable + to the + of the pwm regulator (input pannels). Plug the nude cable - to the - of the pwm regulator (input pannels). | |
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| − | + | Plug the pliers of the 12V/5V usb converter with the + on the + and the - on the - | |
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| + | Plug a rj45 cable of your box or your 4g modem to the orangepi or raspberry pi | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | Plug the usb cable of the orangepi or raspberry pi to the 12V/5V usb converter | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | To automate a switch to power when it's daylight and switch off when it's night, you can use a DRL module (daytime running light) of a car. The module is a switch that lets | ||
| + | current pass when the tension is higher than 13V (when the solar pannel is charging the battery). The switch must be plugged to the + of the IN and to the + of the battery, to the - of the IN on the - of the battery, + of the OUT on the red plier and - of the OUT on the red plier (between the battery and the 12V/5v USB converter) | ||
| − | + | Wait a few minutes that it boots. And here we are, the nextcloud server is available online! :) | |
| − | + | Notice that if you want to power something in AC 220V, the only thing that is missing in this assembly is a DC/AC converter that we easily find in camping shops or on leboncoin. | |
|Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_IMG_20230821_171458_820.jpg | |Step_Picture_00=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_IMG_20230821_171458_820.jpg | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_IMG_20230821_171056_521.jpg | |Step_Picture_01=Serveur_orangepi-raspberry_nextcloud_en_photovolta_que_autonome_IMG_20230821_171056_521.jpg | ||
| Ligne 958 : | Ligne 892 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Securing the server |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=At a security level, the known flaws of the cpu can be found under linux doing: |
<blockquote>grep -r . /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities</blockquote> | <blockquote>grep -r . /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | This command on the orange pi (cpu CortexA55) with dietpi installed gives: <blockquote> /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spectre_v2:Mitigation: Unprivileged eBPF enabled | |
| − | <blockquote> | ||
| − | /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spectre_v2:Mitigation: Unprivileged eBPF enabled | ||
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/itlb_multihit:Not affected | /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/itlb_multihit:Not affected | ||
| Ligne 988 : | Ligne 920 : | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| − | + | After a few tests on the orange pi a raspberry pi and a odroid, the problem is the same <br><br> <u>basics:</u> | |
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | <u> | ||
| − | + | we can spend a whole life trying to raise security of a computer system... | |
| − | + | finding the good tradeoff and evaluate the risks or lure of profits. | |
| − | + | hack is always possible, and considered the number of 0day flaws never published, on any operating system, the question is less to have a flawless system, that to know from which you want to protect from when we talk about "securing" or reducing attack surface. | |
| − | + | I think the opensource/libre philosophy is superior in terms of security because auditable and fixable by the "commu", but we must say the default settings are not tip top because linux was thought to be stable at the start (rememeber all the blue screens in windows 30 yerars ago), and not "secured". | |
| − | + | After undergoing many hacks i consider very advanced and not in the reach of the script kiddie (and on any operating system any machine and any securing level i tried except from kernel compilation), I have tried to secure my digital stuff and i am now at the point i think "digital soveranignty" doesnt exist or not anymore. | |
| − | + | the flaws create a security market, it makes people work... see interesting article of w0nderfall on the subject of security under linux: https://wonderfall.space/linux-securite | |
| − | + | However, a few elements because it is a subject on which i havent found much didactic information gathered. <br> | |
| − | <br> | ||
| − | - | + | -<u>limiting attack surface principle</u> <nowiki>:</nowiki> general principle, securing only diminishes the potential attack surface |
| − | <nowiki>:</nowiki> | ||
| − | <br>- | + | <br>-<u>secured physical access and related software configuration </u> <br> |
| − | <br> | ||
| − | - <u> | + | - <u>physical access</u>: up to you |
| − | -<u> | + | -<u>grub password</u> <br><br> launch in a terminal: <br> <blockquote>grub-mkpasswd-pbkdf2</blockquote> |
| − | <br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | <br> | ||
| − | <blockquote>grub-mkpasswd-pbkdf2</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | Copy the text starting with grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.xy | |
| − | + | where xy is a long string of letters and digits | |
| − | + | Add the following lines to the file /etc/grub.d/42_pw | |
| − | + | replace user by your username in linux and pw by the | |
| − | + | text previously copied | |
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
| Ligne 1 039 : | Ligne 962 : | ||
EOF | EOF | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| − | + | Then launch command | |
<blockquote>update-grub</blockquote> | <blockquote>update-grub</blockquote> | ||
| − | -<u> | + | -<u>good passwords in general</u> |
| − | + | to change the user password type | |
<blockquote>passwd</blockquote> | <blockquote>passwd</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | to change the root user password type | |
<blockquote>sudo passwd root</blockquote> | <blockquote>sudo passwd root</blockquote> | ||
| − | - | + | -optionnally <u>verify boot integrity</u> (see purism computers for example) |
| − | -<u> | + | -<u>encrypt your storage</u>: |
https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/tutoriel/chiffrer_ses_donnees | https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/tutoriel/chiffrer_ses_donnees | ||
| Ligne 1 061 : | Ligne 984 : | ||
https://www.dwarmstrong.org/remote-unlock-dropbear/ | https://www.dwarmstrong.org/remote-unlock-dropbear/ | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>sécurity of a server:</u> |
| − | -<u>apt update | + | -<u>automated apt update</u> : https://www.linuxtricks.fr/wiki/debian-activer-les-mises-a-jour-automatique-avec-unattended-upgrades |
| − | -<u>ssh | + | -<u>reinforced ssh</u> : |
| − | + | lines to include in your ssh configuration (/etc/ssh/sshd_config): <blockquote> | |
| − | <blockquote> | ||
| − | Port 22 # | + | Port 22 #change on other port if you want |
Protocol 2 | Protocol 2 | ||
| Ligne 1 103 : | Ligne 1 025 : | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| − | -<u>firewall | + | -<u>software firewall</u>: |
ufw: https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/ufw | ufw: https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/ufw | ||
| − | + | or iptables configuration file: | |
https://gitlab.com/aurelpere/bp028-hardening/-/blob/main/rhel_iptables_ipv4/files/server_firewall.sh | https://gitlab.com/aurelpere/bp028-hardening/-/blob/main/rhel_iptables_ipv4/files/server_firewall.sh | ||
| − | -<u>backup</u>: | + | -<u>backup</u>: 321 rule: 3 copies, 2 different storage types, 1 copy on another place than others. borgbackup stays a standard for its reliability in the free software community (i confirm after testing several stuff) and offers a cloud which is not expensive to have "remote" backups and invest money in free software development. |
| − | |||
| − | borgbackup | ||
fail2ban: https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/fail2ban | fail2ban: https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/fail2ban | ||
| − | fail2ban | + | fail2ban for nextcloud: https://tuxicoman.jesuislibre.net/2015/01/fail2ban-pour-owncloud-7-sur-debian-jessie.html |
| − | -<u> | + | -<u>deactivate ipv6</u> (or configure the firewall as well for ipv6) |
| − | 3 | + | 3 methods to deactivate ipv6: |
| − | 1. | + | 1.in grub |
| − | 2. | + | 2.with sysctl |
| − | + | add the following lines to /etc/systcl.conf <blockquote> | |
| − | <blockquote> | ||
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1 | net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1 | ||
| Ligne 1 167 : | Ligne 1 086 : | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| − | 3. | + | 3. with network manager nmcli |
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/configuring_and_managing_networking/using-networkmanager-to-disable-ipv6-for-a-specific-connection_configuring-and-managing-networking | https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/configuring_and_managing_networking/using-networkmanager-to-disable-ipv6-for-a-specific-connection_configuring-and-managing-networking | ||
| − | -<u> | + | -<u>secure the server in case multi user or when a user accessed the server</u> |
| − | + | lists of files to secure (permissions etc.): https://linuxfr.org/forums/linux-general/posts/liste-des-fichiers-linux-a-securiser-owner-group-permissions-setuid-setgid-sticky-bit | |
| − | guides | + | guides to harden: https://www.ssi.gouv.fr/guide/recommandations-de-securite-relatives-a-un-systeme-gnulinux |
| − | <u> | + | <u>To go further in terms of security:</u> |
| − | <u>firewall | + | <u>free physical firewall</u>: pcengines/ free software OPNSense |
| − | <u>fail2ban | + | <u>fail2ban with geography lists</u>: https://thecustomizewindows.com/2016/11/fail2ban-geoip-action-script-block-ssh-country/ |
| − | + | Create a <u>connection sas</u> to your online service (MySafeip): https://linuxfr.org/news/mysafeip-un-tiers-de-confiance-pour-votre-pare-feu | |
| − | + | secure the systemd linux services: https://github.com/juju4/ansible-harden-systemd | |
| − | <u> | + | <u>compile a kernel</u> : |
[https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/tutoriel/comment_compiler_un_kernel_de_kernel.orghttps://github.com/robertdebock/ansible-role-kernel https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/tutoriel/comment_compiler_un_kernel_de_kernel.org] | [https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/tutoriel/comment_compiler_un_kernel_de_kernel.orghttps://github.com/robertdebock/ansible-role-kernel https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/tutoriel/comment_compiler_un_kernel_de_kernel.org] | ||
| Ligne 1 194 : | Ligne 1 113 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Activate wifi when installing (for example with a raspberry) |
|Step_Content=wpa2: | |Step_Content=wpa2: | ||
| − | + | When you start for the first time the raspberry with dietpi and the usb stick or the sd card, the installation program will display a menu after an error ("Checking ipv4 | |
| + | network connectivity") [...] ping: connect: Network is unreachabel") | ||
| − | + | Then go to "network-settings" and then follow the menus indicated in the attached images | |
wpa3: voir etape 6 | wpa3: voir etape 6 | ||
| Ligne 1 210 : | Ligne 1 130 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Notes | {{Notes | ||
| − | |Notes= | + | |Notes=No thank you, it was difficul and i was not helped ;) |
| − | + | The tutorial and its content are not based on expertise or specific training but from diy and information gathered on the web, so please be indulgent ;) | |
| − | + | feedback welcomed in comments | |
}} | }} | ||
{{PageLang | {{PageLang | ||
Version actuelle datée du 6 septembre 2024 à 18:24
Description
Tutorial to setup a nextcloud server (equivalent to google drive but free and adapted to collective organisations) on a single board computer (photovoltaics powered)
This tutorial is not really "lowtech" at first look because we talk about computers and photovoltaics
However it is as didactic as possible and follows a lowtech philosophy to share knowledge, avoid unreachable tech by information rentention, complexification by design, or proprietary
dependance by design.
We also give sizign tools for photovoltaics with a few explanation.
It's up to to you to size your computer working hours on a sun schedule, ie respecting human temporalities.
Nextcloud (framasoft offers a service here: https://www.frama.space/abc/fr ) is a cool service to organise collectively and allows to share files, have a directory, a chat, work cooperatively on libreoffice files, and even do visios. We can also imagine mobile infokisosks on this principle.
The tutorial puts into question the vpn market, the phtovoltaics with brand new and expensive batteries (in reality photovoltaics has become too competitive compared to petrleum and even more compared to nuclear power!), and the gafam market and their surveillance design is damaging trust and social links.
The commands are those for a debian system
Finally, the tutorial is made iwth 4G modem (and a wired connection to orange pi which has no wifi card by default), and is updated on this 10th of april for a raspberry pi connected
to a "shared wifi" of your telephone (see stage 6 for a wifi in wpa3 and stage 16 for a wifi in wpa2)
Sommaire
Sommaire
- 1 Description
- 2 Sommaire
- 3 Introduction
- 4 Étape 1 - Tools
- 5 Étape 2 - Nextcloud installation 1/4
- 6 Étape 3 - Install nextcloud 2/4
- 7 Étape 4 - Install nextcloud 3/4
- 8 Étape 5 - Install nextcloud 4/4
- 9 Étape 6 - Configure local ethernet or wifi network
- 10 Étape 7 - configuring a wireguard vpn to make your server more accessible from a 4g box or a 4g modem
- 11 Étape 8 - vpn openvpn configuration to make your server accessible from a 4g box or a 4g modem
- 12 Étape 9 - Redirect all requests of the vpn server to the orangepi-raspberrypi
- 13 Étape 10 - domain name and fixed adress
- 14 Étape 11 - Https Configuration on the vpn proxy gandi server
- 15 Étape 12 - configuration https on dietpi if you are on a box
- 16 Étape 13 - Make your nomad server offgrid with photovoltaics
- 17 Étape 14 - Assembly and test
- 18 Étape 15 - Securing the server
- 19 Étape 16 - Activate wifi when installing (for example with a raspberry)
- 20 Notes et références
- 21 Commentaires
Introduction
Tutorial to setup a nextcloud server (equivalent to google drive but free and adapted to collective organisations) on a single board computer (photovoltaics powered)
This tutorial is not really "lowtech" at first look because we talk about computers and photovoltaics
However it is as didactic as possible and follows a lowtech philosophy to share knowledge, avoid unreachable tech by information rentention, complexification by design, or proprietary dependance by design.
We also give sizign tools for photovoltaics with a few explanation. It's up to to you to size your computer working hours on a sun schedule, ie respecting human temporalities.
Nextcloud (framasoft offers a service here: https://www.frama.space/abc/fr ) is a cool service to organise collectively and allows to share files, have a directory, a chat, work cooperatively on libreoffice files, and even do visios.
We can also imagine mobile infokisosks on this principle.
The tutorial puts into question the vpn market, the phtovoltaics with brand new and expensive batteries (in reality photovoltaics has become too competitive compared to petrleum and even more compared to nuclear power!), and the gafam market and their surveillance design which is damaging trust and social links.
The commands are those for a debian system
Finally, the tutorial is made iwth 4G modem (and a wired connection to orange pi which has no wifi card by default), and is updated on this 10th of april for a raspberry pi connected to a "shared wifi" of your telephone (see stage 6 for a wifi in wpa3 and stage 16 for a wifi in wpa2)
See https://solar.lowtechmagazine.com/ to go further with the low tech internet insights (in particular "how to create a lowtech internet"?)
Matériaux
Outils
autonomie.ods
Étape 1 - Tools
The links to the photovoltaics material are in the autonomie.ods file (readable with libreoffice) attached to this tutorial.
- raspberry pi :
42€ on leboncoin
-Orange pi :
single board computer: Orange pi 5
single board computer with 4,8,16 or 32 Go of ram
2,4Ghz ARM Cortex-A55 CPU
This card is compatible with nvme pcie 2.0 hard drives (2242 or 2230, pcie is retrocompatible ie 3.0, 4.0 and 5.0 work with lower speed on orange pi 5)
Same principle as here but a bit more powerful and we can plug a hard drive (useful for nextcloud which is made to host files) and it starts automatically on a usb stick
Price: 143€ brand new on aliexpress in version 16 Go on the 2nd of august 2023
Second hand on leboncoin: we find more easily raspberry pi at around 100€.
It is necessary to buy a small box at 10€ (or make one) to avoid a naked single board computer
-hard drive
Here we use a kingston usb stick of 32Go and a nvme samsung 512Go card
We can plug a hard drive of higher capacity in usb, or a nvme card (nvme pcie 2.0 ssd 2242 or 2230) compatible with pcie 3.0 4.0 and above but the speed is reduced
A nvme samsung 2242 card of 500Go is about 50€ on the 2nd of august 2023.
-usb stick : 10€
- rj45 cable: 5€
-Internet box or 4G modem according to your internet connection
-solar pannel: here we use a flexible 120W pannel bougth 115€ brand new but we can find second hand ones at 30€ on leboncoin for an equivalente peak power.
Note: for the theoretical need. See file autonomy.ods
-second hand battery: use the previous lead acid battery of your car when it crashes when it's too hot in summer!
-12V/24V-usb 5V battery converter: 20€ avoid amazon if you can
- pwm regulator 30A: 30€ brand new if you dont buy corporate brand
- DRL (day/night switch 13V): 1,5€ brand new
(key word "Kit de feux de jour à LED pour voiture, contrôleur marche/arrêt automatique DRL" in french)
-electric mc4 cable: 20€
Total second hand price for orangepi: 256,50€
Total brand new price for orangepi: 431,50€
Total second hand price for raspberry: 165€
See autonomie.ods
-
Étape 2 - Nextcloud installation 1/4
1. Download dietpi and prepare your usb stick
For installation, i recommend using diepti. It is interesting in particular for it is lightweight for single board computers, but also because the automatic installation of free software
with a relatively "user friendly" menu. We can mention among all the installable software at boot (https://dietpi.com/dietpi-software.html)
domotic apps, interesting to save energy based on weather, but also tor relay to contribute to the relatively anonymous tor network, interesting for any "eco-terrorist" we are.
We must also mention "younohost"(https://yunohost.org/fr) which is french and who does the same job as dietpi for raspberry and which is also "user friendly" or even more. I have not yet tested yunohost because i had put aside raspberry pi after too many weird mouse bugs. My research to avoid these weird mouse bugs have not concluded positively to any solution (purism, odroid, raspberry, orangpi, macbook, windows, see security section), i can only send a feedback on what i have really tried.
( for younohost : https://yunohost.org/fr/install/hardware:arm)
Select the single board computer (orange pi in the present case) and then download
Unzip the obtained archive
Use balena etcher to create a bootable usb stick to install dietpi on your single board computer (orange pi 5 in the present case but it works the same on other single board computers)
https://etcher.balena.io/#download-etcher
Double click on the downloaded file
Select the dietpi downloaded image, select your usb stick, click on flash.
You only need to plug the usb stick on the orangepi and it will boot automatically on the usb stick.
For a raspberry pi, we use a sd card but we can configure the usb boot as well (see here:https://makerhelp.fr/booter-un-raspberry-pi-4-sur-un-disque-dur-ou-un-ssd-en-usb )
Install nextcloud
Power your orangepi/raspberrypi with the usb stick plugged.
The default login at boot is root and the password is dietpi.
Follow the menus at first boot to install the nextcloud service. It is very easy, it is in english and everything is automated. I have put the images of the menus you have to select. to install nextcloud: see in this stage and on stages 3 to 6
You can move the menus with the keyboard and the arrows and the tab key
Select with space and validate with enter
See images at stages 3 to 6 for the installation process and select the entries
Étape 6 - Configure local ethernet or wifi network
If you don't have a box and you have a orange pi or raspberry pi and you want connext to a wifi (for example wifi of a shared connection smartphone)
Dietpi gives a utility to configure automatically the wifi which works on raspberry. At my place it works only if the network is wpa2. If you want to activate wpa3 or if you want to configure your wifi manually, here are the steps to follow.
Linux is a bit complicated for network management. A lot of programs exist allowing to manage networks (networking, network interfaces, ifup, wpa_supplicant, network_manager, ifconfig, ip...) network_manager, ifconfig, ip...).
If you know well, do what you think is best suited for you.
Otherwise, we will use the default programs installed with dietpi for managing wifi interfaces: wpa_supplicant and dhclient.
Begin with plugging a wifi usb adapter to your orangepi or verify your wifi adapter on your raspberry pi is well detected.
On a orangepi: verify the adapter is well detected entering:lsusbThis command will list the usb devices and you should see your wifi usb stick in the list. Then verify that the drivers of your usb stick have been loaded entering:
dmesg
Étape 7 - configuring a wireguard vpn to make your server more accessible from a 4g box or a 4g modem
[Watch out, this section puts into question the vpn market!!]
This section is useful for 4G connections or in wifi on a smartphone (4G or 5G)
The 4g has the advantage to be mobile with a very low power consumption of the modem, around 5W, and you can find 4g modems without wifi to limit the attack surface of your server (example netgear lm1200 around 150€)
what is a vpn?
The vpn are mainly known to be vpn "clients". Ie you use it on your computer to become "anonymous".
The vpn is in fact a tunnel between your computer and another distant computer, from which your requests go on to the internet. Your traffic in direction of the internet goes through this tunnel.
Internet then thinks your requests come from this distant computer. That is to say your public ip becomes distant computer one.
Your internet provided doesnt see the traffic between your computer and this distant computer, which makes you "anonymous"
In reality, you are anonymous for your internet provider, but you only move the trust you had in your internet provider to your vpn provider who can see your traffic.
The vpn has also other uses like giving you access to websites being filtered on a geographic basis (information that can be deducted from your public ip)
You can very well create your own vpn server, and in our case, this vpn server will redirect the internet requests made on this server to your orangepi/raspberry pi going through the tunnel (in the other direction than when you use it as a client to access the internet)
An wee will see how.
Create a server on gandi.net
Create an account on gandi.net, then create a server on gandicloud vps. See images for the 3clicks server creation that costs 5€/month.
To create a ssh key and log in see:
https://docs.gandi.net/fr/cloud/operations_courantes/connexion_serveur.html
https://docs.gandi.net/fr/cloud/operations_courantes/connexion_serveur.html
Once logged onto the server
launch the command to install wireguard and the necessary dependencies
sudo apt update && sudo apt install wireguard resolvconf iptables nano -y
Launch the same command on your orangepi/raspberry pi
then launch the commands on your orangepi/raspberry pi server to create the private and public wireguard keysAfficher la clé publique sur votre orange pi/raspberry pi en tapantsudo mkdir -p /etc/wireguard
sudo sh -c 'wg genkey | (umask 0077 && tee /etc/wireguard/private_key) | wg pubkey > /etc/wireguard/public_key'
Afficher egalement la clé publique sur votre serveur en tapantsudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key
Display the public key on your orangepi/raspberry pi typingsudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key
Afficher egalement la clé publique sur votre serveur en tapantsudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key
sudo cat /etc/wireguard/public_key
Then enter the following commands to create a configuration file /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf on your server:
Type the following lines (replace cle_publique_du_orange_pi_ou_raspberry_pi) by the one previously displayed
Then enter the following command on the server to launch and activate the vpn serviceecho "[Interface]" | sudo tee /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "Address=10.10.0.1/24" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "PrivateKey=$(sudo cat /etc/wireguard/private_key)" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "ListenPort=12345" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "[Peer]" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "PublicKey=cle_publique_du_orange_pi_ou_raspberry_pi" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "AllowedIPs=10.10.0.2/32" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
then entersudo systemctl start wg-quick@wg0
sudo systemctl enable wg-quick@wg0
to obtain the public ip of your servercurl ifconfig.me
Type the following lines (replace cle_publique_du_serveur by the one previously displayed and ip_publique_du_serveur by the one previously displayed) :
echo "[Interface]" | sudo tee /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "Address=10.10.0.2/24" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "PrivateKey=$(sudo cat /etc/wireguard/private_key)" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "[Peer]" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "PublicKey=cle_publique_du_serveur" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "AllowedIPs=10.10.0.1/32" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
echo "Endpoint=ip_publique_du_serveur:12345" | sudo tee -a /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
The line AllowedIPS defines the destination ips (outgoing) that will go through the tunnel and will be encrypted but also the ips authorized to enter. If you want to configure your "client" (orange pi or raspberry pi) to use the vpn to access the internet, replace AllowedIPs=10.10.0.1/32 with AllowedIPs=0.0.0.0/0 Defining 0.0.0.0/0 we indicate that all the traffic of the orangepi/raspberry pi will go through the wireguard tunnel and that all the entering ips will be allowed. It is then important to configure well a firewall for the server!
To verify wireguard works, launch the following command on the vpn server:The ping must workping 10.10.10.2 -c 4
This doesnt work systematically on my computer, but i am sure that if you try, your digitla weather forecast being better than mine, it will work on your computer ;)
Étape 8 - vpn openvpn configuration to make your server accessible from a 4g box or a 4g modem
In the case where it would not work with wireguard, you could user openvpn, (which is configurable with the mouse!)
Gandi.net proxy server configuration:
For that, follow the stages on https://openvpn.net/vpn-server-resources/installing-openvpn-access-server-on-a-linux-system :
27/11/23 update: there is no bookworm version of openvpn-as available for debian. Think about installing bullseye debian version
apt update && apt -y install ca-certificates wget net-tools gnupg
wget https://as-repository.openvpn.net/as-repo-public.asc -qO /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/as-repository.asc
echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/as-repository.asc] http://as-repository.openvpn.net/as/debian bullseye main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/openvpn-as-repo.list
apt update && apt -y install openvpn-as
If the commands above dont owrk, it is possible openvpn has updated elements. Thanks to see https://openvpn.net/access-server/, sign up and follow the installation instructions
Then go on the server configuration adress: https://<adresse_ip_du_serveur>
login openvpn
password: indiqué dans le log de l'installation
screen 1: go to admin panel enter your login/password
screen2: Network settings: Activate UDP only and port 1194 then save settings
screen3: VPN Settings: enter the fields as in the screenshot and then save settings
screen 4 et 5: User Management/User permission : change the password in local password and enter the fixed ip adress on the screenshot and then save. Then update running server..
To reconnect to the configuration interface : https://adresse_ip_du_serveur:943
Rename the downloaded configuration file as openvpn.conf Open the configuration file and find the line auth-user-pass and replace it with the following line:
Configuration of orangepi/raspberrypiauth-user-pass auth.txt
Then launch on the orange pi and raspberry pi :
sudo apt update && sudo apt install openvpn
Copy the downloaded configuration file to /etc/openvpn/client/openvpn.conf on your orangepi/raspberry pi
create a file auth.txt in /etc/openvpn/client/ in which you copy the two following lines replacing password with your password
openvpn
password
Lancer ensuite le client vpn:
If you want the client to connect automatically at the start of your machine typesudo systemctl start openvpn-client@openvpn
sudo systemctl enable openvpn-client@openvpn
Étape 9 - Redirect all requests of the vpn server to the orangepi-raspberrypi
To redirect the requests on the server to the orangepi/raspberry pi, we put in place a http nginx server
sudo apt install nginx -y
We then open the configuration file of this http server:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Replace the content of this file with what follows
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
server_tokens off;
add_header Permissions-Policy "accelerometer=(),autoplay=(),camera=(),display-capture=(),document-domain=(),encrypted-media=(),fullscreen=(),geolocation=(),gyroscope=(),magnetometer=(),microphone=(),midi=(),payment=(),picture-in-picture=(),publickey-credentials-get=(),screen-wake-lock=(),sync-xhr=(self),usb=(),web-share=(),xr-spatial-tracking=()";
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000 ; includeSubDomains";
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "script-src 'self';";
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies none;
add_header Referrer-Policy no-referrer;
add_header Clear-Site-Data "cache,cookies,storage";
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.10.0.2;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
client_max_body_size 20M;
limit_except GET HEAD POST {deny all;}
}
}
Nginx will redirect all requests made on the public ip of your server to your orangepi/raspberry pi nextcloud (line proxy_pass http://10.10.0.2;)
you can test if this works when going on the page:
http://ip_publique_de_votre_serveur_gandi/nextcloud
(note it's http and not https)
Watch out, many navigators dont accept very well the http redirections, see https section to configure https (it will need a domain name)
Étape 10 - domain name and fixed adress
the domain name is the adress in your navigator: for example lowtechlab.org
It will allow you to have your server reachable more easily with an adress you can remember. It only associates the domain name and the ip adress of your vpn server or the ip adress of your box.
Wether you register a domain name to redirect to your ip adress or not (it's necessary to get the https however), we must note that by default, the internet providers give you a different ip adress on each connection.
If you want a fixed ip adress, you will have to ask your internet provider. It is unfortunately not very well spread in the mainstream internet packages. Orange offers instead a "Dyndns" that allows to have a correspondance in letters to your ip but with which you can not attach easily a domain name. A few domain name registrar like infomaniak, offer however to register a domain name for the dyndns which is easily reachable without extra cost on most operators.
If you have a 4G internet connection, it is not possible to get a fixed ip and your public ip is usually a"pool" ip. That is to say that the operator gives you a public ip adress which is shared among several clients, and doesnt allow you to use the NAT/Port Forwarding technique to have your dietpi available on the internet.
You will then have to take a domain for your vpn server that redirects the requests to your dietpi.
See image attached for the recording of a domain: it is the line "@" type A you have to fill with the public ip adress of your box or your vpn proxy server.
Étape 11 - Https Configuration on the vpn proxy gandi server
If you have a proxy server
On your gandi server, do the following :
Create a file /etc/nginx/conf.d/dietpi.conf and paste the following lines:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
server_tokens off;
add_header Permissions-Policy "accelerometer=(),autoplay=(),camera=(),display-capture=(),document-domain=(),encrypted-media=(),fullscreen=(),geolocation=(),gyroscope=(),magnetometer=(),microphone=(),midi=(),payment=(),picture-in-picture=(),publickey-credentials-get=(),screen-wake-lock=(),sync-xhr=(self),usb=(),web-share=(),xr-spatial-tracking=()";
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000 ; includeSubDomains";
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "script-src 'self';";
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies none;
add_header Referrer-Policy no-referrer;
#add_header Clear-Site-Data "cache,cookies,storage";
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
location / {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
}
Then launch the following commands:
sudo apt install letsencrypt
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/certbot/certbot/master/certbot-nginx/certbot_nginx/_internal/tls_configs/options-ssl-nginx.conf
sudo cp options-ssl-nginx.conf /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/certbot/certbot/master/certbot/certbot/ssl-dhparams.pem
sudo cp ssl-dhparams.pem /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem
sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
sudo apt remove certbot
sudo apt install python3-certbot-nginx
obtain the certificates (replace __domain__ with your domain)
sudo certbot certonly --nginx -d __domain__
then copy the following lines in your file /etc/nginx/conf.d/dietpi.conf
replacing __domain__ by your domain
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
server_tokens off;
add_header Permissions-Policy "accelerometer=(),autoplay=(),camera=(),display-capture=(),document-domain=(),encrypted-media=(),fullscreen=(),geolocation=(),gyroscope=(),magnetometer=(),microphone=(),midi=(),payment=(),picture-in-picture=(),publickey-credentials-get=(),screen-wake-lock=(),sync-xhr=(self),usb=(),web-share=(),xr-spatial-tracking=()";
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000 ; includeSubDomains";
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "script-src 'self';";
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies none;
add_header Referrer-Policy no-referrer;
#add_header Clear-Site-Data "cache,cookies,storage";
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
location / {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name localhost;
server_tokens off;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/__domain__/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/__domain__/privkey.pem;
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf;
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem;
add_header Permissions-Policy "accelerometer=(),autoplay=(),camera=(),display-capture=(),document-domain=(),encrypted-media=(),fullscreen=(),geolocation=(),gyroscope=(),magnetometer=(),microphone=(),midi=(),payment=(),picture-in-picture=(),publickey-credentials-get=(),screen-wake-lock=(),sync-xhr=(self),usb=(),web-share=(),xr-spatial-tracking=()";
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000 ; includeSubDomains";
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "script-src 'self';";
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies none;
add_header Referrer-Policy no-referrer;
#add_header Clear-Site-Data "cache,cookies,storage";
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.10.10.2;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
client_max_body_size 20M;
limit_except GET HEAD POST {deny all;}
}
}
restart nginx
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Once you have completed these steps, your server is reachable online in https typing in your browser https://votre_domaine/nextcloud
Vous pouvez alors configurer nextcloud en ligne par le compte administrateur login par défaut sur dietpi: admin mot de passe par défaut sur dietpi: mot de passe entrée à l'installation de dietpi
Étape 12 - configuration https on dietpi if you are on a box
I dont have a box, i will update when it will be the case and prooftested! :)
Étape 13 - Make your nomad server offgrid with photovoltaics
Wether it be for ecology reasons, or any other reasons, it is interesting to have a energy offgrid server,
that will not rely on the grid hazards
NB: for a slightly modified version of the photovoltaics sizing (mean production/range based with jrc model in december instead of minimum sunlight hours) see my other tutorial here:
Dimensionner une installation photovoltaïque autonome
videos:
beginner basis (pannels, regulator, inverter, consumption/production): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Ft4XQj9lQ4
simple myshop solaire kit assembly for 230V: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SvmPEhPq_S8
ready for use kits (if you have subsidies and colleagues who cooperate well):
integrated energy storage (expensive and not very lowtech)
Portable energy station : 230V BLUETTI AC200MAX
EcoFlow River 2 pro
semi lowtech kits (the one used in this guide):
120W photovoltaics pannels and lead acid car battery.
really lowtech kit:
build lithium battery from waste: see barnabé chaillot on youtube
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_hwj7Ds50lU
basis recall: plugging in serie (+ on + and - on -) we add voltage and we keep same amperage, plugging in paralell (+ on +, - on -) we add amperage and we keep same
same for batteries: keep in paralell to keep the same voltage
the first problematic in lowtech photovoltaics offgrid is sizing (see other tutorial
Dimensionner une installation photovoltaïque autonome)
To do so you will find a lot of information on the web.
You can use the libreoffice calc sheet attached to this tutorial for a diy sizing
Sizing-daily need:
Orangepi consumes approx. 20W
An additional usb hard drive consumes approx. 5W
A 4G modem consumes approx. 5W
So a constant need of approx 35W taking 16% of error margin
The daily need for a 24h powered server is approx: 35W*24=840Wh
The daily need for a server working by day only is :
in summer: 35W*14h=490Wh
in winter: 35W*8h=280Wh
Note this is a mean daily need and if you want to size
for varying needs, it is recommeded to proceed more precisely
calculating real time needs
Battery sizing based on autonomy time:
Estimate loss to 20% and increase the needs in consequence:
need 24h=840/0,8=1050Wh
Estimate wanted autonomy time:
example 24h
We will size batteries to hold 24h
For 12V batteries: 1050Wh/12V=87,5Ah
Considered we want to limit battery discharge to 50% we will get:
87,5Ah/05=175Ah
So 2100Wh in 12V
Based on the pannel characteristics (see calc sheet), we can estimate battery charging when the sunlight is minimal (in december)
Sizing with "full charge in x day" method:
If we want to be able to charge the batteries in one day in winter, we must consider the power produced by your pannels a day in winter with the less sunlight
If we take 3,5h for the minimum, the number of necessary pannels of X Watt will be:
C_battery: battery capacity in Wh
In our example 2100Wh
T_winter: minimum daily need in winter (in h)
In our example 3,5h
B_winter: daily need outside of sunlight time in winter (Wh)
in our example: (24h-3,5h)*35W=897Wh
n_wanted: number of wanted days to fully charge the batteries
in our example 1
I: output amperage of a pannel
in our example 7A
U: output voltage of a pannel
in our example 12V
Nb_pannels=C_battery+B_winter*n_wanted/T_wanted*I*U*n_wanted
In the example:
nb_pannel=(2100+897*1)/(3,5*12*7*1)
We will therefore need 10 pannels of 84W 7A in 12V
Notice the cardinal value here is at line 42 of the attached file, it is
daily minimal sunlight in december at nominal production. Reference values can be found at
https://re.jrc.ec.europa.eu/api/v5_2/seriescalc?lat=44.203142&lon=0.616363&loss=14&angle=45&aspect=0&startyear=2005&endyear=2005&pvcalculation=1&peakpower=1&pvtechchoice=crystSi&browser=0&outputformat=csv
But nothing compares to an empirical measurement to verify all that.
The graph in illustrationg comes from monitoring two 400km away installations from an entreprise who install and monitors photovoltaics since 2018. I'm waiting to measure all that with a reliable voltmeter on different second hand pannels to update this tutorial in december! :)
Any comment and feedback is welcome on this matter at the bottom of this page!
Sizing with try and errors method
The calc sheet offers at lines 41 and 42 to adjust the number of pannels and the mean sunlight time in december and gives the daily need outside of sunlight time in winter (Wh) and the maximum battery charge in winter (Ah and Wh). Doing try and errors on these two parameters, we can get the minimum number of pannels so the battery get charged positively in winter.
The main problematic of lowtech photovoltaics offgrid is how to store the energy.
You can read the pannel characteristics :
-peak power: they add up to obtain the necessary power found when sizing
-voltage: 12V,24V or 48V. see serie/paralell rules to add up
-amperage: varying among the models but often below 10A. see serie/paralell rules to add up
To charge batteries, in principle, if you connect the pannels directly on a battery, you only need the output pannel voltage is the same as the battery so it gets charged
There is one important component you have to think about to charge correctly your batteries:
the regulator or charging controler
Three types exist: the tor (everything or nothing), the mppt (maximum power point tracking) and the pwm (pulse width modulation)
They are built with a DC/DC adapter (direct current to dirrect current) and a circuit breaker. The mppt also has an impedance adapter (it has a resistance to adapt amperag injected in the battery). the mppt accept higher nominal power, ie higher tensions and intensity
The regulator or charging controler mainly allows to break the circuit when the battery is fully charged surveilling voltage and amperage charge levels. It breas the circuit if their values get higher than the reference range (so the charging regulator stops the charge temporarily and measures the voltage at the battery)
The mppt has an integrated "electronic algorithm" that seeks the optimal power point thanks to its impedance adapter.
If you connect several pannels and several batteries, it is recommended to have a regulator to break the charging circuit correctly when the battery is fully charged.
The charging reference voltage is 12V,24V and 48V.
However, the model prices get higher with the nominal power (that will depend on amperage) they accept
To limit amperage and photovoltaics production, it is better to use higher power pannels which generally have higher voltage output
recall: P=U*I
recall E=P*t and is kept equal in a closed system).
notice: if the storage system with batteries or the device connected to your pannels doesnt absorb all the produced power, and if the charging regulator doesnt cut the circuit, the rest will be outputed as heat.
Amperage will also depend on the battery capacity, sized so as to cover your needs for a period defined at sizing.
The charge amperage is calculated dividing by 4 or 5 the nominal capacity of the battery expressed in Ah that should then discharge in 4 or 5h. However a battery will also charge with a charge amperage calculated as nominal battery capacity divided by 20 but more slowly (in 20h).
Sizing and/or arranging your pannels in consequence.
Pannel arrangements can allow to adjust voltage and amperage
There is finally a last point on which i would like to bring attention to: the trigger of the battery charging by the charging regulator (that triggers if the voltage of the battery goes below a treshold).
Indeed, if the power taken from the battery is too low, it is possible the necessary time to discharge the battery with your daily consumption to trigger the charge in the regulator goes longer than the daily sunlight time. Then the battery won't charge during the day.
In that case, the battery will charge every other day (depending on the charging regulator treshold)
It is a parameter to take into account in the sizing (not included in the calc sheet)
The regulator has 3 phases:
1.bulk: the regulator let the current pass
2.floating: the regulator switches open and closed at a given frequency to maintain the battery charged
In addition some precautions must be taken because charging batteries can be risky
3.absorption (for mppt): the charging voltage raises a bit to create enough potential difference to continue charging the battery which is almost full.
In theory, the charging current goes low when the battery is almost fully charged (queue current etc.)
Charging the batteries in paralell or in serie on old batteries that do not have the same amperage or voltage is theoretically risky. Indeed, you can read a bit everywhere on the web that the wire resistance to link them
creates potential differences between the batteries producing discharges from one battery to another, etc.
creating risks of explosion, degassing for lead batteries, etc.
We have to remember batteries are assemblies of unit components of weak voltage put in series and in paralell to obtain a generator of a given amperage and tension and therefore doing the same with entire batteries is not really risky...
We often talk of battery management system (bms) "integrated" for lithium ion batteries.
In reality the charging regulator is already a "bms". In theory, the integrated bms makes sure the intensity and voltage of each unit of the battery is the same and balances them at need
We can of course wonder if all this is not a way to make energy storage more expensive with bms components artificially expensive and if this is not a way to avoid to reuse old batteries.
It is amazing no bms exist to balance automatically old lead acid batteries, which would make reusable all old car batteries of the car industry to store energy without risks
In any case, if you reuse old lead acide batteries, use a charging regulator to avoid continuing charging your already charged batteries (hydrogen production risk) -or if you dont use a regulator, size with a lot of precaution-, avoid profound discharges, and maintain the batteries at a constant temperature as much as possible.
Étape 14 - Assembly and test
We begin sizing on 1/10 of the peak power of the pannels and 1/4 of the storage capacity given by the theoretical calculations to be offgrid 24h/24h and able to charge in one day in winter, so a pannel of 120W and an old car battery of 45Ah in 12V.
It's ok with a lowtech thinking to have the server only run when it's daylight, and for computers respecting human temporality.
To be ok in winter (hypothesis : a mean of 3,5h of sunlight), we would need a battery of more than 58Ah, but for budget reasons, we do with what we have! :)
The charging regulator doesnt accept 40V pannels so we did not use the second hand 180W pannel at 20€ found on leboncoin, but i will update this tutorial with assembly of pannels and batteries as soon as i will have the material and with the winter production digits if i manage to!
Assembly stages
Plug an electric cable to the + of the battery and to the + of the pwm regulator (battery output). Plug an electric cable to the - of the battery and to the - of the pwm regulator (battery ouput)
Plug the pannels to the mc4 cables. Plug the nude cable + to the + of the pwm regulator (input pannels). Plug the nude cable - to the - of the pwm regulator (input pannels).
Plug the pliers of the 12V/5V usb converter with the + on the + and the - on the -
Plug a rj45 cable of your box or your 4g modem to the orangepi or raspberry pi
Plug the usb cable of the orangepi or raspberry pi to the 12V/5V usb converter
To automate a switch to power when it's daylight and switch off when it's night, you can use a DRL module (daytime running light) of a car. The module is a switch that lets
current pass when the tension is higher than 13V (when the solar pannel is charging the battery). The switch must be plugged to the + of the IN and to the + of the battery, to the - of the IN on the - of the battery, + of the OUT on the red plier and - of the OUT on the red plier (between the battery and the 12V/5v USB converter)
Wait a few minutes that it boots. And here we are, the nextcloud server is available online! :)
Notice that if you want to power something in AC 220V, the only thing that is missing in this assembly is a DC/AC converter that we easily find in camping shops or on leboncoin.
Étape 15 - Securing the server
At a security level, the known flaws of the cpu can be found under linux doing:
This command on the orange pi (cpu CortexA55) with dietpi installed gives:grep -r . /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spectre_v2:Mitigation: Unprivileged eBPF enabled
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/itlb_multihit:Not affected
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/mmio_stale_data:Not affected
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/mds:Not affected
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/l1tf:Not affected
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spec_store_bypass:Mitigation: Speculative Store Bypass disabled via prctl
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/tsx_async_abort:Not affected
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spectre_v1:Mitigation: __user pointer sanitization
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/retbleed:Not affected
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/srbds:Not affected
/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/meltdown:Not affected
After a few tests on the orange pi a raspberry pi and a odroid, the problem is the same
basics:
we can spend a whole life trying to raise security of a computer system...
finding the good tradeoff and evaluate the risks or lure of profits.
hack is always possible, and considered the number of 0day flaws never published, on any operating system, the question is less to have a flawless system, that to know from which you want to protect from when we talk about "securing" or reducing attack surface.
I think the opensource/libre philosophy is superior in terms of security because auditable and fixable by the "commu", but we must say the default settings are not tip top because linux was thought to be stable at the start (rememeber all the blue screens in windows 30 yerars ago), and not "secured".
After undergoing many hacks i consider very advanced and not in the reach of the script kiddie (and on any operating system any machine and any securing level i tried except from kernel compilation), I have tried to secure my digital stuff and i am now at the point i think "digital soveranignty" doesnt exist or not anymore. the flaws create a security market, it makes people work... see interesting article of w0nderfall on the subject of security under linux: https://wonderfall.space/linux-securite
However, a few elements because it is a subject on which i havent found much didactic information gathered.
-limiting attack surface principle : general principle, securing only diminishes the potential attack surface
-secured physical access and related software configuration
- physical access: up to you
-grub passwordlaunch in a terminal:
grub-mkpasswd-pbkdf2
Copy the text starting with grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.xy
where xy is a long string of letters and digits
Add the following lines to the file /etc/grub.d/42_pw
replace user by your username in linux and pw by the
text previously copied
cat << EOF
set superusers=user
password_pbkdf2 pw
EOF
Then launch command
update-grub
-good passwords in general
to change the user password type
passwd
to change the root user password type
sudo passwd root
-optionnally verify boot integrity (see purism computers for example)
-encrypt your storage:
https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/tutoriel/chiffrer_ses_donnees
https://www.dwarmstrong.org/remote-unlock-dropbear/
sécurity of a server:
-automated apt update : https://www.linuxtricks.fr/wiki/debian-activer-les-mises-a-jour-automatique-avec-unattended-upgrades
-reinforced ssh :
lines to include in your ssh configuration (/etc/ssh/sshd_config):Port 22 #change on other port if you want
Protocol 2
PermitRootLogin no
StrictModes yes
PermitEmptyPasswords no
X11Forwarding no
Ciphers chacha20-poly1305@openssh.com,aes256-gcm@openssh.com,aes128-gcm@openssh.com,aes256-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes128-ctr
MACs hmac-sha2-512-etm@openssh.com,hmac-sha2-256-etm@openssh.com,umac-128-etm@openssh.com,hmac-sha2-512,hmac-sha2-256,umac-128@openssh.com
KexAlgorithms curve25519-sha256,curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,diffie-hellman-group14-sha256,diffie-hellman-group16-sha512,diffie-hellman-group18-sha512,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256
AllowTcpForwarding no
MaxSessions 1
UsePAM yes
AllowUsers user #remplacer par les utilisateurs autorisées
AllowGroups group #remplacer par les groupes autorisés
PasswordAuthentication no
AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys
-software firewall:
ufw: https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/ufw
or iptables configuration file:
https://gitlab.com/aurelpere/bp028-hardening/-/blob/main/rhel_iptables_ipv4/files/server_firewall.sh
-backup: 321 rule: 3 copies, 2 different storage types, 1 copy on another place than others. borgbackup stays a standard for its reliability in the free software community (i confirm after testing several stuff) and offers a cloud which is not expensive to have "remote" backups and invest money in free software development.
fail2ban: https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/fail2ban
fail2ban for nextcloud: https://tuxicoman.jesuislibre.net/2015/01/fail2ban-pour-owncloud-7-sur-debian-jessie.html
-deactivate ipv6 (or configure the firewall as well for ipv6)
3 methods to deactivate ipv6:
1.in grub
2.with sysctl
add the following lines to /etc/systcl.confnet.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.all.router_solicitations = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.router_solicitations = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_ra_rtr_pref = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_rtr_pref = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_ra_pinfo = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_pinfo = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_ra_defrtr = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_defrtr = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.autoconf = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.autoconf = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_source_route = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.max_addresses = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.max_addresses = 1
3. with network manager nmcli
-secure the server in case multi user or when a user accessed the server
lists of files to secure (permissions etc.): https://linuxfr.org/forums/linux-general/posts/liste-des-fichiers-linux-a-securiser-owner-group-permissions-setuid-setgid-sticky-bit
guides to harden: https://www.ssi.gouv.fr/guide/recommandations-de-securite-relatives-a-un-systeme-gnulinux
To go further in terms of security:
free physical firewall: pcengines/ free software OPNSense
fail2ban with geography lists: https://thecustomizewindows.com/2016/11/fail2ban-geoip-action-script-block-ssh-country/
Create a connection sas to your online service (MySafeip): https://linuxfr.org/news/mysafeip-un-tiers-de-confiance-pour-votre-pare-feu
secure the systemd linux services: https://github.com/juju4/ansible-harden-systemd
compile a kernel :
https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/tutoriel/comment_compiler_un_kernel_de_kernel.org
Étape 16 - Activate wifi when installing (for example with a raspberry)
wpa2:
When you start for the first time the raspberry with dietpi and the usb stick or the sd card, the installation program will display a menu after an error ("Checking ipv4 network connectivity") [...] ping: connect: Network is unreachabel")
Then go to "network-settings" and then follow the menus indicated in the attached images
wpa3: voir etape 6
Notes et références
No thank you, it was difficul and i was not helped ;)
The tutorial and its content are not based on expertise or specific training but from diy and information gathered on the web, so please be indulgent ;)
feedback welcomed in comments
Published
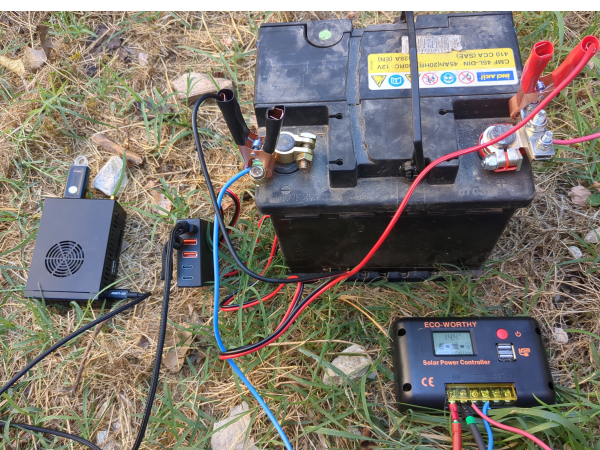
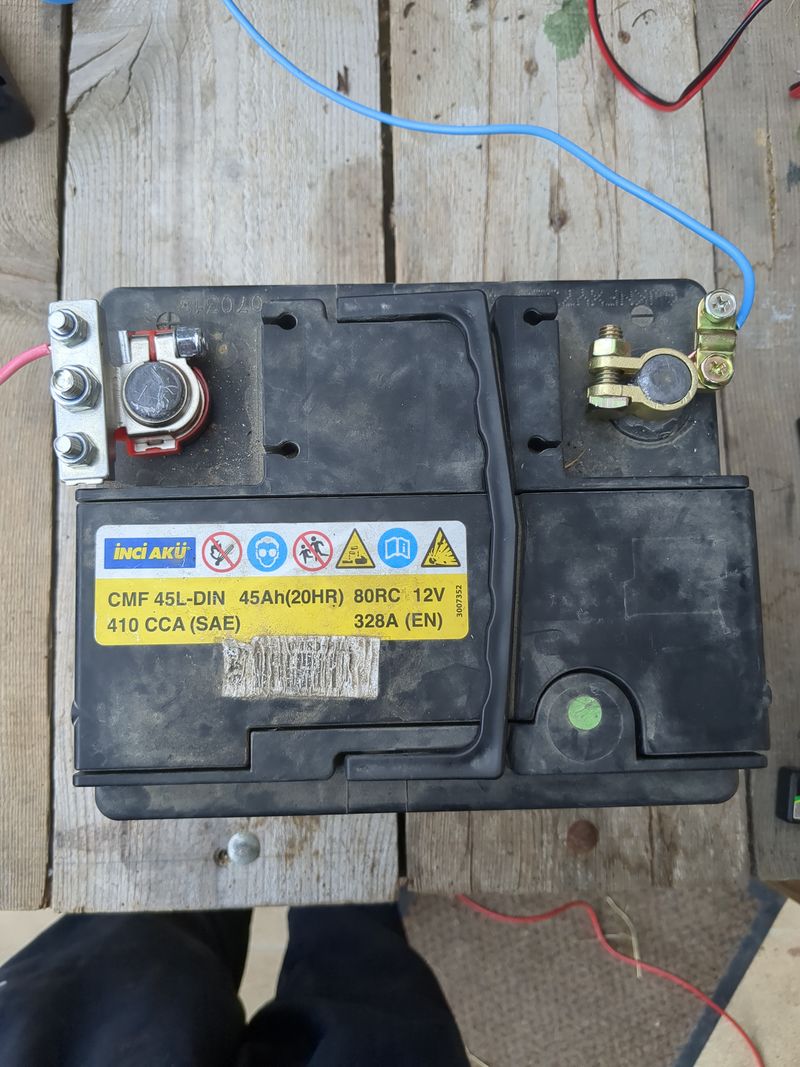
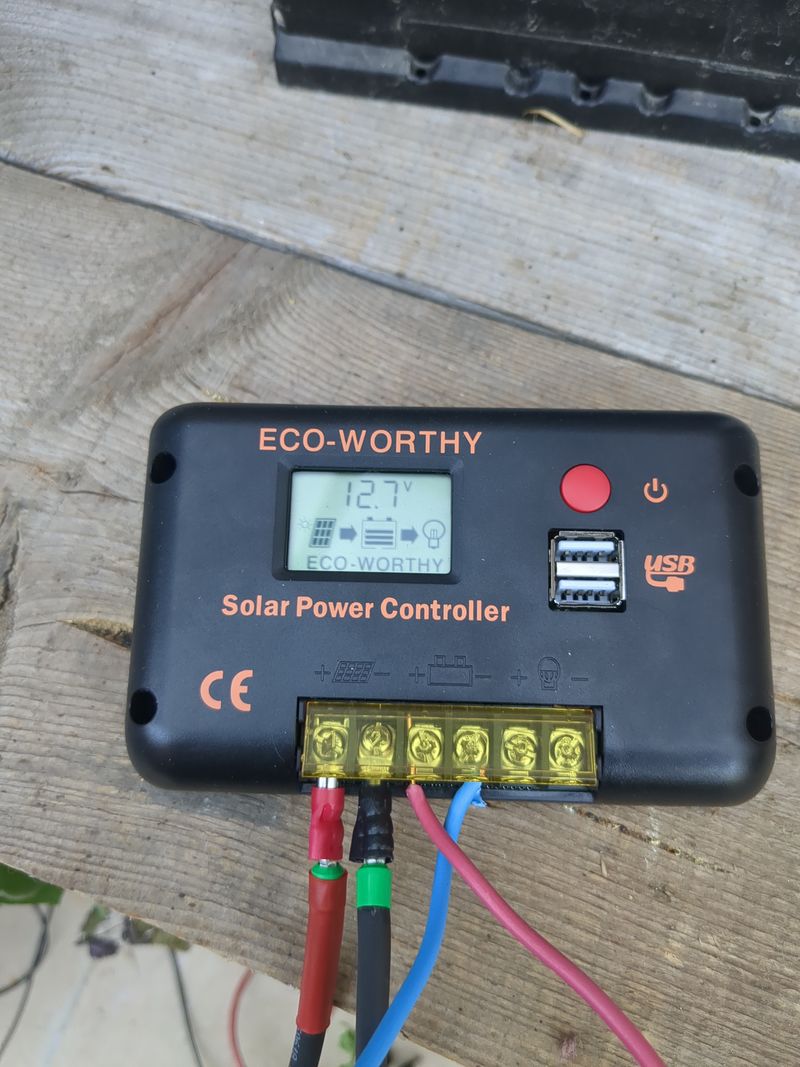
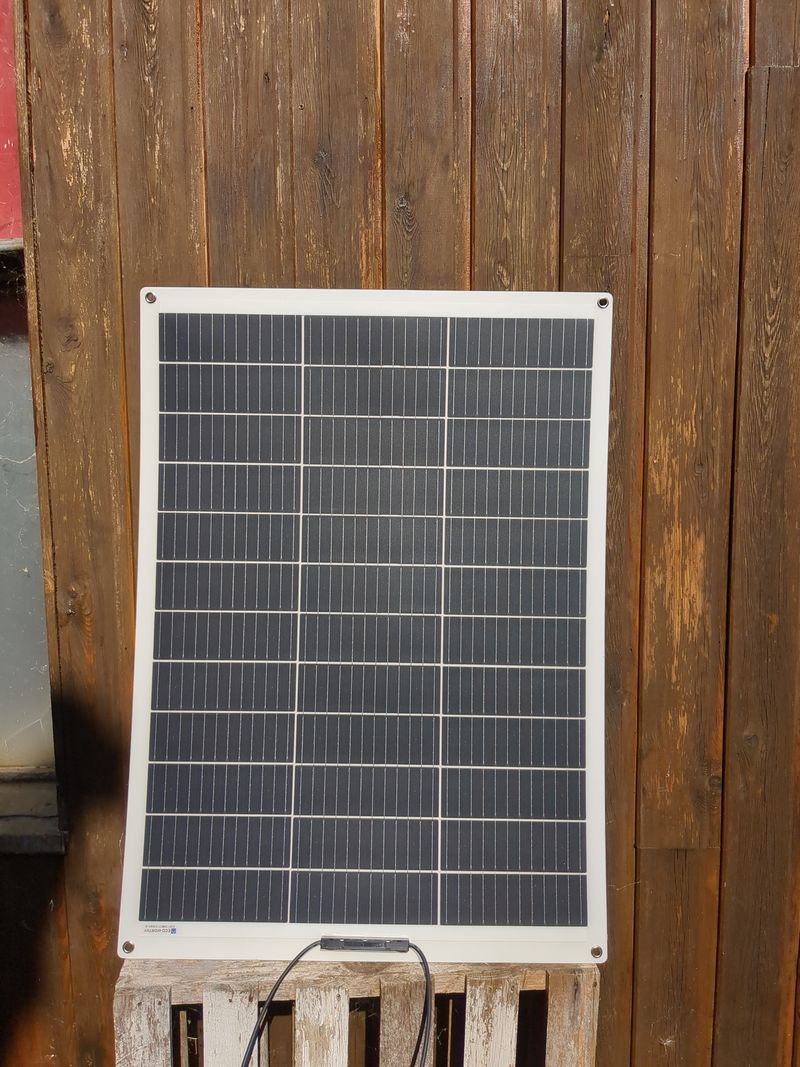
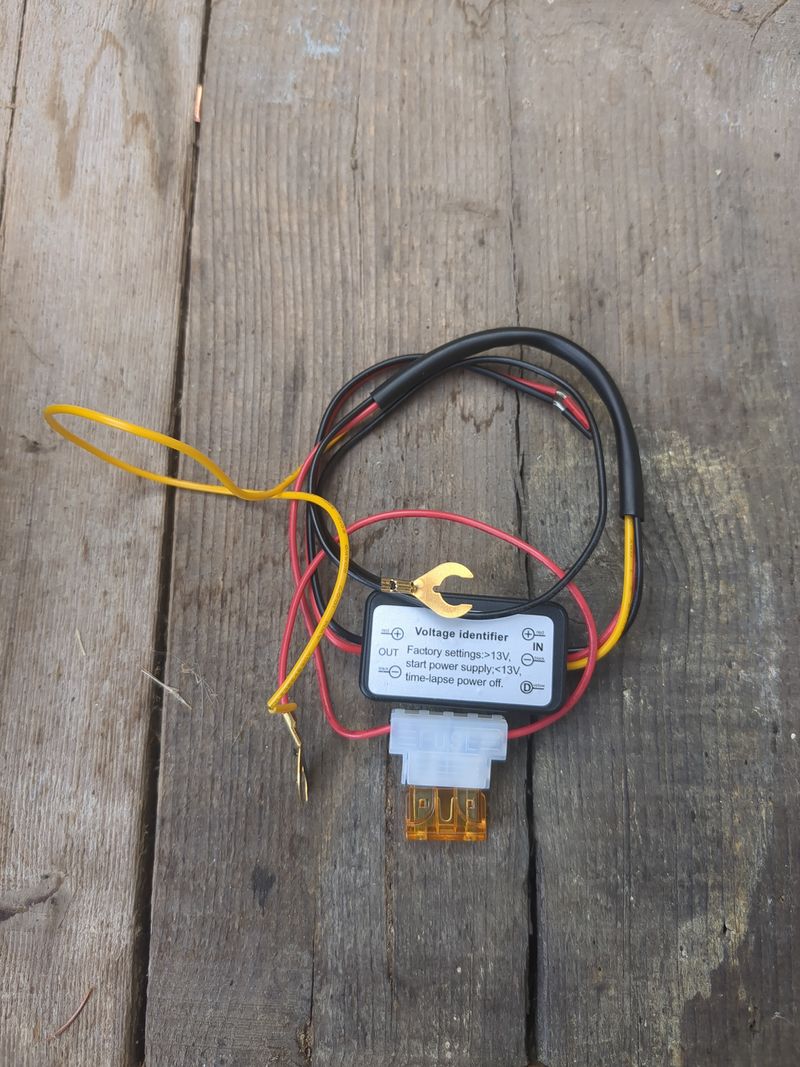
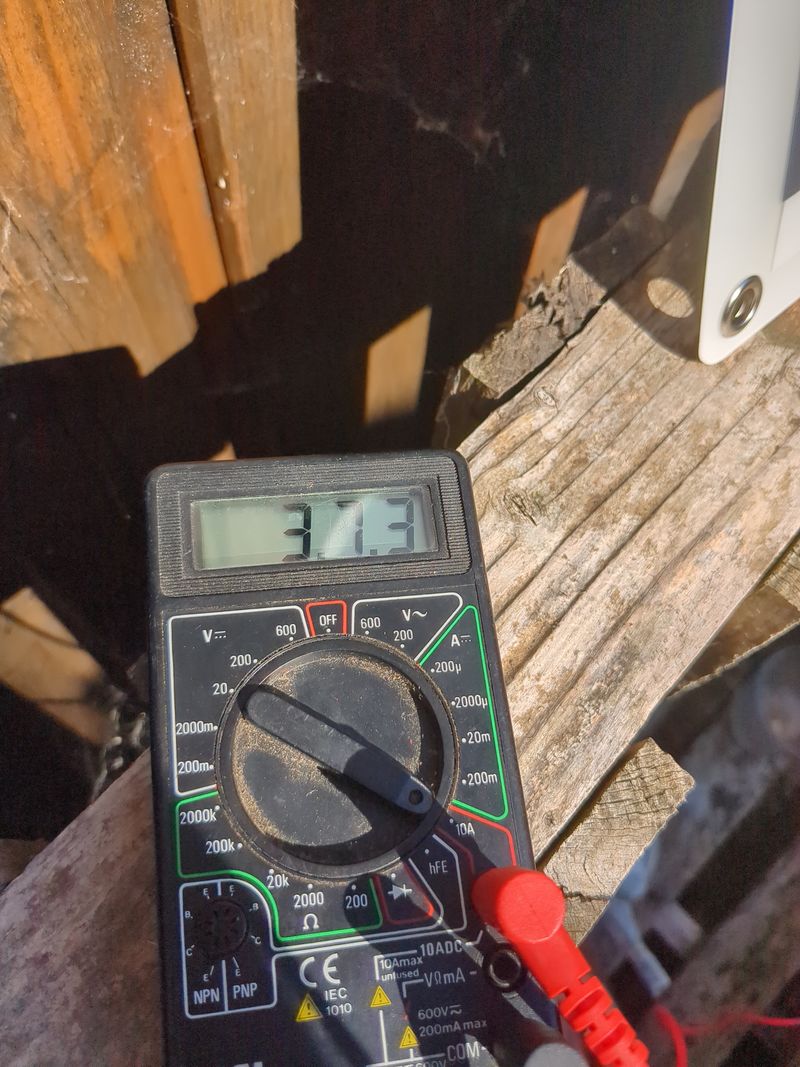







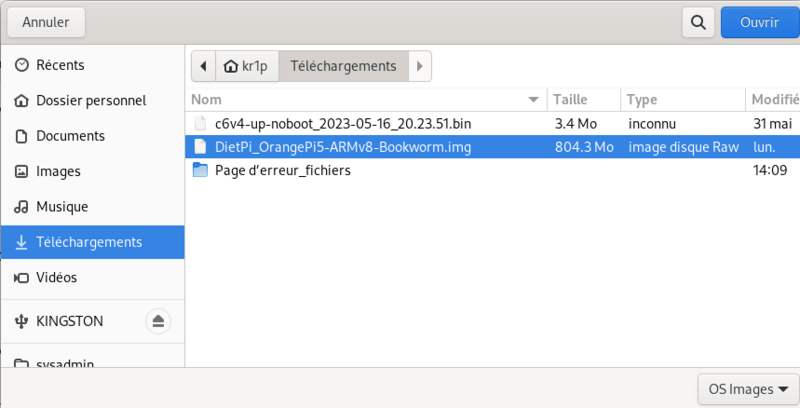
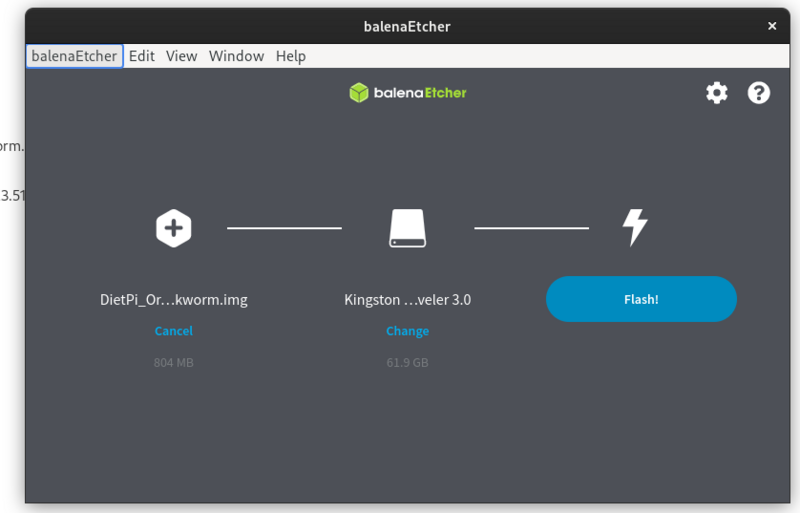
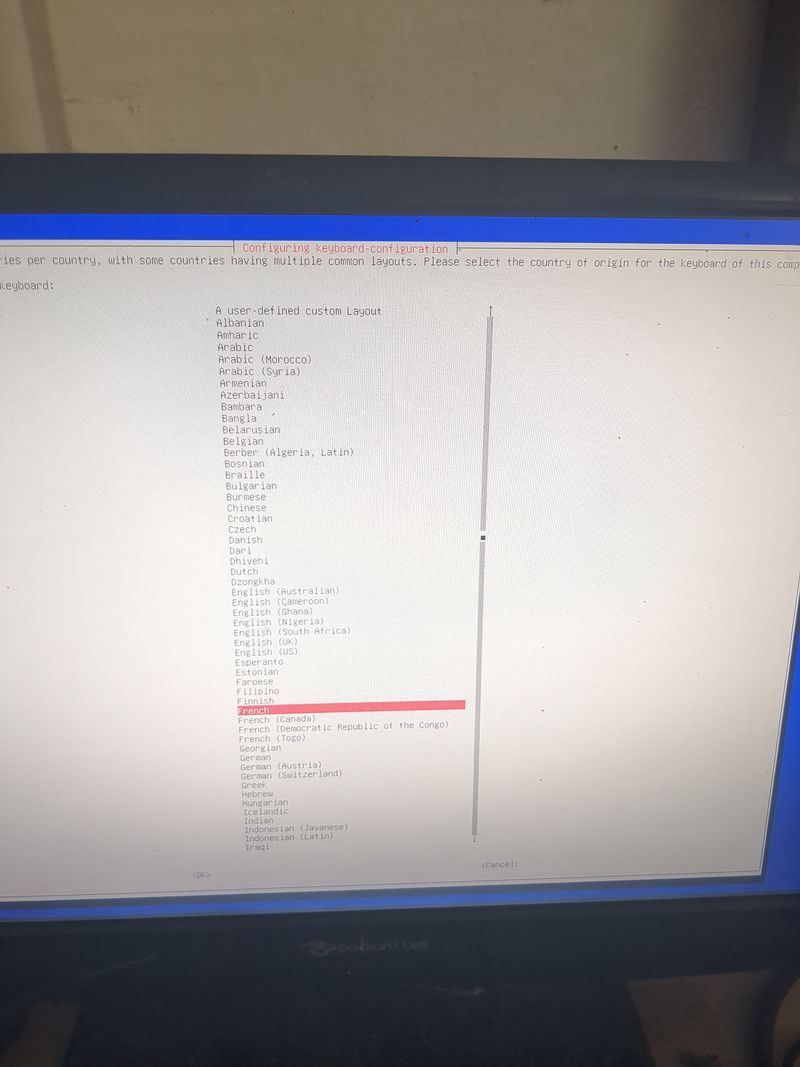
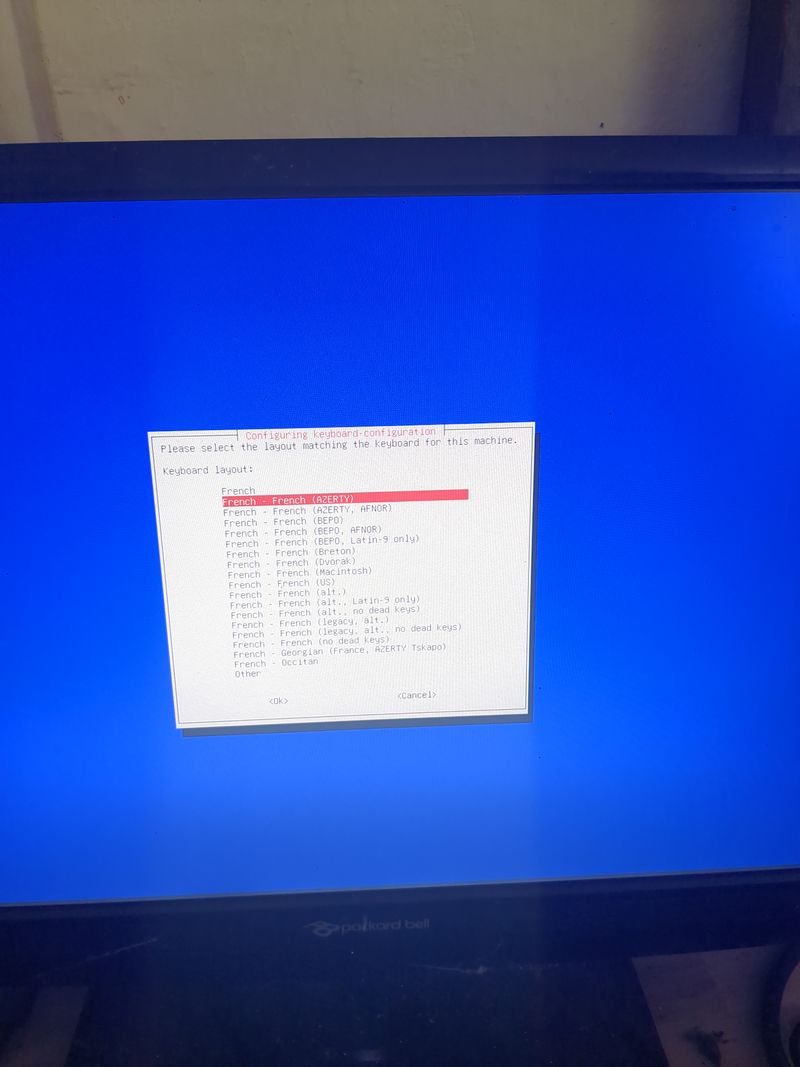
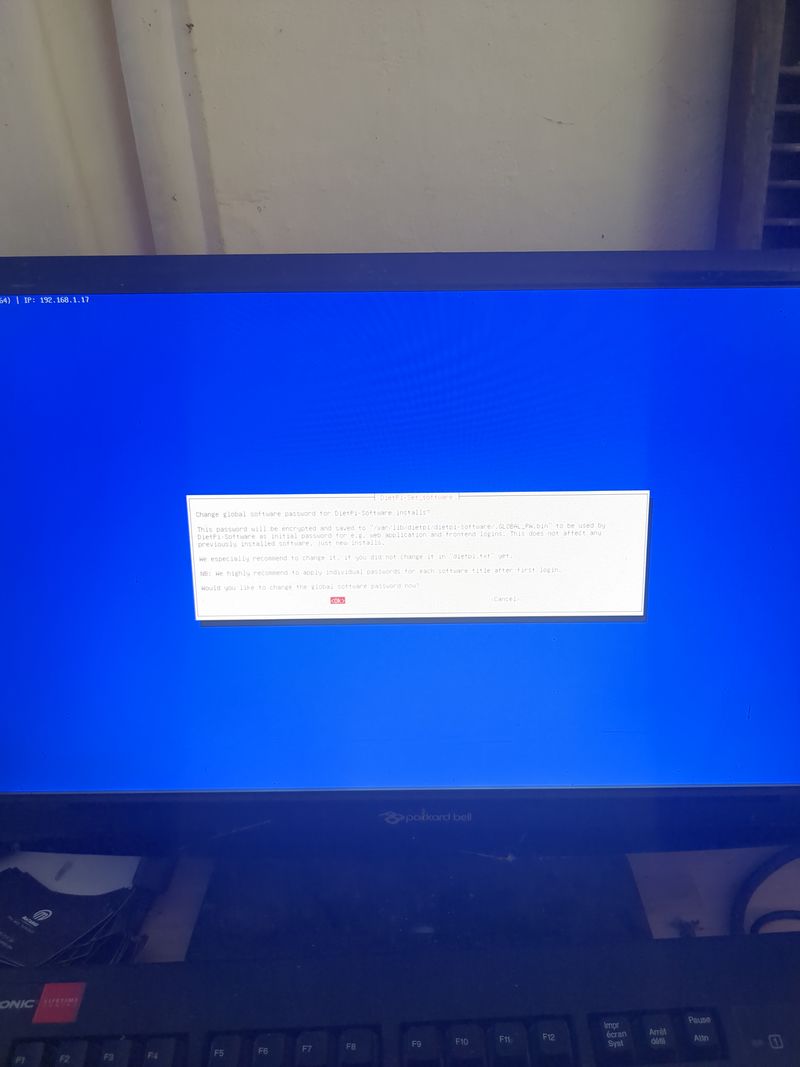
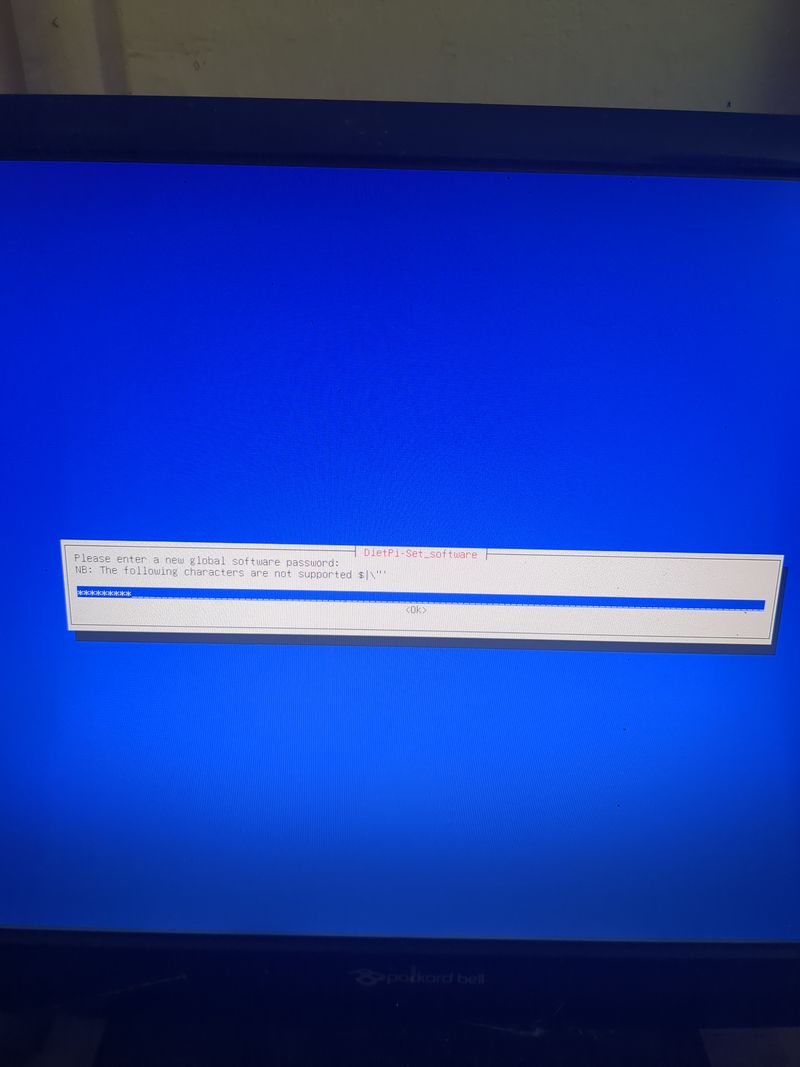
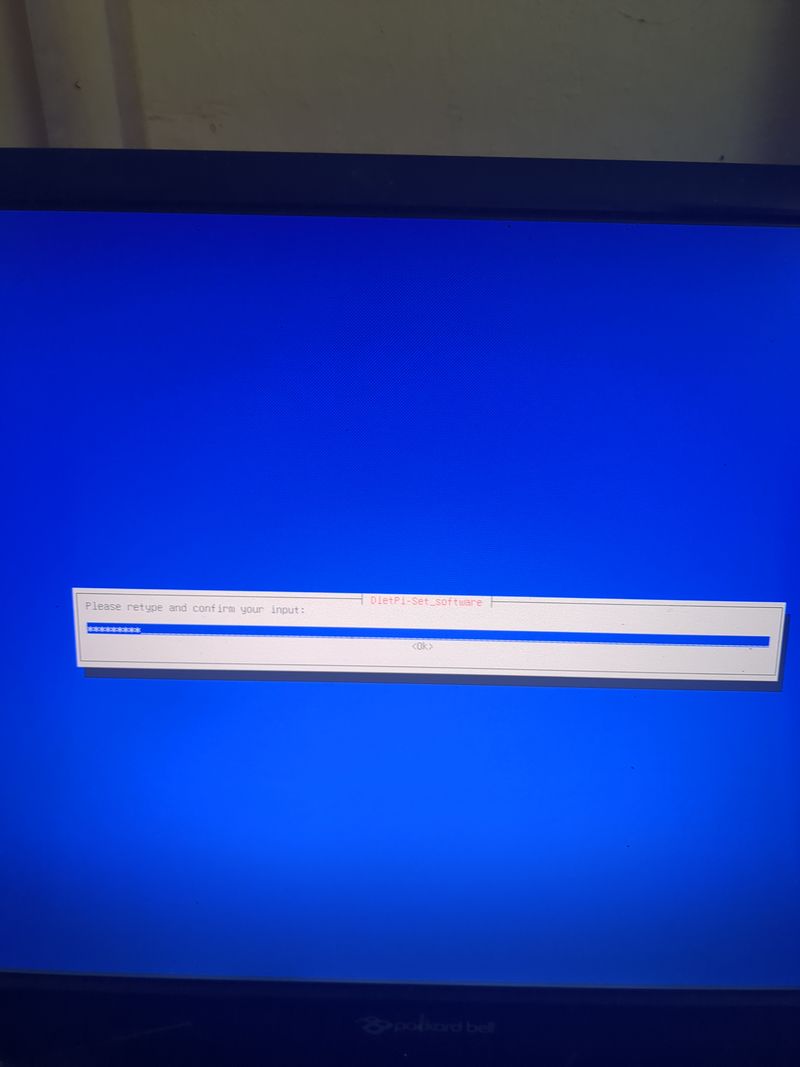
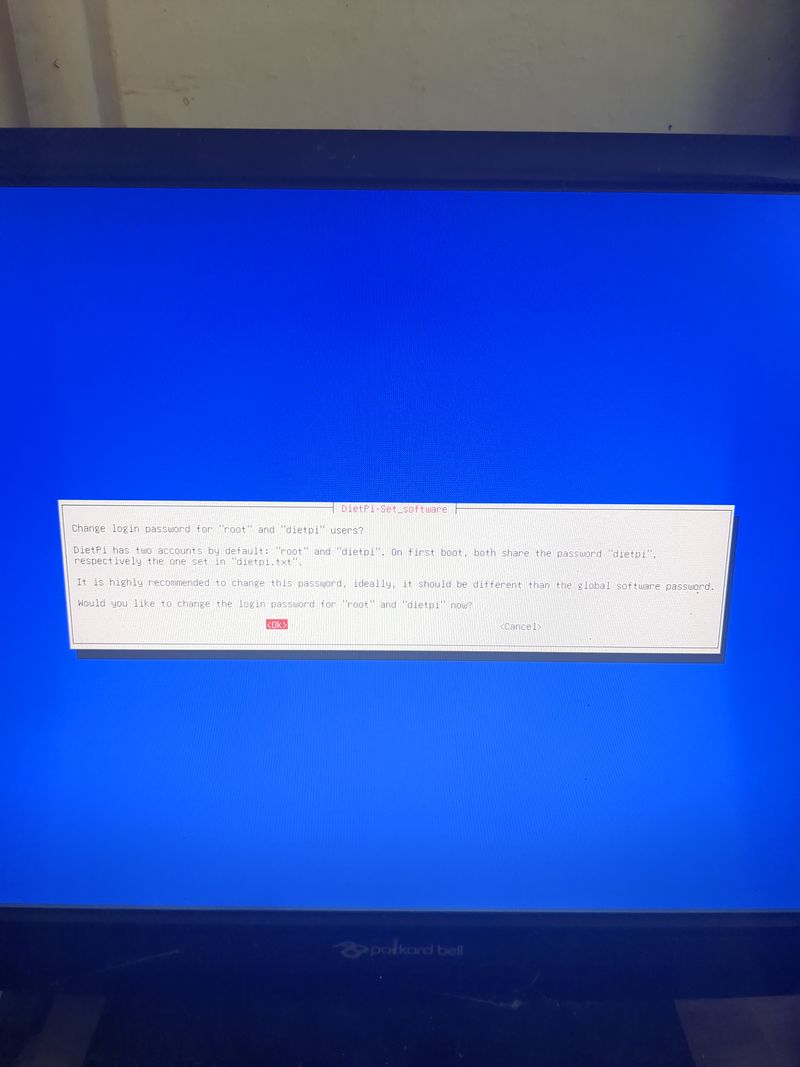
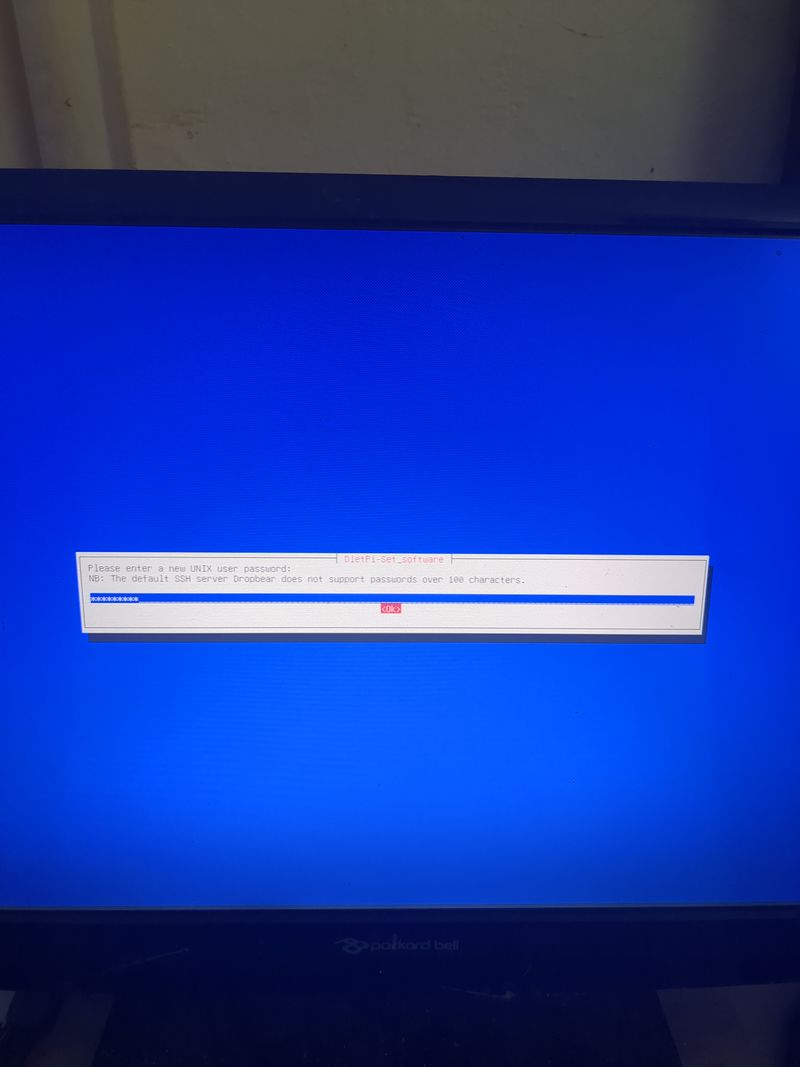
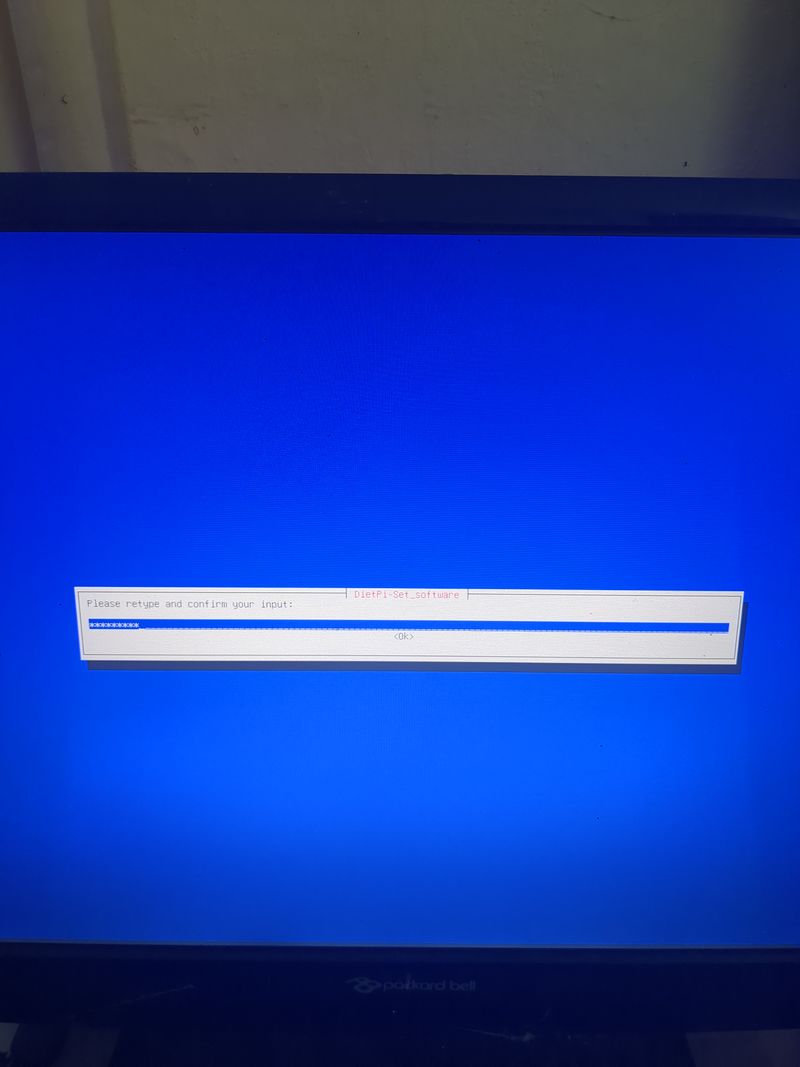
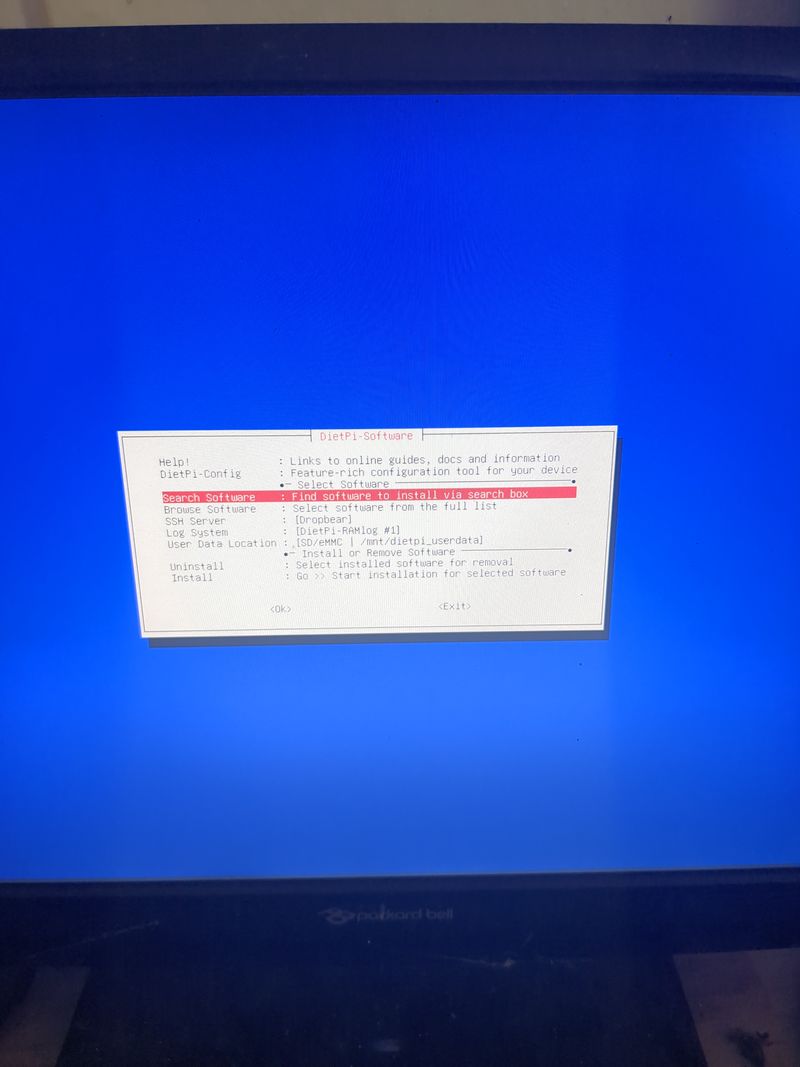

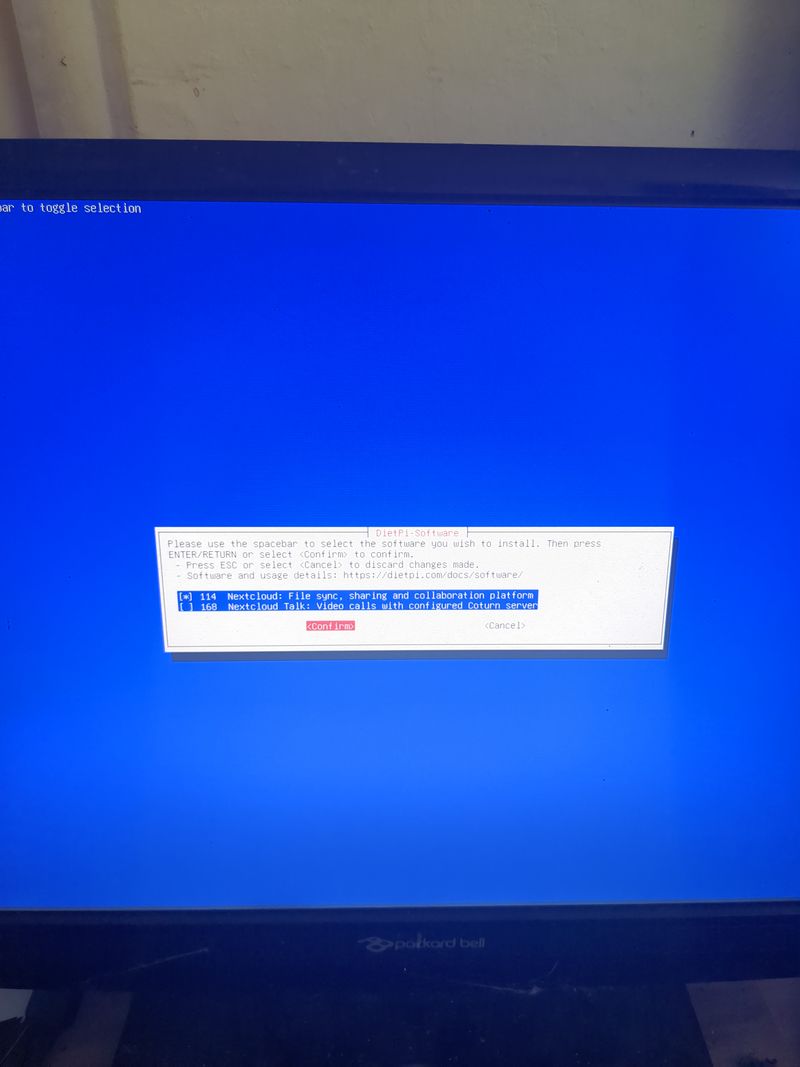
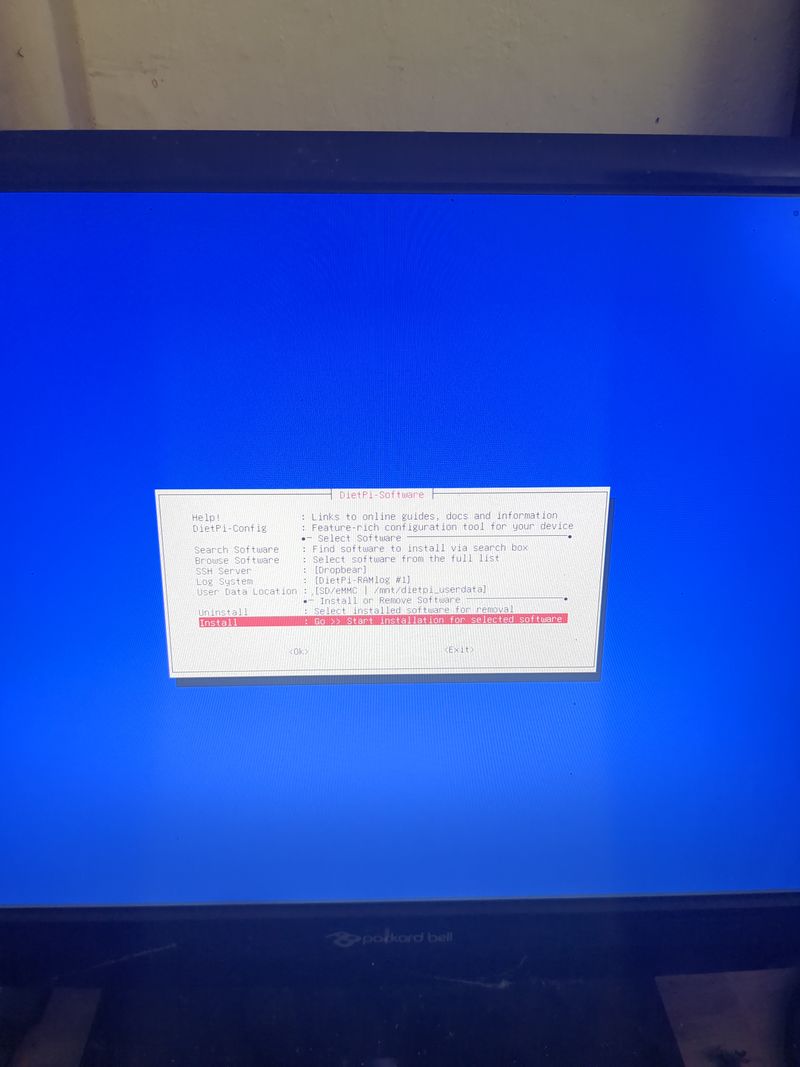
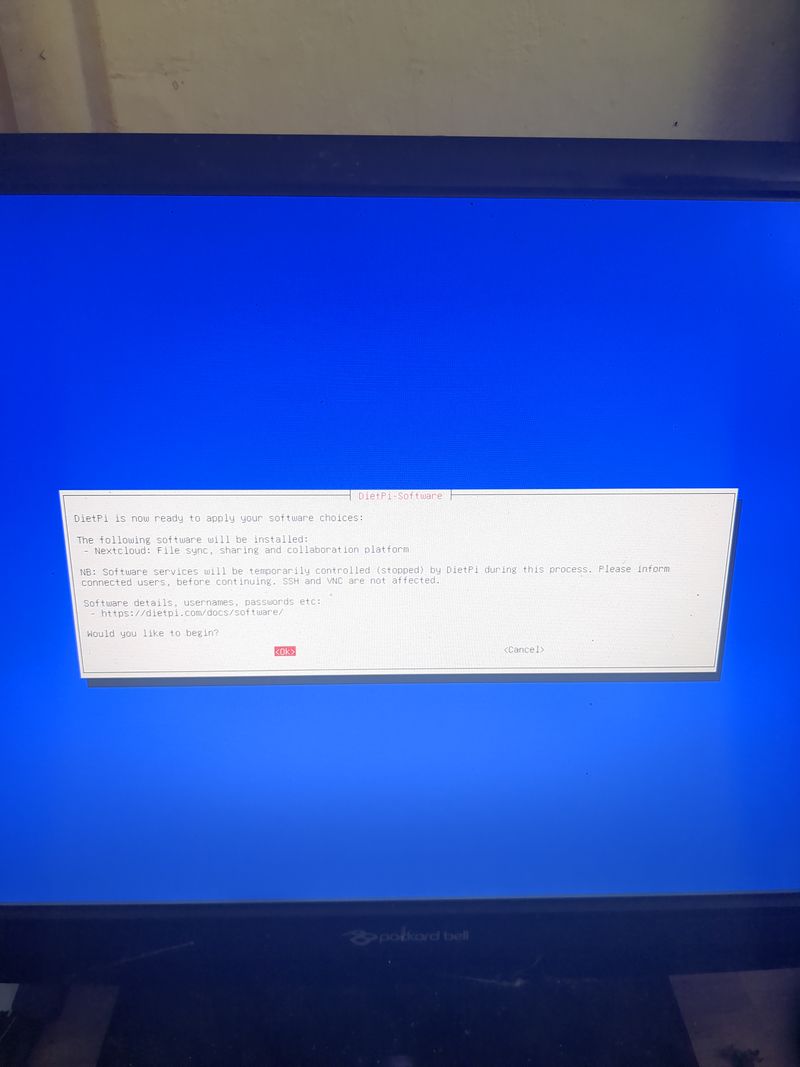
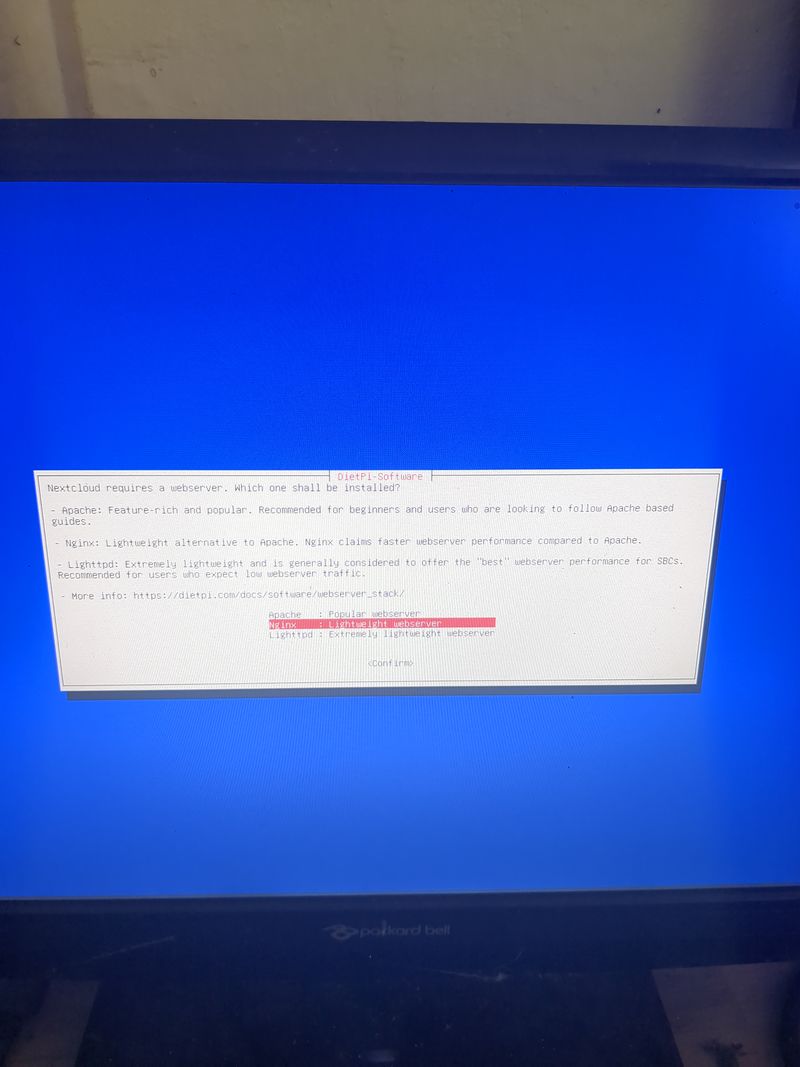
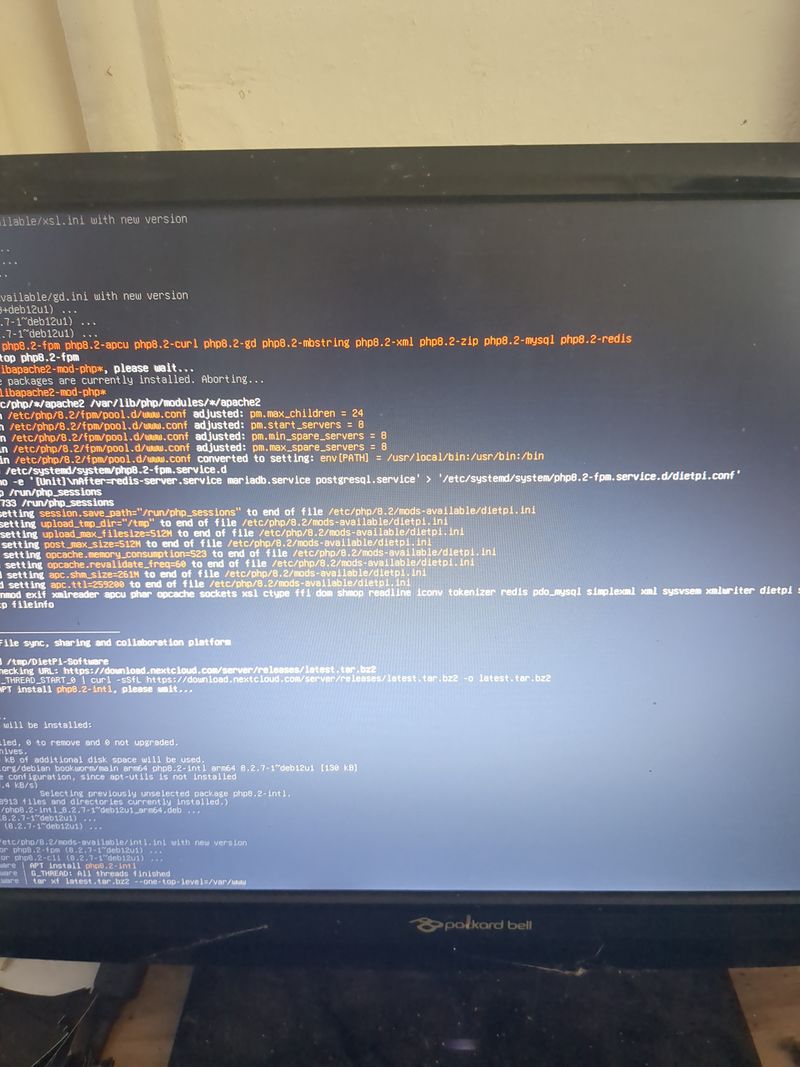
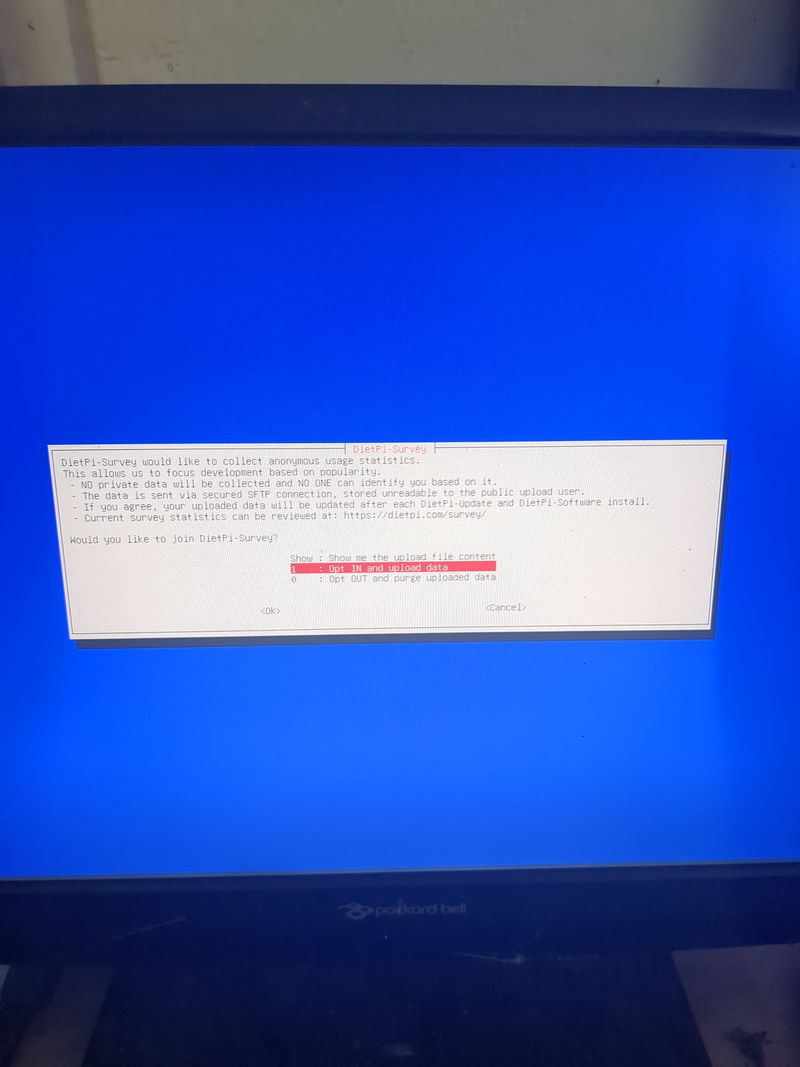
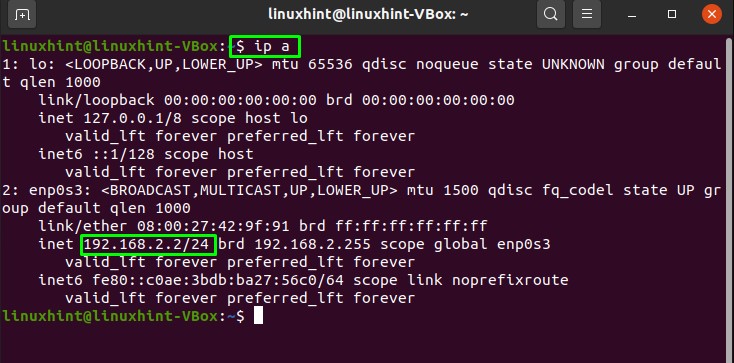
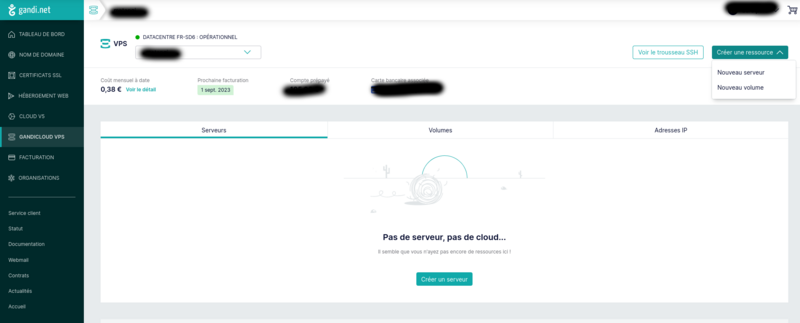
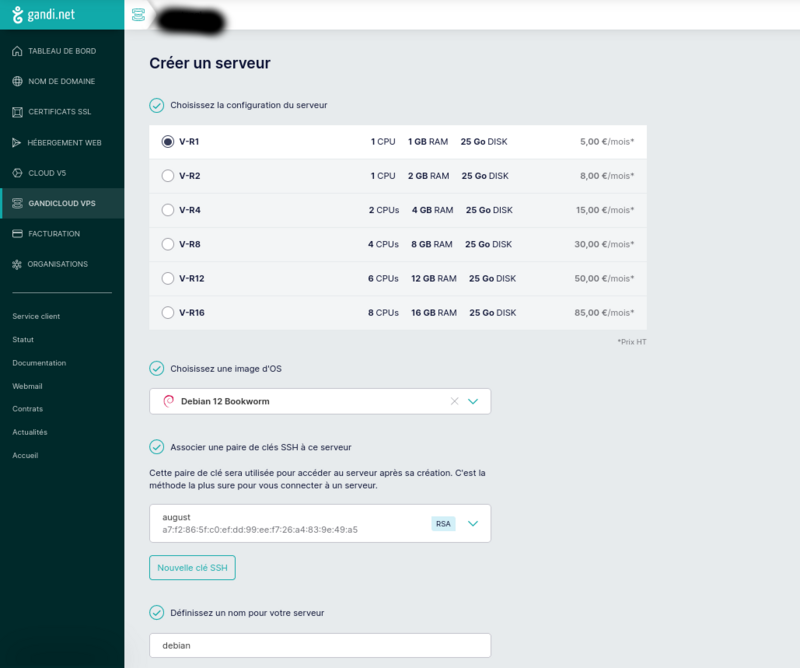
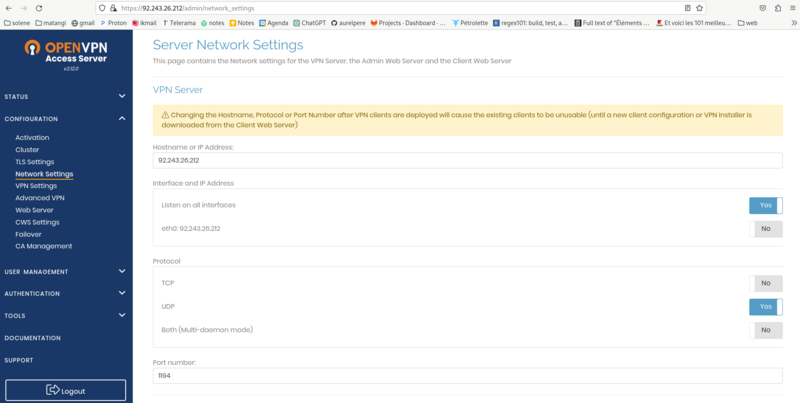
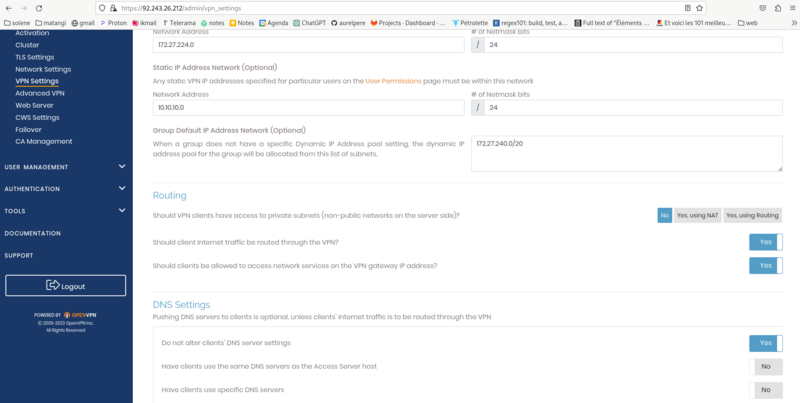
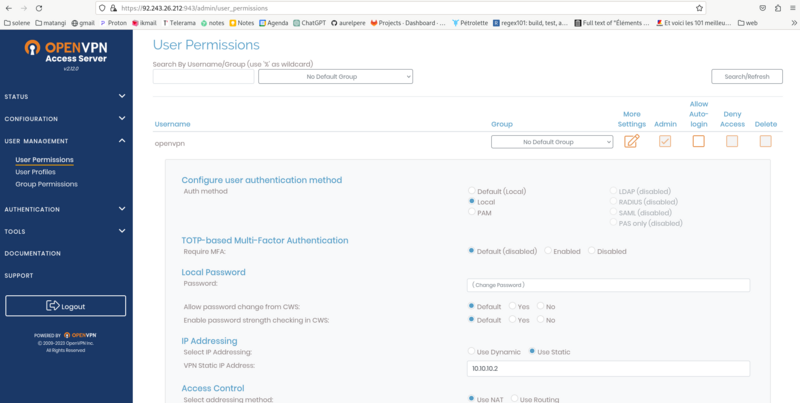
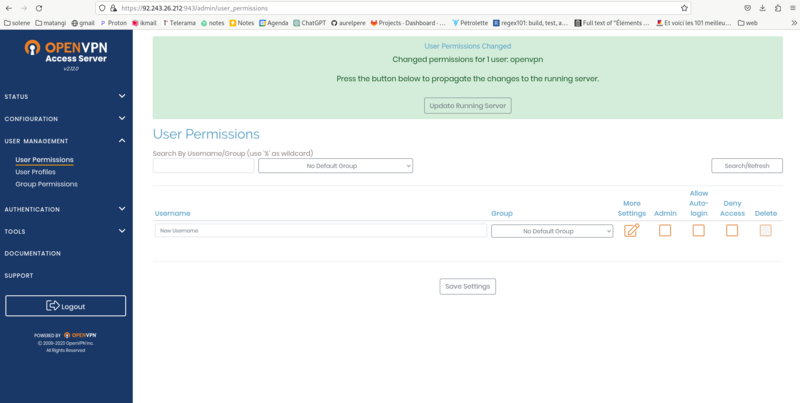
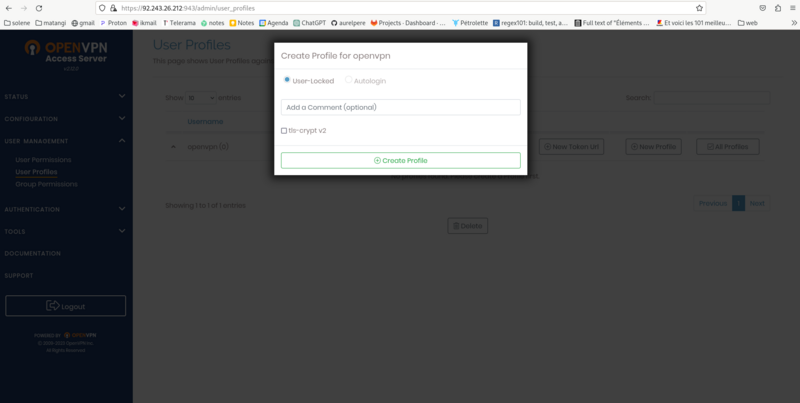
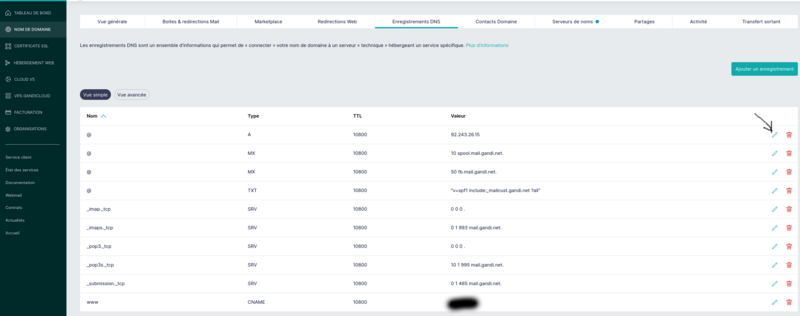
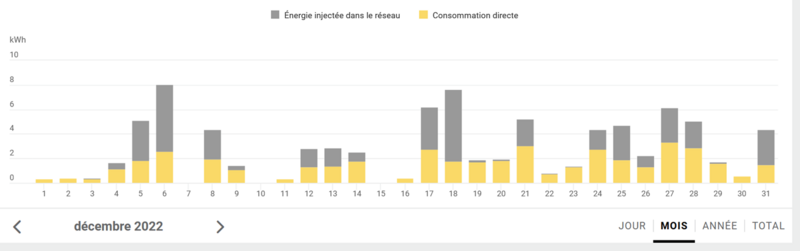
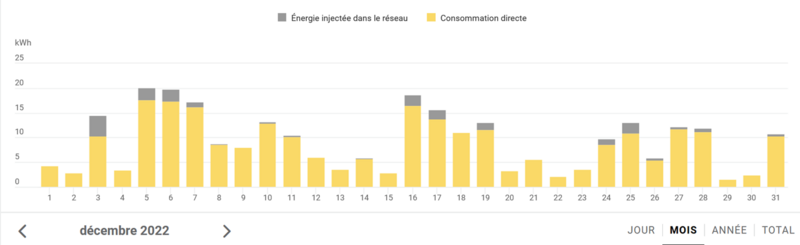
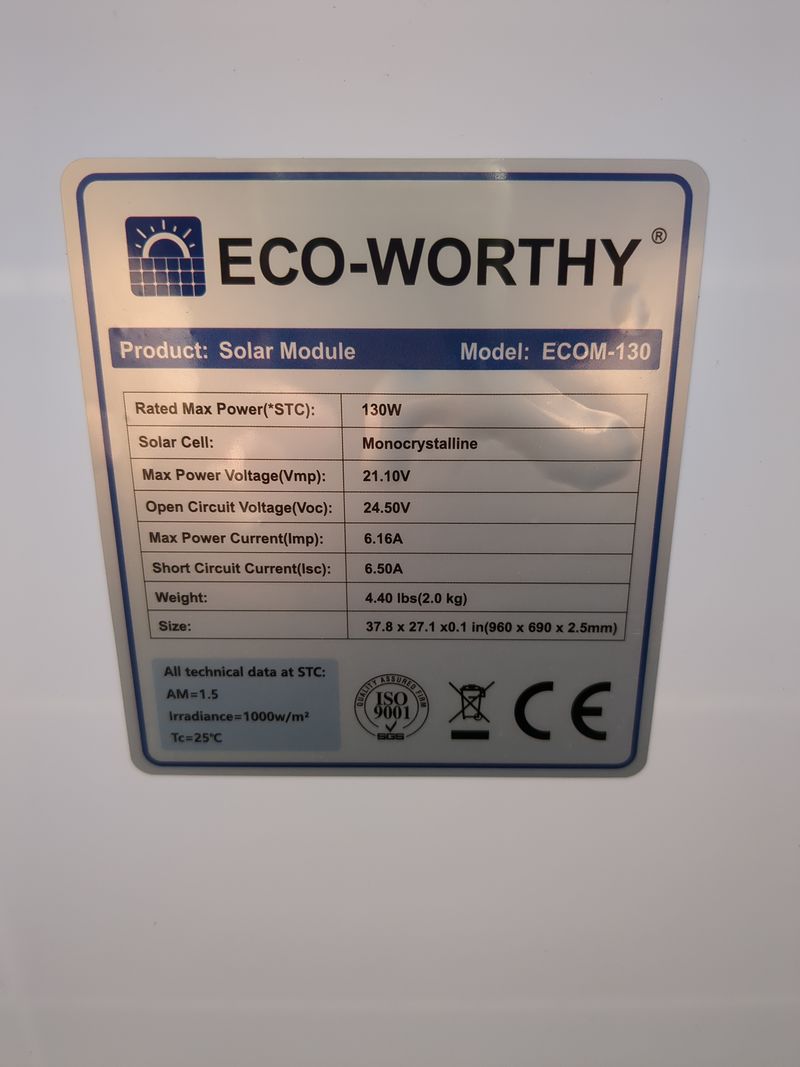
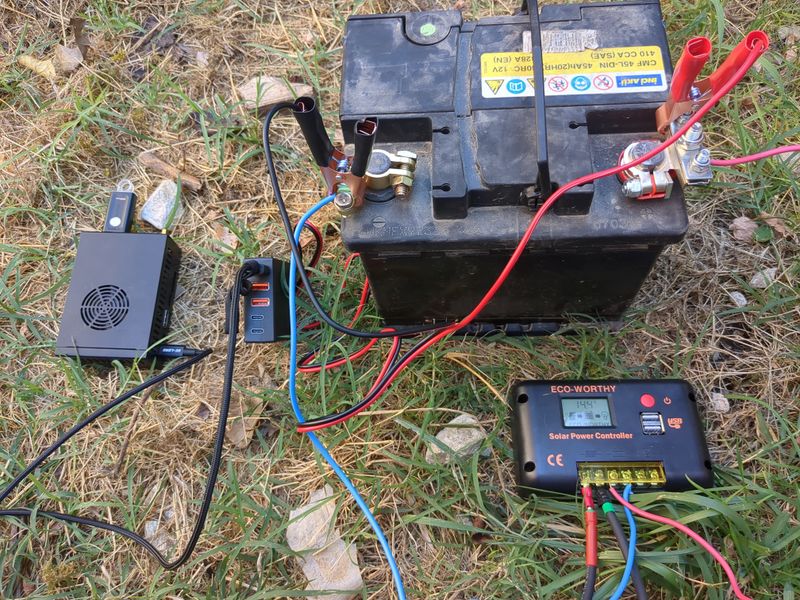


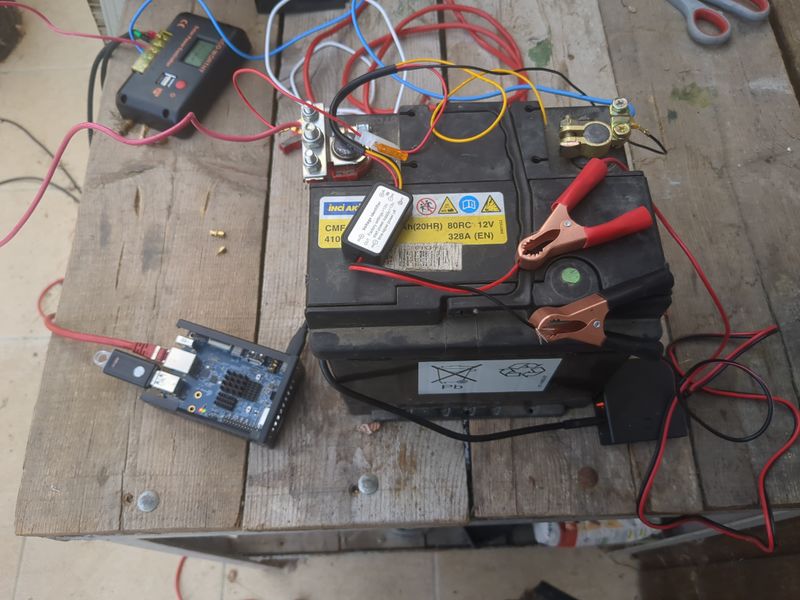
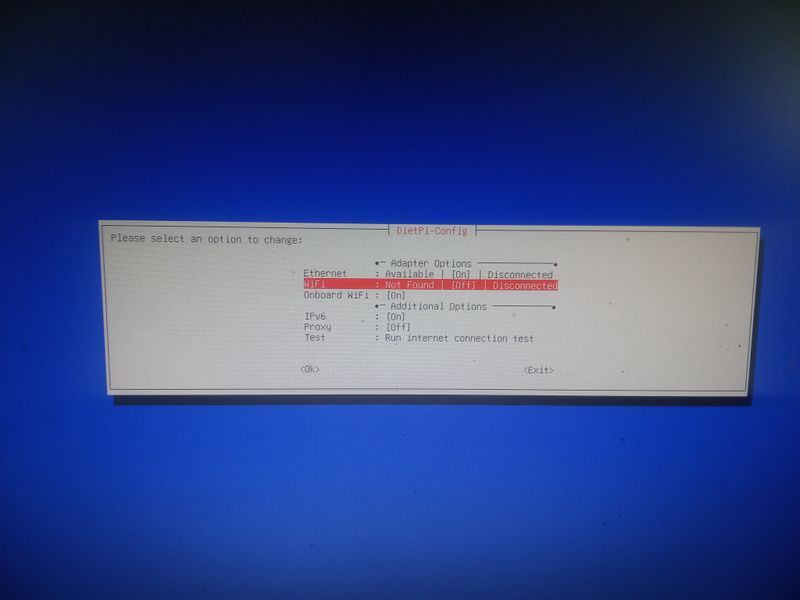
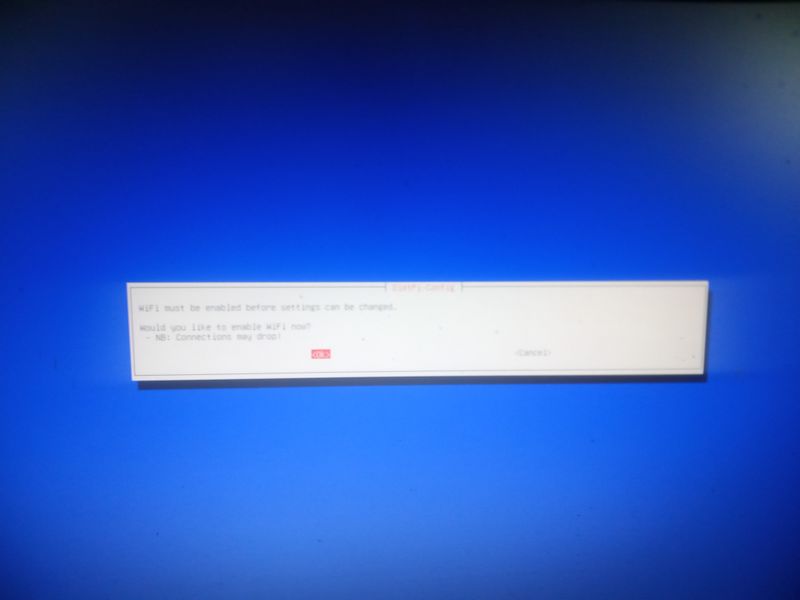
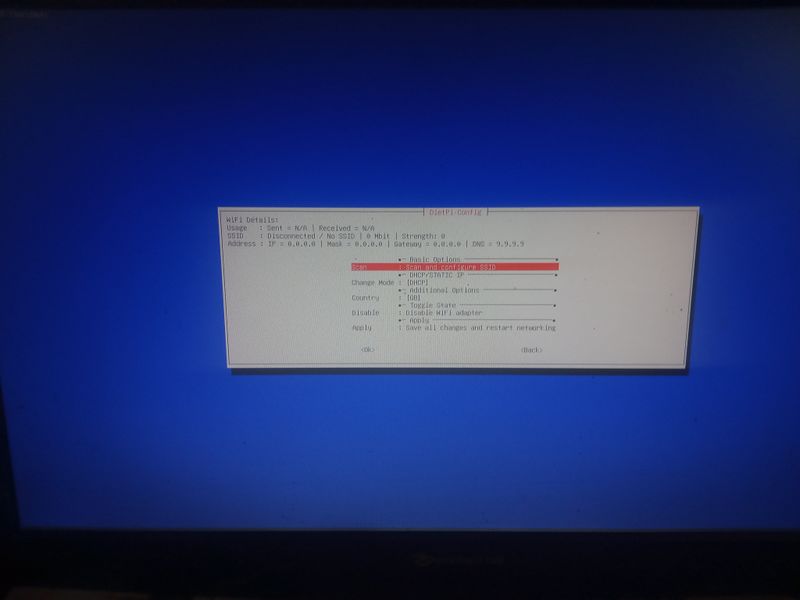
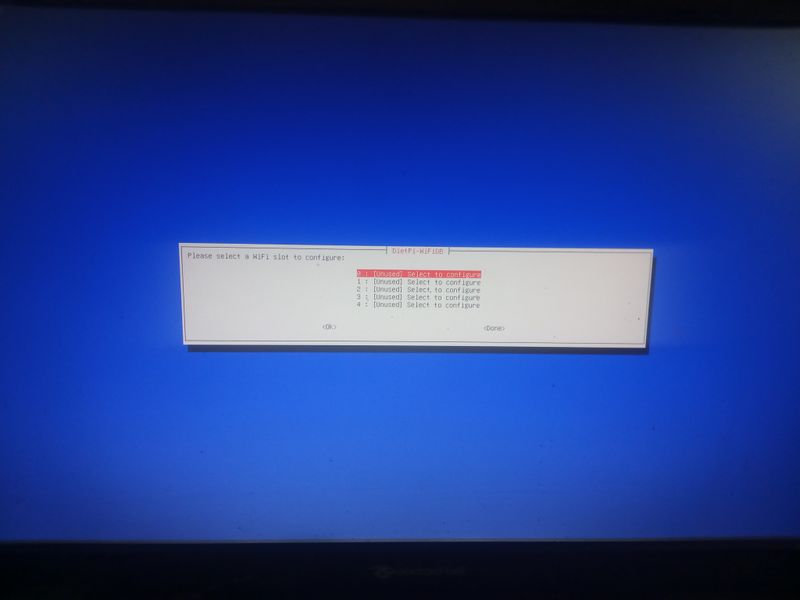
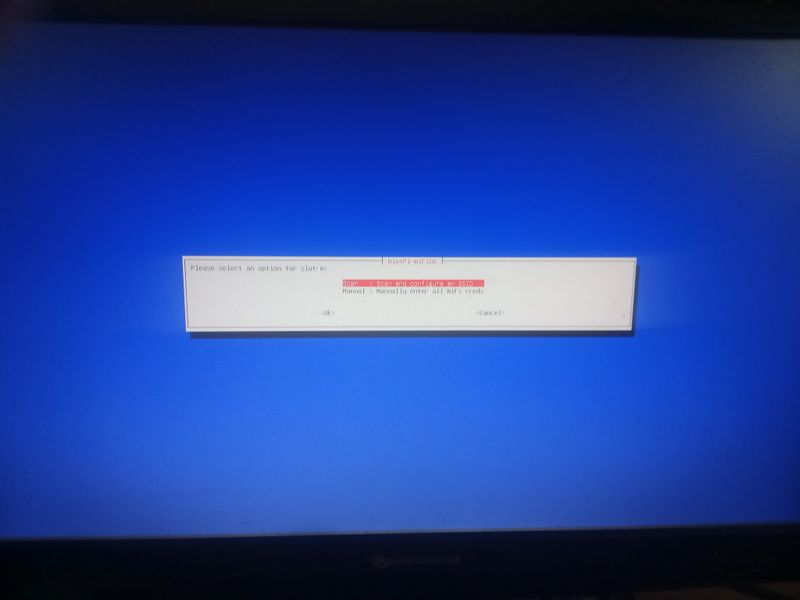
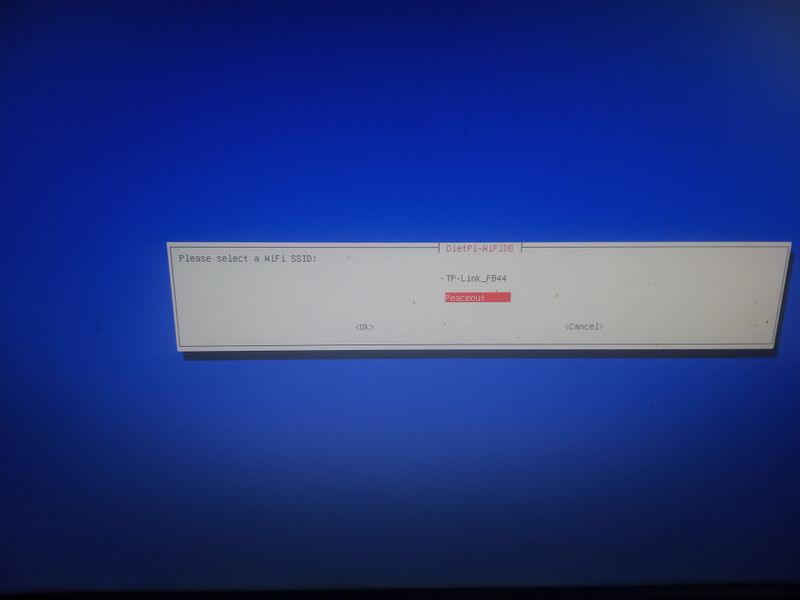
 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português