Description
A project by engineering students to build a low-tech solar watermaker to help disadvantaged communities.
Sommaire
Sommaire
- 1 Description
- 2 Sommaire
- 3 Introduction
- 4 Étape 1 - Nomenclature
- 5 Étape 2 - General operating principle
- 6 Étape 3 - Solar concentrator 1 - Presentation
- 7 Étape 4 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.2 - Step 1
- 8 Étape 5 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.2 - Step 2
- 9 Étape 6 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.2 - Step 3
- 10 Étape 7 - Solar concentrator 1 - Pipe support 1.3.1 - Step 1
- 11 Étape 8 - Solar concentrator 1 - Pipe support 1.3.1 - Step 2
- 12 Étape 9 - Solar concentrator 1 - Pipe support 1.3.1 - Step 4
- 13 Étape 10 - Solar concentrator 1 - Pipe support 1.3.1 - Step 5
- 14 Étape 11 - Solar concentrator 1 - Secondary reflector 1.3 - Presentation
- 15 Étape 12 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.3 - Step 1
- 16 Étape 13 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.3 - Step 2
- 17 Étape 14 - Watermaker 2 - Presentation
- 18 Étape 15 - Watermaker 2 - Evaporation tank 2.1 - Step 1
- 19 Étape 16 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve évaporation 2.1 - Etape 2
- 20 Étape 17 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve évaporation 2.1 - Etape 3
- 21 Étape 18 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve de condensation 2.2 - Etape 1
- 22 Étape 19 - Dessalinisateur 2 -Cuve de condensation 2.2 - Etape 2
- 23 Étape 20 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve de condensation 2.2- Etape 3
- 24 Étape 21 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve de condensation 2.2 - Etape 4
- 25 Étape 22 - Circuit total 3
- 26 Étape 23 - Pompe 3.2
- 27 Commentaires
Introduction
L'EauTech is a project run by six students from the Ecole Centrale de Lille in collaboration with the Gold Of Bengal association. The aim of the project is to build a low-tech solar watermaker, based on two projects already carried out at the Ecole Centrale de Lille: the Opensol project, which created a low-tech solar concentrator, and the Delta project, which created a low-tech watermaker.
You can find and download a summary of this tutorial in PDF format by clicking on this link: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1aqvStMdIfSuhj4bioxSa0Zk8wiuJO1vL .
Matériaux
1. Solar concentrator
1.1. Frame
- Strong wooden board, minimum size 1x2m
1.2 Main reflector
1.2.1. Main reflector support
- Wooden board minimum size 0.9x2m
1.2.2. Mirrors
- Around 35 sheets of mirrors measuring 10x80cm
OR
- Around 35 aluminium sheets, minimum size 10x80cm
- A self-adhesive mirror to cut out, approx. 0.1x1m (if possible)
1.3. Secondary reflector
1.3.1. Copper pipe and reflector support
- 2 wooden battens, 2.4m long and 27x27mm in cross-section
- Wooden board (thickness: approx. 5mm, surface: enough to make two slabs approx. 8x8cm)
- 2 clamps diameter 28mm
- 6 screws
- 28mm diameter copper pipe, 1m long
- 2mm thick sheet metal
1.3.2. Secondary reflector and copper pipe
- PVC tube: 1m long and 10cm in diameter
- Soda cans
- Black paint
2. Watermaker
2.1. Evaporation tank
2.1.1. Frame
- 6 stainless steel sheets 2mm thick (2 sheets 15cmx4cm, 2 sheets 1mx1cm, 1 sheet 1mx1cm, 1 sheet 1.02mx6cm)
2.1.2. Stages
- 2 stainless steel sheets 2mm thick: 1mx3.6cm
2.1.3. Copper pipe
- 14mm diameter copper tube 1m long
2.2 Condensation tank
2.2.1. Frame
- 2mm-thick stainless steel sheet measuring at least 200x2100mm
2.2.2. Copper pipe
- 14mm diameter copper tube 2,5m long
2.2.2.1. Copper condensing coil 2.2.2.2. Copper water inlet pipe 2.2.2.3. Copper water outlet pipe
2.2.3. Cover
- 8 screws 6mm diameter with washers and nuts
- 2mm thick stainless steel sheet: 250x250mm
3. Total circuit
3.1 Circuit-closing pipes
- 20 rubber seals
- Valve
- 5 flexible tubes 1m or 50 cm to close the circuit
- Any fittings
3.2. Pump
- Oil pump
- Vegetable oil
Outils
- Screws
- Drills
- Saw
- Scissors
- Measuring tape
- Wood glue
- Strong glue for all materials
- Pencil
- Screwdrivers
- Welding machine
- Hacksaw
Étape 1 - Nomenclature
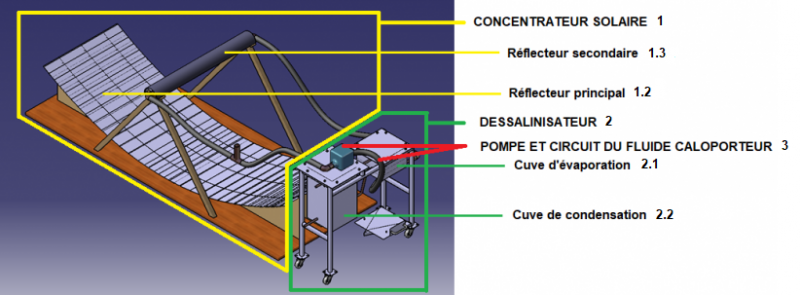
1 Solar concentrator
1.1 Frame
1.2 Main reflector
1.2.1 Support for main reflector
1.2.2 Mirrors
1.3 Secondary reflector
1.3.1 Support for secondary reflector
1.3.2 Secondary reflector and copper pipe
2 Watermaker
2.1 Evaporation tank
2.1.1 Frame
2.1.2 Stages
2.1.3 Copper pipe
2.2 Condensation tank
2.2.1 Frame
2.2.2 Copper pipes
2.2.2.1 Copper condensing coil
2.2.2.2 Copper water inlet pipe
2.2.2.3 Copper water outlet pipe
2.2.3 Cover
3 Total circuit
3.1 Circuit closing pipes4 3.2 Pump
Étape 2 - General operating principle
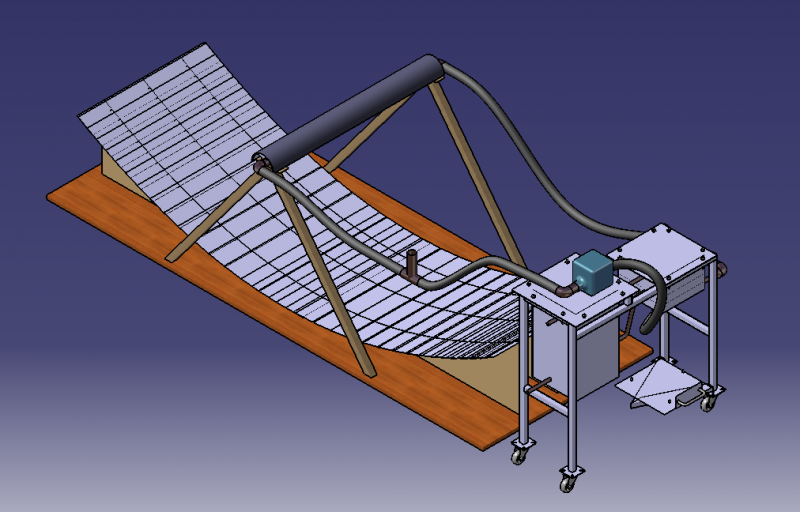
The system can be split into two sub-systems: the solar concentrator 1 and the watermaker 2.
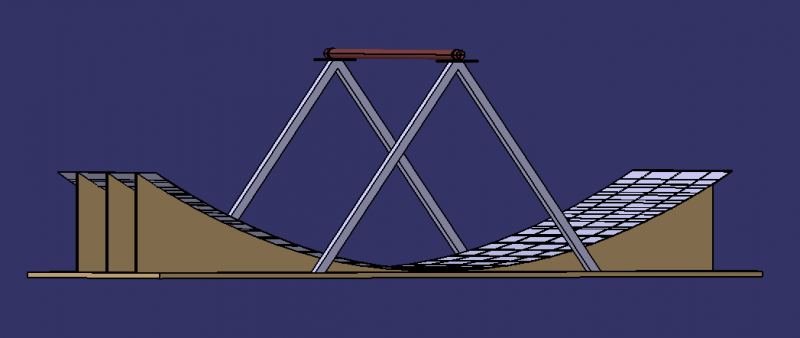
In the solar concentrator 1, the sun's rays are reflected by the main reflector 1.2 and the secondary reflector 1.3 towards a copper tube 1.3.2 in which a heat transfer fluid (oil) circulates. This fluid is then heated until it boils. It circulates in a closed circuit thanks to a pump 3.2.
This circuit goes through an evaporation tank 2.1 filled with dirty water, which is heated to boiling point by the heat transfer fluid. This water vapour then goes through two successive distillation stages 2.1.2 in the evaporation tank 2.1, before reaching the condensation tank 2.2 in which the water vapour is condensed by a coil 2.2.2.1 through which it travels before emerging as clean liquid water.
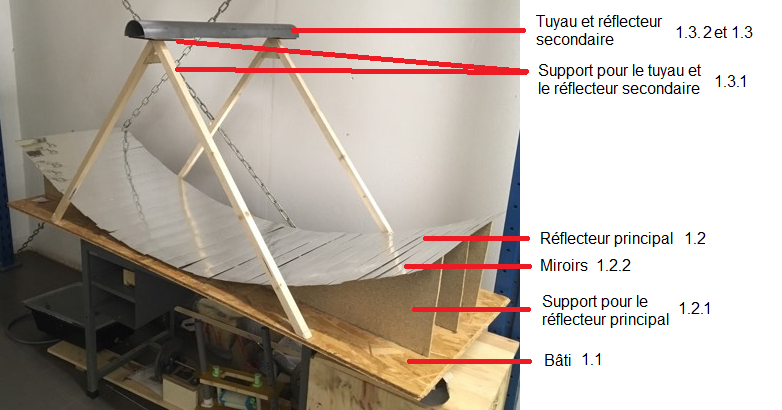
Étape 3 - Solar concentrator 1 - Presentation
- Name of the different parts of the solar concentrator 1
- Material: wood
- Copper tubes
- Mirrors (or aluminium plates)
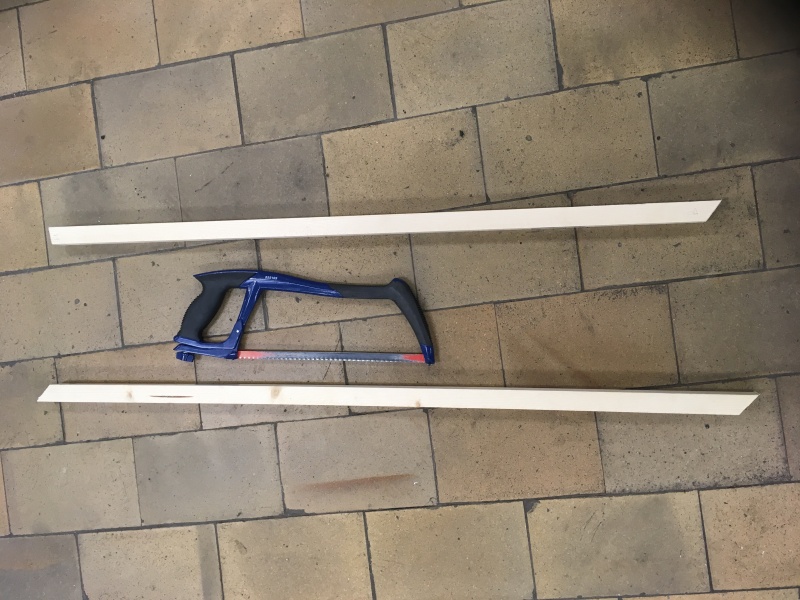
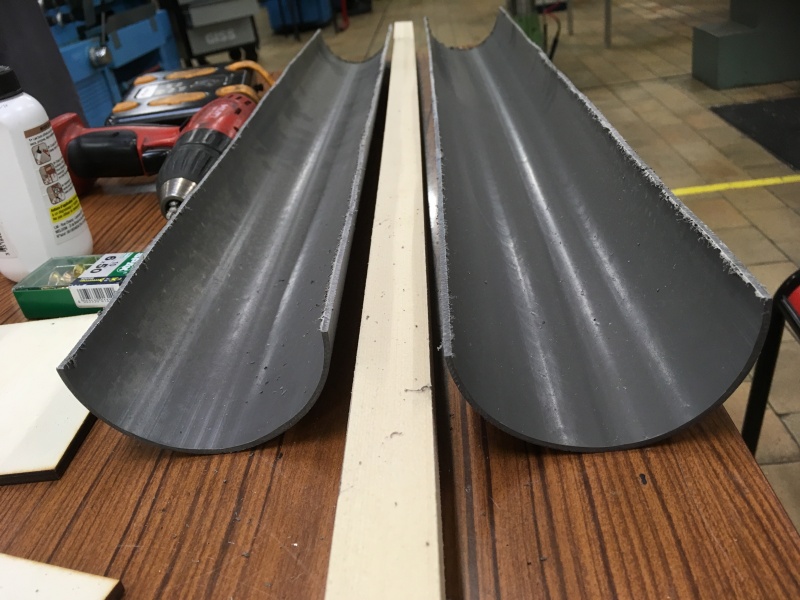
Étape 4 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.2 - Step 1
Step 1: Frame 1.1
- Cut the frame 1.1 out of the strong wooden board: 1mx2m
Étape 5 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.2 - Step 2
Step 2: Main reflector brackets 1.2.1
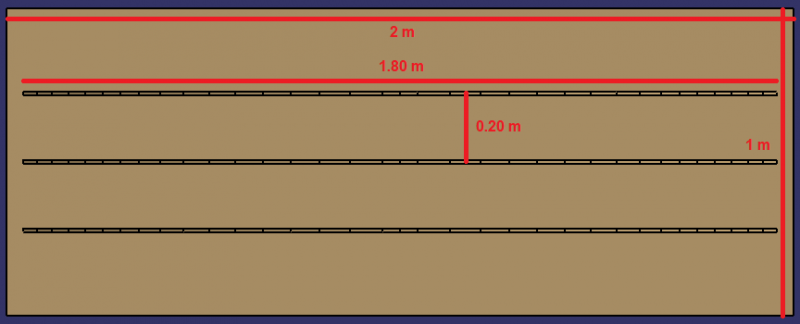
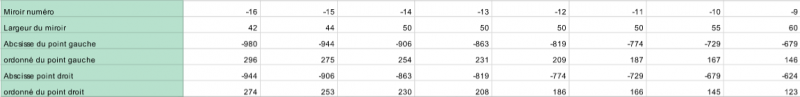
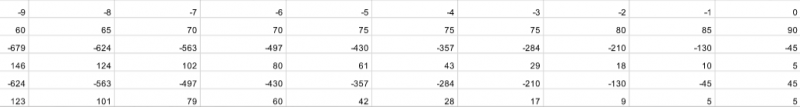
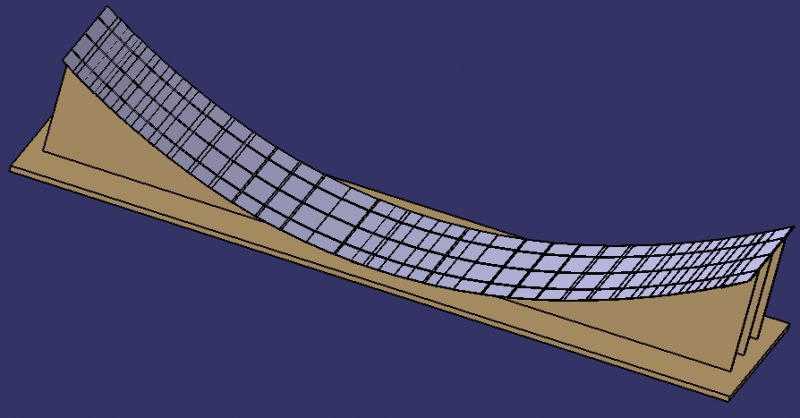
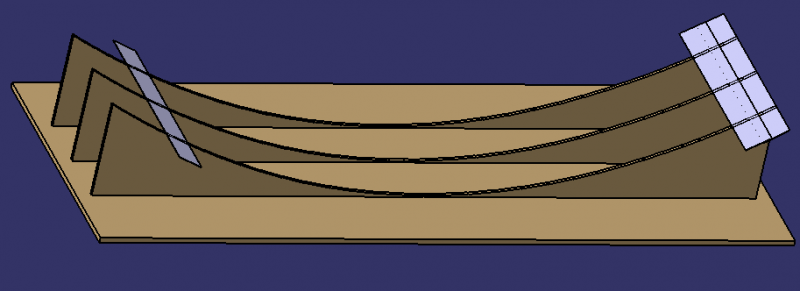
- Cut out the 3 1.2.1 supports for the main reflector using wooden planks.
- For the parabolic shape: see dimensions in the table.
Étape 6 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.2 - Step 3
Step 3: Mirrors 1.2.2
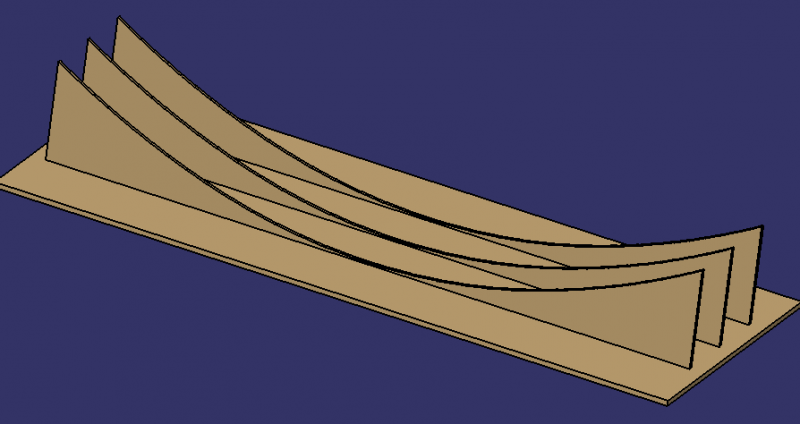
- Main reflector 1.2: cut the mirror plates 1.2.2 into rectangular shapes (dimensions from previous table).
- Fix the plates 1.2.2 with glue to the support 1.2.1 and check that they are correctly oriented: the sun's rays should converge towards a pipe located at a height of 80cm.
Note: The 1.2.2 mirror can be replaced by an aluminium plate that can be covered with self-adhesive mirror.
Étape 7 - Solar concentrator 1 - Pipe support 1.3.1 - Step 1
Step 1: Cutting the battens
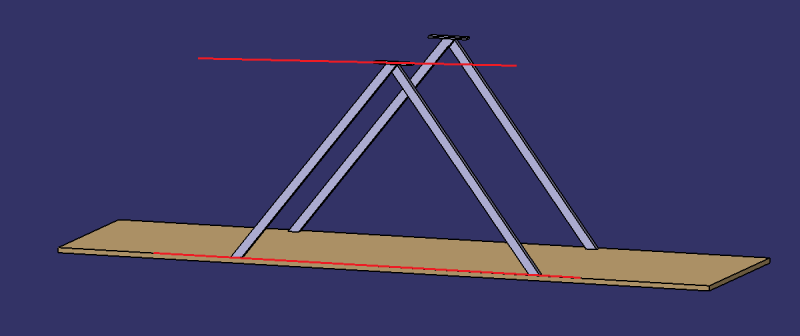
- Cut the battens into four pieces approximately 65 cm long.
- Cut inclined planes at the end of the 4 pieces so that they can be glued together 2 by 2 (see photo). After gluing, the top should be 80cm above the frame.
- Cut other inclined surfaces on the other side of the 4 pieces so that they can be fixed to the 1.1 frame.
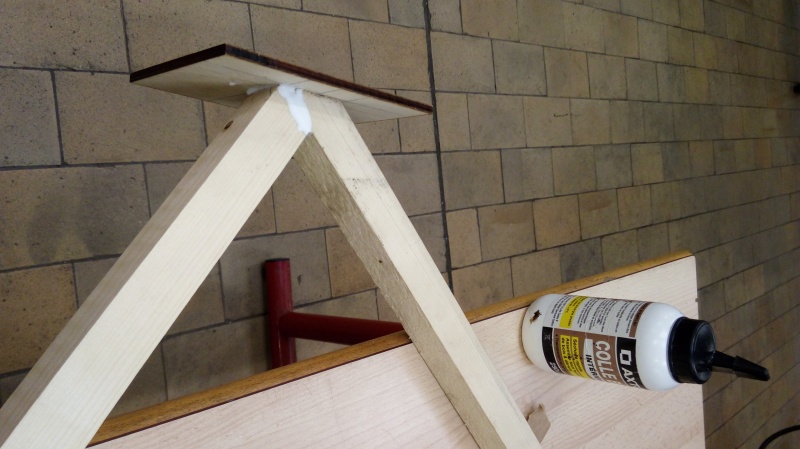
Étape 8 - Solar concentrator 1 - Pipe support 1.3.1 - Step 2
Step 2: Secondary reflector support 1.3.1 and clamps
- Grind the cut surfaces to make the glue more effective.
- Glue the cleats C from the previous step in pairs. Board B must be 80cm above the frame.
- Screw the two boards B to the battens C (see photo) using the clamp support A.
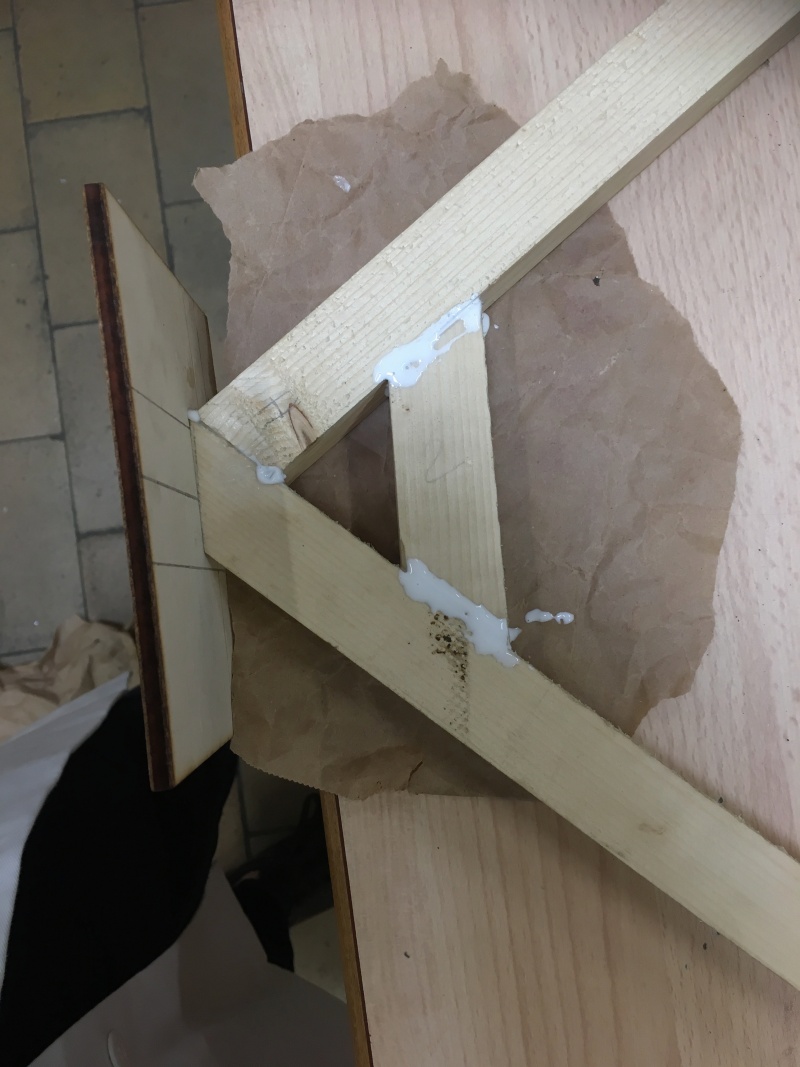
Étape 9 - Solar concentrator 1 - Pipe support 1.3.1 - Step 4
Step 4: Consolidation
- Using the off-cuts of battens, cut pieces and glue them to the supports, taking care to sand them as before, so as to consolidate the structure.
Étape 10 - Solar concentrator 1 - Pipe support 1.3.1 - Step 5
Step 5: Screwing
- All that remains is to screw the two pieces of the pipe support structure 1.3.1 to the frame 1.1 from underneath the structure.
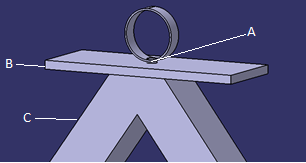
Étape 11 - Solar concentrator 1 - Secondary reflector 1.3 - Presentation
The secondary reflector 1.3 reflects light rays not intercepted by the copper tube 1.3.2 back onto it. It is located above the tube 1.3.2.
Étape 12 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.3 - Step 1
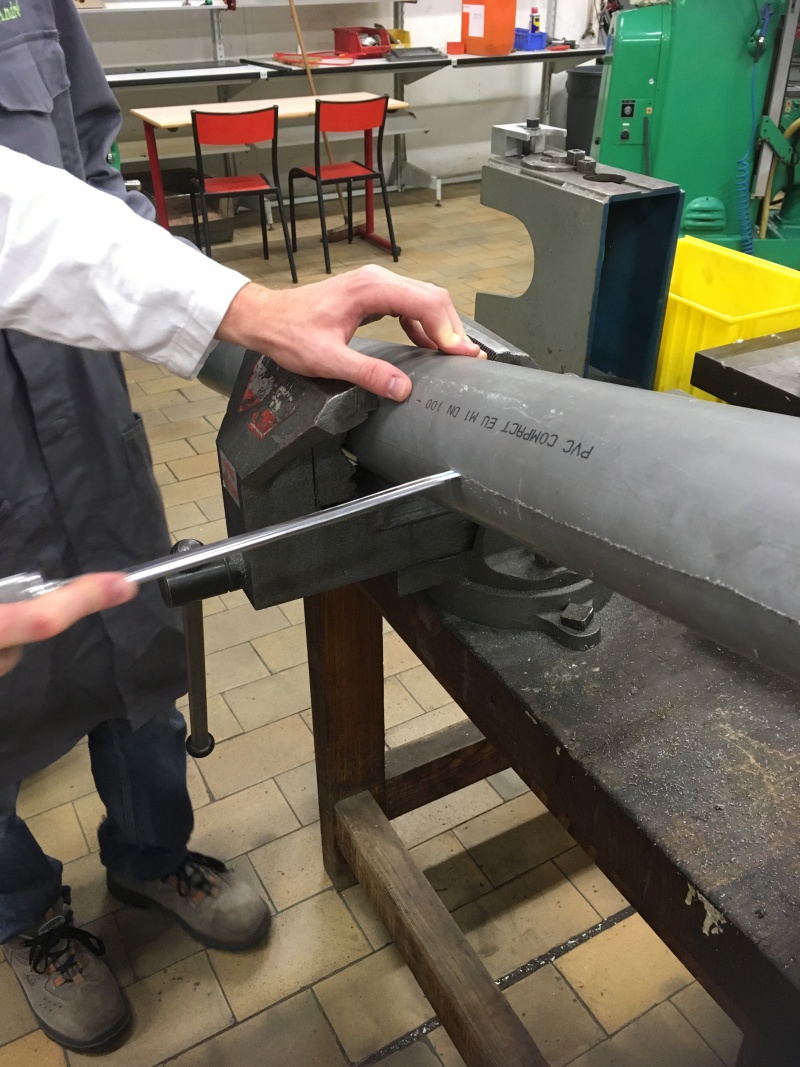
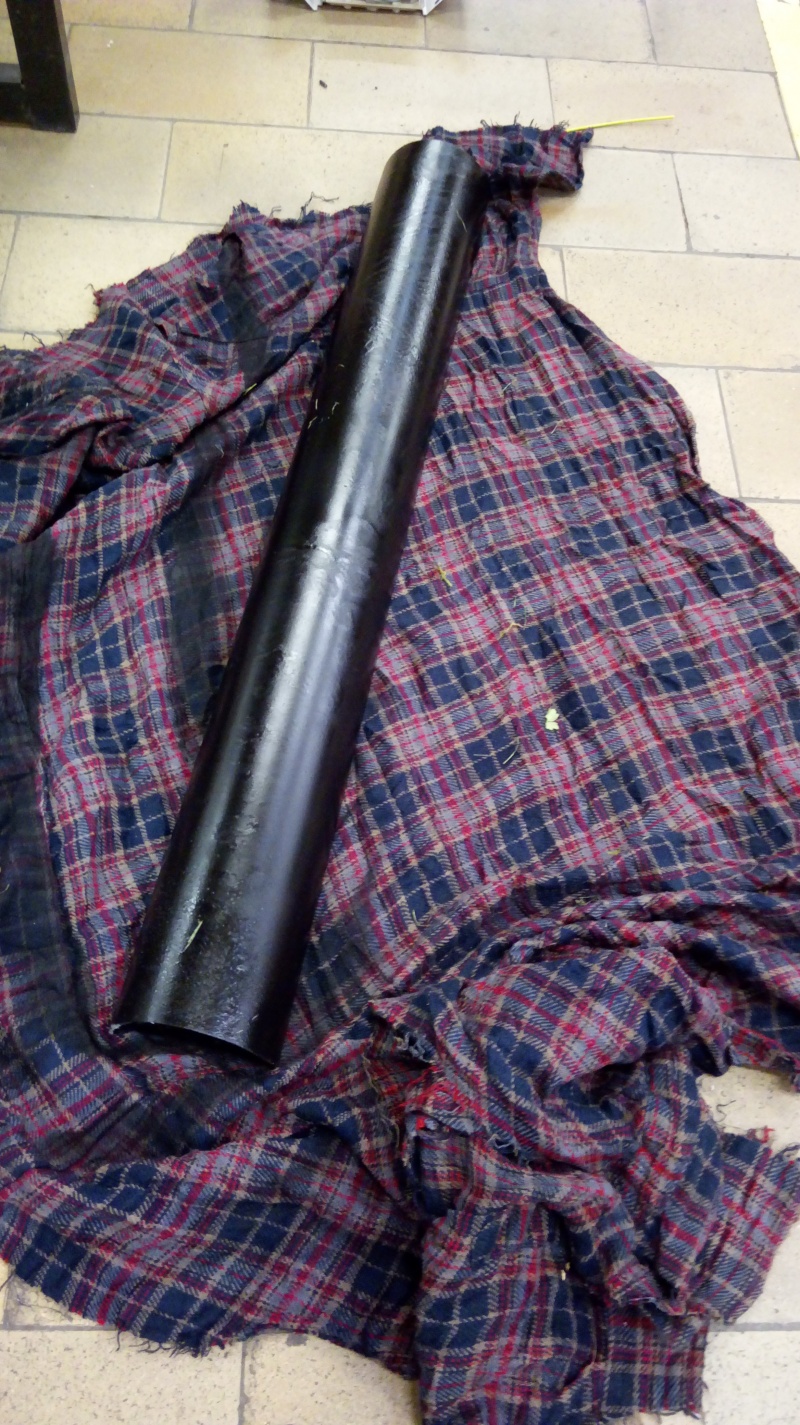
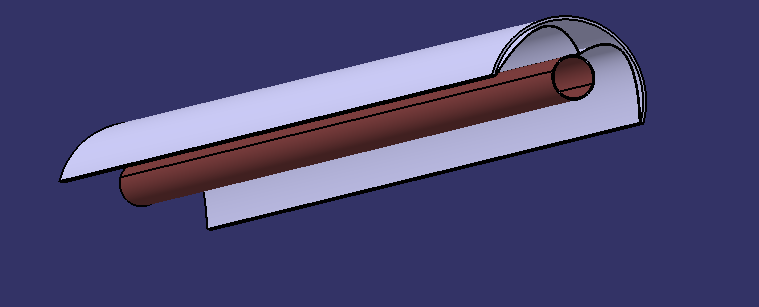
Step 1: Cutting the PVC pipe
The PVC tube is what supports the secondary reflector 1.3. It holds the soda cans that reflect the light rays.
- Cut the PVC pipe in half lengthways.
- Colour the outside of the PVC pipe black with paint.
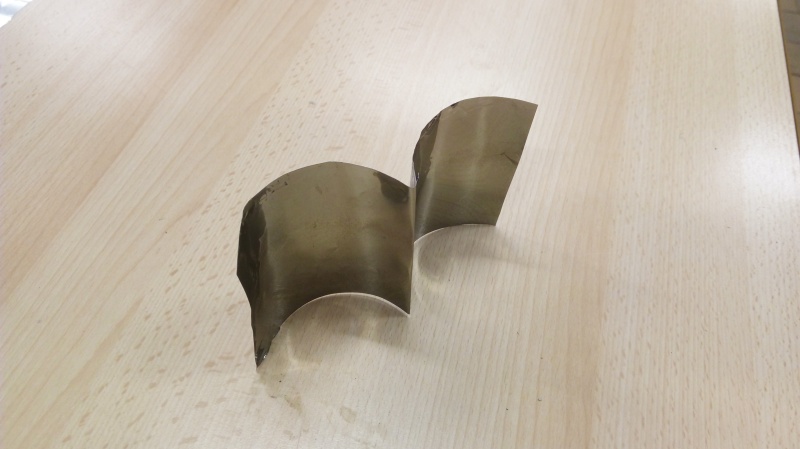
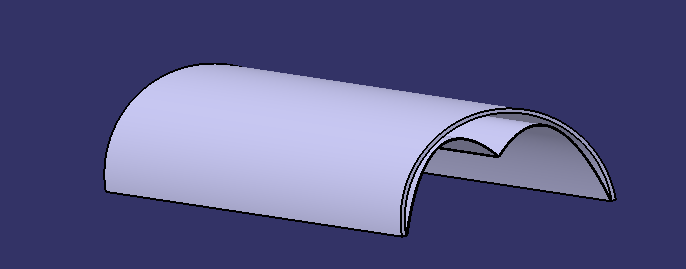
Étape 13 - Solar concentrator 1 - Main reflector 1.3 - Step 2
Step 2: Cutting and gluing the cans
As the cans are made of aluminium, the inside of the can proved to be a good alternative for reflecting light rays.
- Cut the cans into rectangles 9cm wide, there are no length constraints for the other sides.
- Fold in half widthways to make two parts 4.5cm wide.
- Glue the cans into the PVC tube (they will have a rounded W shape) using strong glue.
- Note: you can stick self-adhesive mirrors in the cans to improve reflection.
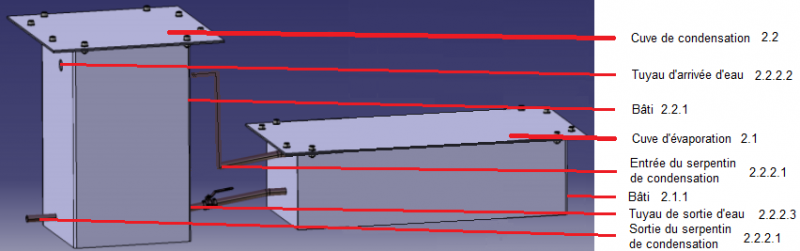
Étape 14 - Watermaker 2 - Presentation
- Name of the different parts of the watermaker 2
- Material: steel
- Copper tubes
- The condensation tank 2.2 is used to store brackish water before the evaporation tank 2.1. In this tank, the steam created by the evaporation tank 2.1 circulates in a coil 2.2.2.1.
- The evaporation vat 2.1, consisting of 2 stages 2.1.2, is used to convert brackish water into steam. The vapour created circulates through a coil 2.2.2.1 in the condensation tank 2.2 in order to cool it and convert it into a liquid state.
- Desalinated water is thus obtained.
Étape 15 - Watermaker 2 - Evaporation tank 2.1 - Step 1
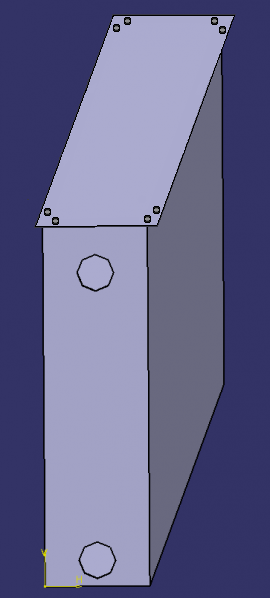
Step 1: Manufacture of the frame 2.1.1
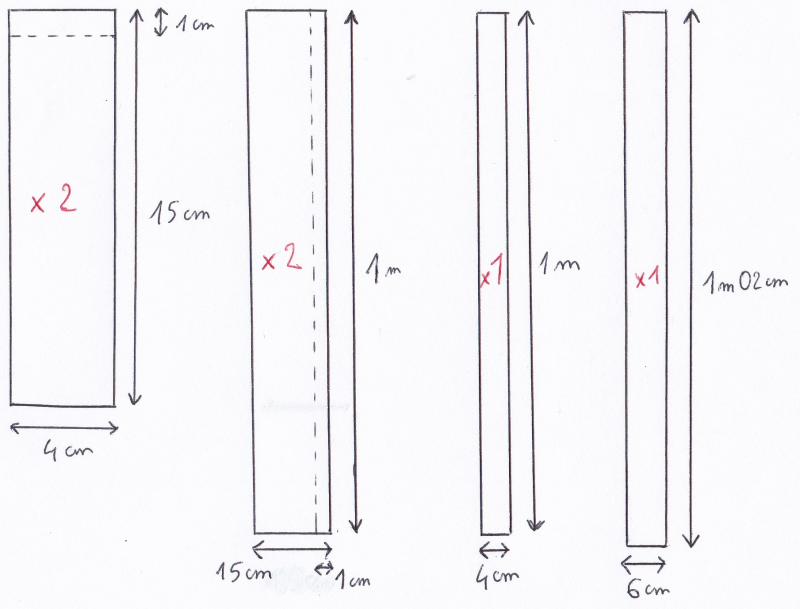
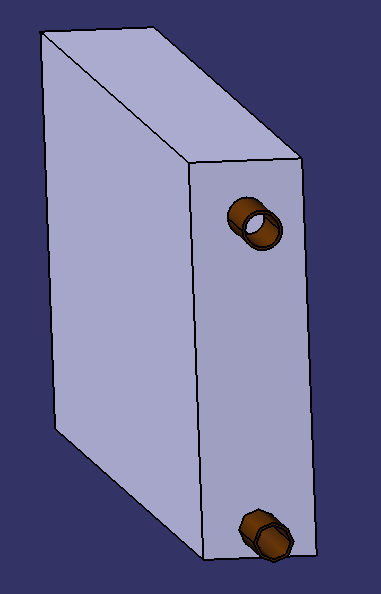
- Cut the metal sheet into 6 rectangles (2 rectangles of 4cm*15cm; 2 of 1m*15cm; 1 of 1m*4cm; 1 of 6cm*1.02m). See photo.
- Fold at right angles over 1 cm as shown in the dotted lines in the photo, then make holes in the folded part to fit the screws.
- Note 1: Be careful to ensure that the walls of tank 2.1 are watertight (soldering is required)!
- Note 2: Be careful to seal between the lid and the folded walls (use a bicycle inner tube, for example, before screwing)!
Étape 16 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve évaporation 2.1 - Etape 2
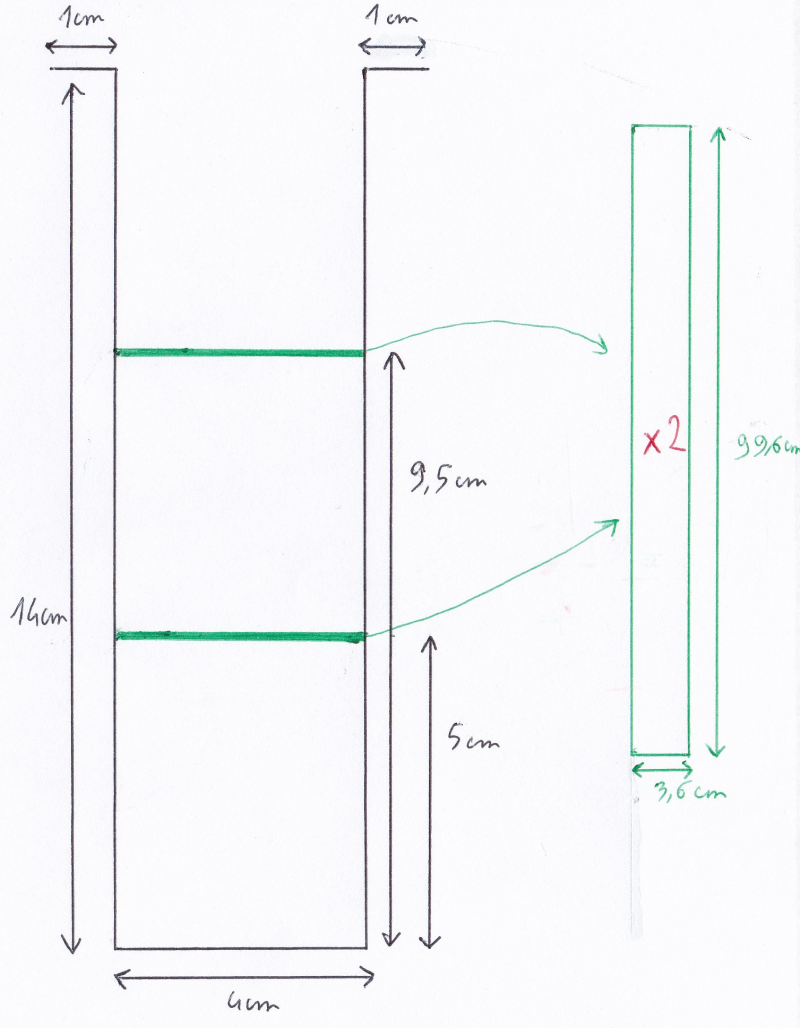
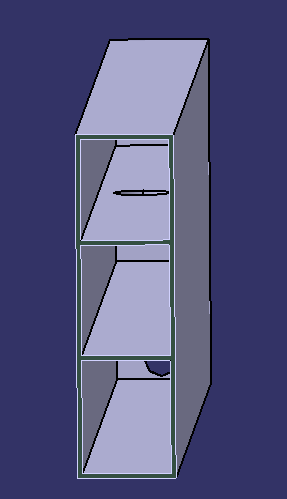
Etape 2 : Fabrication des étages 2.1.2
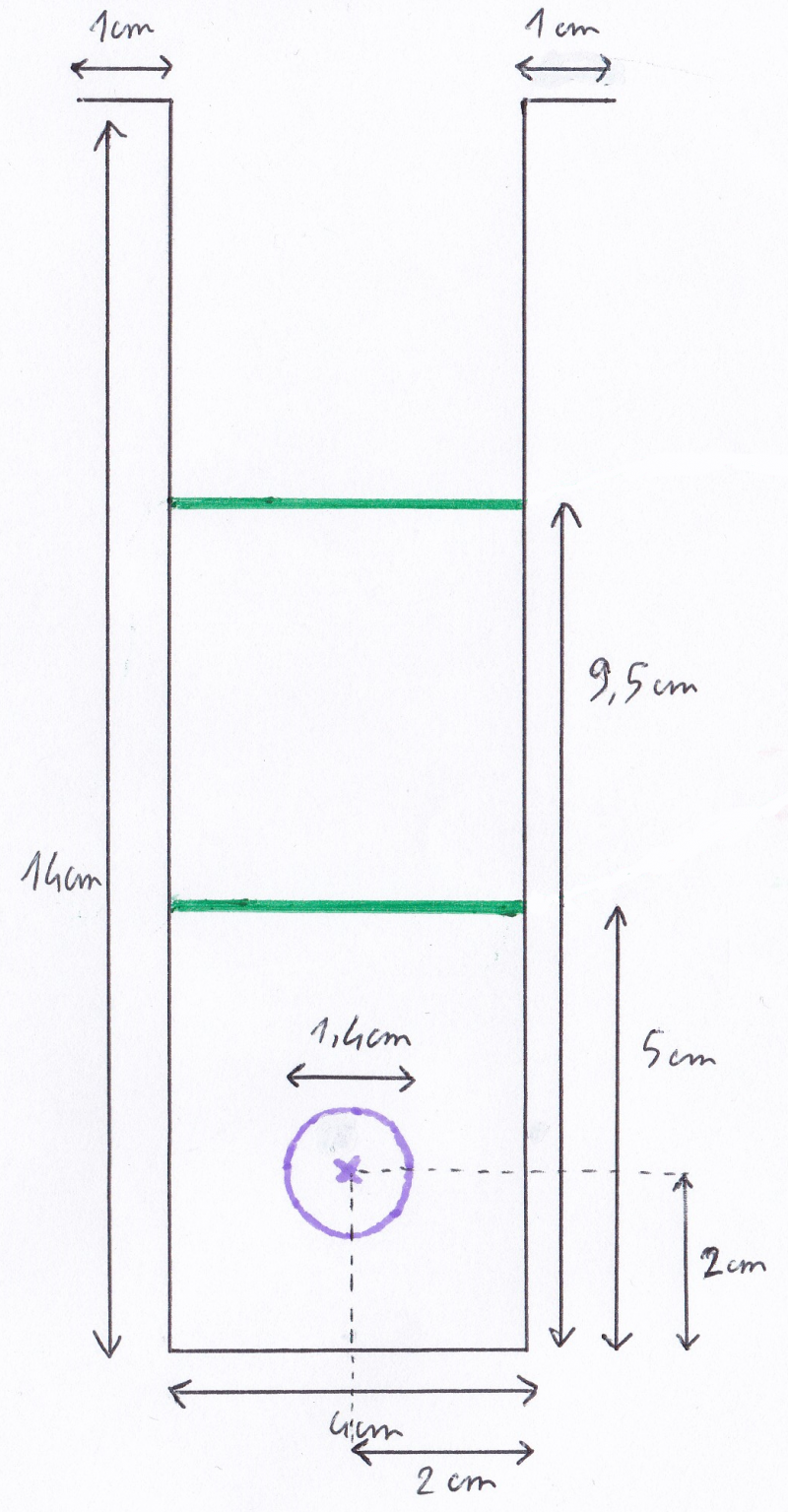
- Découper 2 plateaux de dimensions 99.6cm*3.6cm.
- Ajouter de la matière par soudure sur les parois latérales de la cuve 2.1 afin de pouvoir y poser les plateaux (voir la photo pour la hauteur des 2 plateaux et donc pour la hauteur des 2 ajouts de matière).
- Percer des trous de diamètre 5 cm à une extrémité de chaque plateau (afin que la vapeur circule dans tous les étages) et placer les 2 plateaux dans la cuve 2.1. avec leurs trous situés aux extrémités opposées.
Étape 17 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve évaporation 2.1 - Etape 3
Etape 3 : Fabrication des 3 trous pour les tuyaux de cuivre entrée du serpentin de condensation 2.2.2.1 et tuyau 2.2.2.3 qui traverse la cuve 2.1 par l'étage du bas
- Dans les 2 parois latérales les plus éloignées de la cuve 2.1 : faire un trou de diamètre 14 mm (voir la photo pour la position) dans l'étage du bas pour le tuyau 2.2.2.3.
- Dans une de ces mêmes parois latérales, faire un trou de diamètre 14 mm dans l'étage du haut (pour le tuyau 2.2.2.1 permettant d'évacuer la vapeur).
- Souder afin de faire l’étanchéité entre les tuyaux et la cuve !
Étape 18 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve de condensation 2.2 - Etape 1
Etape 1 : Découpe de la tôle en 5 faces
- Découpe des 5 faces
* Face de base: 200x200mm * 4 faces de côté: 200x355mm
- Pliage des faces de côté sur le dessus afin de créer des rebords pour pouvoir y visser un couvercle (par le même système qu'à l'étape précédente).
- Soudage de la base et des 4 faces
Étape 19 - Dessalinisateur 2 -Cuve de condensation 2.2 - Etape 2
Etape 2 : Trous
Quatre trous à percer:
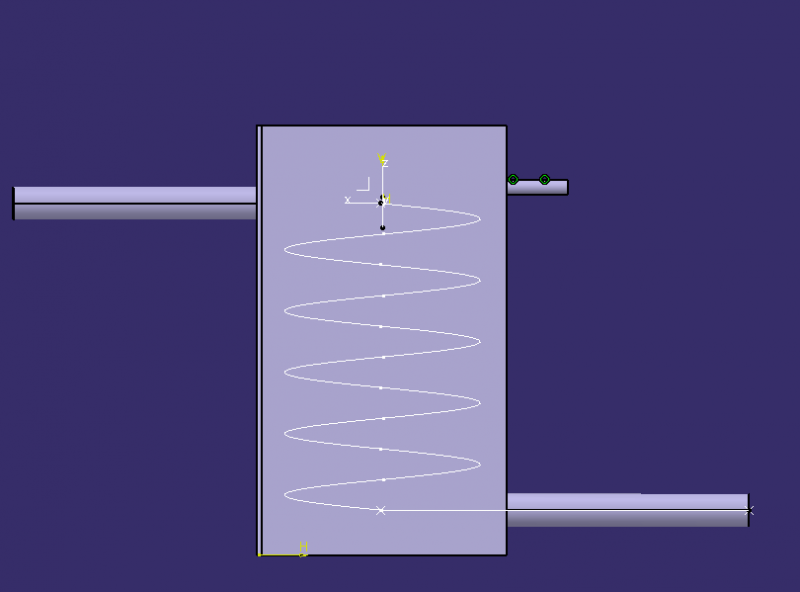
- Un trou d’arrivée d’eau de la cuve de stockage, qui accueille un régulateur de débit (de type chasse d’eau par exemple pour l’autonomisation, mais une simple vanne manuelle peut suffir). Ce trou doit se situer sur le haut de la cuve. Le tuyau 2.2.2.2 y passe.
- Un trou de sortie d'eau saumâtre préchauffée par la condensation de la vapeur, en bas de la cuve 2.2, en direction de la cuve d'évaporation 2.1. Le tuyau 2.2.2.3 y passe.
- Un trou d'arrivée de vapeur depuis la cuve d'évaporation 2.1 (entrée du serpentin de condensation 2.2.2.1), se situant sous le niveau d’eau contenu dans la cuve 2.2.
- Un trou de sortie d'eau potable (sortie du serpentin de condensation 2.2.2.1), plus bas que le trou précédent.
- Remarque : ces trous doivent être fait en fonction des autres parties du prototype (notamment pour le serpentin de condensation 2.2.2.1 où il est conseillé de le fabriquer avant de percer les trous : voir l’étape suivante).
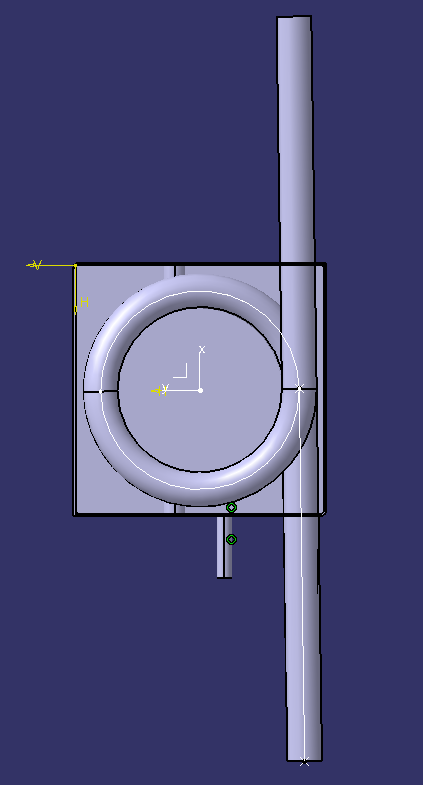
- Voir l’image où le trou de sortie de l’eau saumâtre n’est pas représenté (arrivée d’eau : en haut à droite et les 2 extrémités du serpentin de condensation 2.2.2.1 sont en haut à gauche et en bas à droite).
Étape 20 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve de condensation 2.2- Etape 3
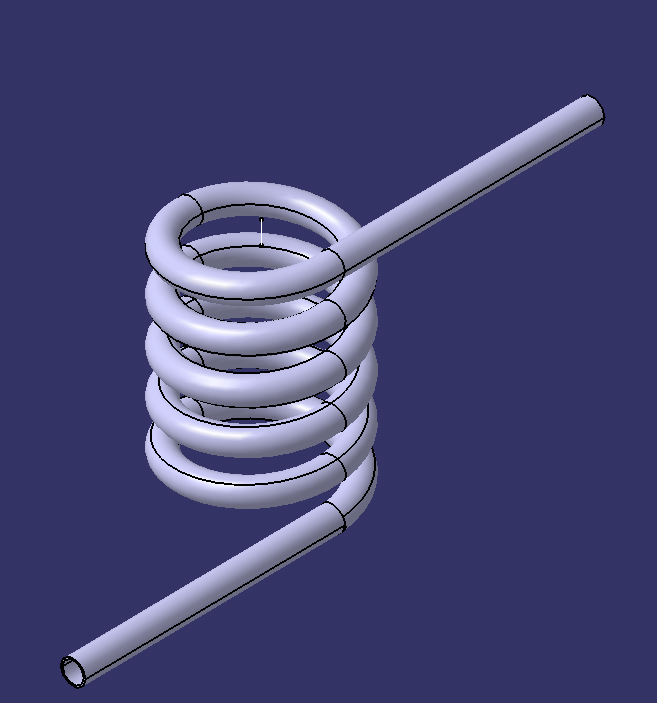
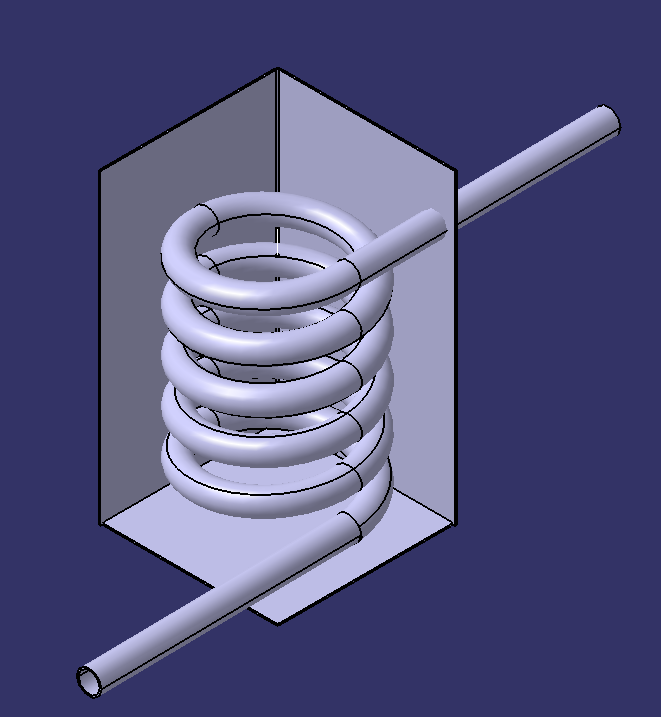
Etape 3: Serpentin de condensation 2.2.2.1 (là où se condense la vapeur)
- Entourer le tube de cuivre 2.2.2.1 d'un ressort rigide (il permet d'obtenir une forme circulaire)
- Si le cuivre n'est pas recuit, il faut le chauffer jusqu'à ce qu'il atteigne une couleur rouge et le plonger dans de l'eau froide immédiatement.
- Il faut ensuite lui donner une forme hélicoïdale en l'enroulant petit à petit autour d'un cylindre.
- Insérer le serpentin 2.2.2.1 dans la cuve 2.2 à travers les 2 trous précédemment fait
Étape 21 - Dessalinisateur 2 - Cuve de condensation 2.2 - Etape 4
Etape 4: Couvercle 2.3 de la cuve 2.2
- Percer au moins 8 trous sur les rebords de la cuve 2.2 pour les vis qui fixeront le couvercle 2.3.
- Découper une tôle carré de 250x250mm qui fera office de couvercle 2.3 et y percer au moins 8 trous correspondants aux précédents afin de pouvoir visser ce couvercle;
- Une chambre à air de vélo peut être insérée entre les rebords de la cuve 2.2 et le couvercle 2.3 pour une meilleure étanchéité.
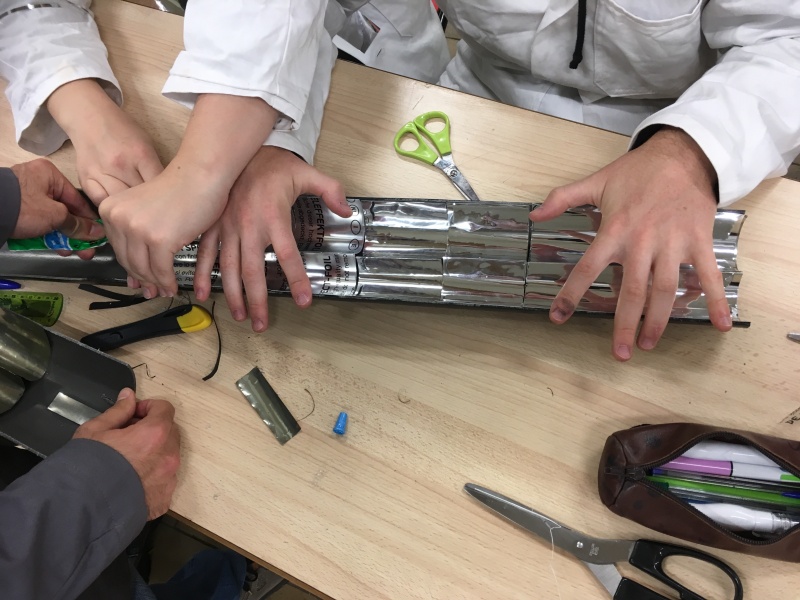
Étape 22 - Circuit total 3
Les deux parties principales étant construites, il ne reste plus qu’à fermer le circuit où circulera le fluide caloporteur ! Ce fluide caloporteur est une huile végétale qui circulera grâce à la pompe 3.2 intégrée au circuit. Privilégier des tuyaux 3.1 bien isolés thermiquement (isoler soi-même au besoin), flexibles (pour pouvoir déplacer facilement le prototype).
Étape 23 - Pompe 3.2
Pour le choix de la pompe 3.2, il faut bien faire attention à utiliser une pompe à huile. Une telle pompe peut être une pompe de récupération et peut se trouver sur des motos ou des voitures ou toute autre machine dont le fonctionnement nécessite une pompe à huile.
Published










 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português