Description
Offgrid rainwater harvesting sizing
Sommaire
Sommaire
- 1 Description
- 2 Sommaire
- 3 Introduction
- 4 Étape 1 - Software prerequisites
- 5 Étape 2 - Needs evaluation
- 6 Étape 3 - Retrospective calculus of daily and seasonal precipitations
- 7 Étape 4 - Harvesting surface sizing and storage sizing
- 8 Étape 5 - Storage optimisation and extra water use in summer season
- 9 Étape 6 - Utiliser des data du changement climatique
- 10 Commentaires
Introduction
In cases where we want to be offgrid, the water issue is essential
It is actually the first element to consider for example when considering site settlement in permaculture (observation stage).
I initially made the piece of logic below to make a mobilhome offgrid with the idea to use photovoltaic modules to harvest rainwater, as in the ulta chaata realisation (https://www.facebook.com/weultachaata/?locale=fr_FR et https://fr.futuroprossimo.it/2023/03/ulta-chaata-ombrello-magico-che-puo-dare-acqua-e-luce-allindia/)
We can wonder on the correct way to size rainwater harvesting devices
To do that, we can use meteorological data (meteo france in france) to get a retrospective view on the seasonal precipitations and adjust the harvesting device sizes
Interactive web demo here:
Étape 1 - Software prerequisites
In this tutorial, we use meteorological synop data available here:
http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/ with description here:
http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/doc_parametres_synop_168.pdf
You can also download the data on Meteo France website:
https://donneespubliques.meteofrance.fr/?fond=produit&id_produit=90&id_rubrique=32
Download all csv files with months and years with which you want to make the computing, put them in a directory of your choice and unzip them (archive format is gz).
Also put in this directory the file processing.py containing the code shared in this tutorial.
Example in debian linux command line to download and unzip all csv of year 2020 in a directory ~/synop:
(In the tutorial we use all data from 2010 to 2020)
cd ~ mkdir -p synop && cd synop wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202001.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202001.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202002.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202002.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202003.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202003.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202004.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202004.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202005.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202005.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202006.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202006.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202007.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202007.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202008.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202008.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202009.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202009.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202010.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202010.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202011.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202011.csv.gz wget http://data.cquest.org/meteo-france/synop/synop.202012.csv.gz && gzip -d synop.202012.csv.gz
To use python under another operating system, please get by with your proprietary and intrusive crap.
Under linux, python is usually installed and o use the code shared here, you'll just have to copy and paste the code in a text file called processing.py and then enter
python processing.py
However, you will have to install pandas library which is massively used in finance and science industries, in particular for its efficient timeseries handling and vectorisation capacities.
To do so, here are the commands to enter in a linux debian system before running processing.py to be ok:
sudo apt install python3 python3-venv python3-pip python-is-python3 cd ~ && python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate pip install pandas
Mind to activate virtual environment where pandas is installed each time you use the script (after a reboot or if you close and open again the terminal) with this command:
cd ~ && source venv/bin/activate
We are in 2024 and if you are being targetted and shackled as ecoterrorists like me, you will want to inspect your measurements instruments before use, so you can inspect the source code of pandas, which is of course free software, here:
https://github.com/pandas-dev/pandas
Or you can arguably suppose you can trust a software so massively used in finance and science industries.
Python relies on C libraries for some basics operations, and hack, including scientific hack, is never impossible, but we will let these pro-lowtech considerations aside that are out-of-scope of the perspectives of this tutorial.
Étape 2 - Needs evaluation
To evaluate the needs for domestic installations, nothing is more efficient thant a water meter. A first approach is to make a rule of 3 from your weekly consumption. You can also measure individually each consumption entry (shower, washing machine, cooking, gardening, toilet, etc.) so you can make more accurate seasonal projections.
For a mobilhome with dry toilets we have:
conso solo - 2 showers weekly (L) shower (L) 50 drinks 4 dish washing 10 cooking 4 washing machine 50 week (2 showers, 1 machine) 276 daily 39 quarter (13 weeks) 3588 conso for two - 4 showers a week (L) shower 50 drinks 4 dish washing 10 cooking 4 washing machine 50 week (4 showers, 1 machine) 752 daily 107 quarter (13 weeks) 9776
Étape 3 - Retrospective calculus of daily and seasonal precipitations
For correct storage sizing, we first need mean precipitations on previous years.
To do so, we provide the following piece of logic coded in python (fitting meteo france data but adapted to other meteorological data, as synop is an encoding standard used by OMM)
import math
import os
import pandas as pd
# Watch out if you use this piece of code in other countries, you have to add adhoc meteorological stations
# data processing
print("\ndata processing\n")
files=os.listdir('.')
csv=[a for a in files if a[-3:]=='csv']
combined_df = pd.concat((pd.read_csv(f,sep=';') for f in csv), ignore_index=True)
#07510 bordeaux
#07535 gourdon
#"hard coded" meteorological stations
stations=[{'ID': '07005', 'Nom': 'ABBEVILLE', 'Latitude': '50.136000', 'Longitude': '1.834000', 'Altitude': '69'}, {'ID': '07015', 'Nom': 'LILLE-LESQUIN', 'Latitude': '50.570000', 'Longitude': '3.097500', 'Altitude': '47'}, {'ID': '07020', 'Nom': 'PTE DE LA HAGUE', 'Latitude': '49.725167', 'Longitude': '-1.939833', 'Altitude': '6'}, {'ID': '07027', 'Nom': 'CAEN-CARPIQUET', 'Latitude': '49.180000', 'Longitude': '-0.456167', 'Altitude': '67'}, {'ID': '07037', 'Nom': 'ROUEN-BOOS', 'Latitude': '49.383000', 'Longitude': '1.181667', 'Altitude': '151'}, {'ID': '07072', 'Nom': 'REIMS-PRUNAY', 'Latitude': '49.209667', 'Longitude': '4.155333', 'Altitude': '95'}, {'ID': '07110', 'Nom': 'BREST-GUIPAVAS', 'Latitude': '48.444167', 'Longitude': '-4.412000', 'Altitude': '94'}, {'ID': '07117', 'Nom': "PLOUMANAC'H", 'Latitude': '48.825833', 'Longitude': '-3.473167', 'Altitude': '55'}, {'ID': '07130', 'Nom': 'RENNES-ST JACQUES', 'Latitude': '48.068833', 'Longitude': '-1.734000', 'Altitude': '36'}, {'ID': '07139', 'Nom': 'ALENCON', 'Latitude': '48.445500', 'Longitude': '0.110167', 'Altitude': '143'}, {'ID': '07149', 'Nom': 'ORLY', 'Latitude': '48.716833', 'Longitude': '2.384333', 'Altitude': '89'}, {'ID': '07168', 'Nom': 'TROYES-BARBEREY', 'Latitude': '48.324667', 'Longitude': '4.020000', 'Altitude': '112'}, {'ID': '07181', 'Nom': 'NANCY-OCHEY', 'Latitude': '48.581000', 'Longitude': '5.959833', 'Altitude': '336'}, {'ID': '07190', 'Nom': 'STRASBOURG-ENTZHEIM', 'Latitude': '48.549500', 'Longitude': '7.640333', 'Altitude': '150'}, {'ID': '07207', 'Nom': 'BELLE ILE-LE TALUT', 'Latitude': '47.294333', 'Longitude': '-3.218333', 'Altitude': '34'}, {'ID': '07222', 'Nom': 'NANTES-BOUGUENAIS', 'Latitude': '47.150000', 'Longitude': '-1.608833', 'Altitude': '26'}, {'ID': '07240', 'Nom': 'TOURS', 'Latitude': '47.444500', 'Longitude': '0.727333', 'Altitude': '108'}, {'ID': '07255', 'Nom': 'BOURGES', 'Latitude': '47.059167', 'Longitude': '2.359833', 'Altitude': '161'}, {'ID': '07280', 'Nom': 'DIJON-LONGVIC', 'Latitude': '47.267833', 'Longitude': '5.088333', 'Altitude': '219'}, {'ID': '07299', 'Nom': 'BALE-MULHOUSE', 'Latitude': '47.614333', 'Longitude': '7.510000', 'Altitude': '263'}, {'ID': '07314', 'Nom': 'PTE DE CHASSIRON', 'Latitude': '46.046833', 'Longitude': '-1.411500', 'Altitude': '11'}, {'ID': '07335', 'Nom': 'POITIERS-BIARD', 'Latitude': '46.593833', 'Longitude': '0.314333', 'Altitude': '123'}, {'ID': '07434', 'Nom': 'LIMOGES-BELLEGARDE', 'Latitude': '45.861167', 'Longitude': '1.175000', 'Altitude': '402'}, {'ID': '07460', 'Nom': 'CLERMONT-FD', 'Latitude': '45.786833', 'Longitude': '3.149333', 'Altitude': '331'}, {'ID': '07471', 'Nom': 'LE PUY-LOUDES', 'Latitude': '45.074500', 'Longitude': '3.764000', 'Altitude': '833'}, {'ID': '07481', 'Nom': 'LYON-ST EXUPERY', 'Latitude': '45.726500', 'Longitude': '5.077833', 'Altitude': '235'}, {'ID': '07510', 'Nom': 'BORDEAUX-MERIGNAC', 'Latitude': '44.830667', 'Longitude': '-0.691333', 'Altitude': '47'}, {'ID': '07535', 'Nom': 'GOURDON', 'Latitude': '44.745000', 'Longitude': '1.396667', 'Altitude': '260'}, {'ID': '07558', 'Nom': 'MILLAU', 'Latitude': '44.118500', 'Longitude': '3.019500', 'Altitude': '712'}, {'ID': '07577', 'Nom': 'MONTELIMAR', 'Latitude': '44.581167', 'Longitude': '4.733000', 'Altitude': '73'}, {'ID': '07591', 'Nom': 'EMBRUN', 'Latitude': '44.565667', 'Longitude': '6.502333', 'Altitude': '871'}, {'ID': '07607', 'Nom': 'MONT-DE-MARSAN', 'Latitude': '43.909833', 'Longitude': '-0.500167', 'Altitude': '59'}, {'ID': '07621', 'Nom': 'TARBES-OSSUN', 'Latitude': '43.188000', 'Longitude': '0.000000', 'Altitude': '360'}, {'ID': '07627', 'Nom': 'ST GIRONS', 'Latitude': '43.005333', 'Longitude': '1.106833', 'Altitude': '414'}, {'ID': '07630', 'Nom': 'TOULOUSE-BLAGNAC', 'Latitude': '43.621000', 'Longitude': '1.378833', 'Altitude': '151'}, {'ID': '07643', 'Nom': 'MONTPELLIER', 'Latitude': '43.577000', 'Longitude': '3.963167', 'Altitude': '2'}, {'ID': '07650', 'Nom': 'MARIGNANE', 'Latitude': '43.437667', 'Longitude': '5.216000', 'Altitude': '9'}, {'ID': '07661', 'Nom': 'CAP CEPET', 'Latitude': '43.079333', 'Longitude': '5.940833', 'Altitude': '115'}, {'ID': '07690', 'Nom': 'NICE', 'Latitude': '43.648833', 'Longitude': '7.209000', 'Altitude': '2'}, {'ID': '07747', 'Nom': 'PERPIGNAN', 'Latitude': '42.737167', 'Longitude': '2.872833', 'Altitude': '42'}, {'ID': '07761', 'Nom': 'AJACCIO', 'Latitude': '41.918000', 'Longitude': '8.792667', 'Altitude': '5'}, {'ID': '07790', 'Nom': 'BASTIA', 'Latitude': '42.540667', 'Longitude': '9.485167', 'Altitude': '10'}, {'ID': '61968', 'Nom': 'GLORIEUSES', 'Latitude': '-11.582667', 'Longitude': '47.289667', 'Altitude': '3'}, {'ID': '61970', 'Nom': 'JUAN DE NOVA', 'Latitude': '-17.054667', 'Longitude': '42.712000', 'Altitude': '9'}, {'ID': '61972', 'Nom': 'EUROPA', 'Latitude': '-22.344167', 'Longitude': '40.340667', 'Altitude': '6'}, {'ID': '61976', 'Nom': 'TROMELIN', 'Latitude': '-15.887667', 'Longitude': '54.520667', 'Altitude': '7'}, {'ID': '61980', 'Nom': 'GILLOT-AEROPORT', 'Latitude': '-20.892500', 'Longitude': '55.528667', 'Altitude': '8'}, {'ID': '61996', 'Nom': 'NOUVELLE AMSTERDAM', 'Latitude': '-37.795167', 'Longitude': '77.569167', 'Altitude': '27'}, {'ID': '61997', 'Nom': 'CROZET', 'Latitude': '-46.432500', 'Longitude': '51.856667', 'Altitude': '146'}, {'ID': '61998', 'Nom': 'KERGUELEN', 'Latitude': '-49.352333', 'Longitude': '70.243333', 'Altitude': '29'}, {'ID': '67005', 'Nom': 'PAMANDZI', 'Latitude': '-12.805500', 'Longitude': '45.282833', 'Altitude': '7'}, {'ID': '71805', 'Nom': 'ST-PIERRE', 'Latitude': '46.766333', 'Longitude': '-56.179167', 'Altitude': '21'}, {'ID': '78890', 'Nom': 'LA DESIRADE METEO', 'Latitude': '16.335000', 'Longitude': '-61.004000', 'Altitude': '27'}, {'ID': '78894', 'Nom': 'ST-BARTHELEMY METEO', 'Latitude': '17.901500', 'Longitude': '-62.852167', 'Altitude': '44'}, {'ID': '78897', 'Nom': 'LE RAIZET AERO', 'Latitude': '16.264000', 'Longitude': '-61.516333', 'Altitude': '11'}, {'ID': '78922', 'Nom': 'TRINITE-CARAVEL', 'Latitude': '14.774500', 'Longitude': '-60.875333', 'Altitude': '26'}, {'ID': '78925', 'Nom': 'LAMENTIN-AERO', 'Latitude': '14.595333', 'Longitude': '-60.995667', 'Altitude': '3'}, {'ID': '81401', 'Nom': 'SAINT LAURENT', 'Latitude': '5.485500', 'Longitude': '-54.031667', 'Altitude': '5'}, {'ID': '81405', 'Nom': 'CAYENNE-MATOURY', 'Latitude': '4.822333', 'Longitude': '-52.365333', 'Altitude': '4'}, {'ID': '81408', 'Nom': 'SAINT GEORGES', 'Latitude': '3.890667', 'Longitude': '-51.804667', 'Altitude': '6'}, {'ID': '81415', 'Nom': 'MARIPASOULA', 'Latitude': '3.640167', 'Longitude': '-54.028333', 'Altitude': '106'}, {'ID': '89642', 'Nom': "DUMONT D'URVILLE", 'Latitude': '-66.663167', 'Longitude': '140.001000', 'Altitude': '43'}]
def distance(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2):
"""
distance computing between two geographic points using euclidian distance formula.
"""
return math.sqrt((lat2 - lat1)**2 + (lon2 - lon1)**2)
def station_la_plus_proche(x, y, stations):
"""
Find closest meteorological station using x and y coordinates (latitude and longitude).
"""
distance_min = float('inf')
station_proche = None
for station in stations:
lat_station = float(station['Latitude'])
lon_station = float(station['Longitude'])
d = distance(x, y, lat_station, lon_station)
if d < distance_min:
distance_min = d
station_proche = station
return station_proche
# Ask user to enter latitude and longitude
x_input = input("Enter your latitude: ")
y_input = input("Enter your longitude: ")
# Replace comma with points
x_input = float(x_input.replace(',', '.'))
y_input = float(y_input.replace(',', '.'))
# Use values entered by user as x and y variables to find the closest meteorological station
station_proche = station_la_plus_proche(x_input, y_input, stations)
print("The closest meteorological station is :", station_proche['Nom'])
result=combined_df[combined_df['numer_sta']==int(station_proche['ID'])]
# Convert 'date_column'in a datetime format and make it a sorted index
result['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(result['date'], format='%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
result.set_index('datetime', inplace=True)
result = result.sort_index()
# replace missing data with 0
result['rr3']=result['rr3'].replace('mq','0')
result['rr3']=result['rr3'].astype('float')
# Only keep precipitations columns of last 3 hours
result=result['rr3']
# Calculate daily precipitations sums
resultday=result.resample('D').sum()
print("\nDaily mean (mm):\n", resultday.mean())
print("Daily minimum (mm):\n", resultday.min())
print("Daily maximum (mm):\n", resultday.max())
# Calculate weekly precipitations sums
resultweek=result.resample('W').sum()
# Calculate montly precipitation sums
resultmonth=result.resample('ME').sum()
# Calculate quarterly precipitations sum
resulttrim=result.resample('QE').sum()
resulttrim=resulttrim.rename_axis('trimestre')
print(resulttrim)
# Calculate yeraly precipitations sum
resultyear=result.resample('YE').sum()
print("\nYearly mean precipitations (mm):\n",resultyear.mean())
# Calculate maximum consecutive rainless days
max_streak = 0
current_streak = 0
for value in resultday:
if value == 0:
current_streak += 1
max_streak = max(max_streak, current_streak)
else:
current_streak = 0 # Reset the streak if the value is not zero
print(f"\nMaximum number of rainless consecutive days: {max_streak}")
# Quarterly mean for each quarter
moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre = resulttrim.groupby(resulttrim.index.quarter).mean()
# Quarterly minimum for each quarter
min_trimestrielle_par_trimestre = resulttrim.groupby(resulttrim.index.quarter).min()
# Quarterly maximum for each quarter
max_trimestrielle_par_trimestre = resulttrim.groupby(resulttrim.index.quarter).max()
# Print results
print("\nQuarterly mean for each quarter (mm):\n", moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre)
print("\nQuarterly minimum for each quarter (mm):\n", min_trimestrielle_par_trimestre)
print("\nQuarterly maximum for each quarter (mm):\n", max_trimestrielle_par_trimestre)
# Daily minimum for each quarter
min_par_jour_par_trimestre = resultday.groupby(resultday.index.quarter).min()
min_par_jour_par_trimestre=min_par_jour_par_trimestre.rename_axis('trimestre')
# Daily maximum for each quarter
max_par_jour_par_trimestre = resultday.groupby(resultday.index.quarter).max()
max_par_jour_par_trimestre=max_par_jour_par_trimestre.rename_axis('trimestre')
# Daily mean for each quarter
moyenne_par_jour_par_trimestre = resultday.groupby(resultday.index.quarter).mean()
moyenne_par_jour_par_trimestre=moyenne_par_jour_par_trimestre.rename_axis('trimestre')
# Print results
print("\n Daily minimum for each quarter (mm):\n", min_par_jour_par_trimestre)
print("\n Daily maximum for each quarter (mm):\n", max_par_jour_par_trimestre)
print("\n Daily mean for each quarter (mm):\n", moyenne_par_jour_par_trimestre)
For latitude 44.2 and longitude 0.6 we get:
processing des data Enter your latitude: 44.2 Enter your longitude: 0.6 The closest meteorological station is : GOURDON Daily mean (mm): 2.022896963663514 Daily minimum (mm): -0.6000000000000001 Daily maximum (mm): 55.0 trimestre 2010-03-31 202.0 2010-06-30 245.4 2010-09-30 132.2 2010-12-31 201.2 2011-03-31 126.7 2011-06-30 102.2 2011-09-30 164.6 2011-12-31 207.0 2012-03-31 99.8 2012-06-30 341.0 2012-09-30 100.0 2012-12-31 188.8 2013-03-31 248.4 2013-06-30 307.5 2013-09-30 136.6 2013-12-31 247.8 2014-03-31 253.8 2014-06-30 201.8 2014-09-30 192.8 2014-12-31 139.0 2015-03-31 176.4 2015-06-30 155.7 2015-09-30 184.6 2015-12-31 82.6 2016-03-31 322.1 2016-06-30 300.4 2016-09-30 29.0 2016-12-31 115.1 2017-03-31 213.0 2017-06-30 216.3 2017-09-30 133.2 2017-12-31 155.3 2018-03-31 252.8 2018-06-30 251.9 2018-09-30 103.7 2018-12-31 199.3 2019-03-31 100.1 2019-06-30 203.5 2019-09-30 138.8 2019-12-31 350.9 2020-03-31 149.5 2020-06-30 150.9 2020-09-30 66.9 2020-12-31 237.4 Freq: QE-DEC, Name: rr3, dtype: float64 Yearly mean precipitations (mm): 738.9090909090909 Maximum rainless consecutive days: 44 Quarterly mean for each quarter (mm): trimestre 1 194.963636 2 225.145455 3 125.672727 4 193.127273 Name: rr3, dtype: float64 Quarterly minimum for each quarter (mm): trimestre 1 99.8 2 102.2 3 29.0 4 82.6 Name: rr3, dtype: float64 Quarterly maximum for each quarter (mm): trimestre 1 322.1 2 341.0 3 192.8 4 350.9 Name: rr3, dtype: float64 Daily minimum for each quarter (mm): trimestre 1 -0.6 2 -0.4 3 -0.3 4 -0.5 Name: rr3, dtype: float64 Daily maximum for each quarter (mm): trimestre 1 42.8 2 55.0 3 50.2 4 28.0 Name: rr3, dtype: float64 Daily mean for each quarter (mm): trimestre 1 2.159718 2 2.474126 3 1.366008 4 2.099209 Name: rr3, dtype: float64
Étape 4 - Harvesting surface sizing and storage sizing
For correct storage sizing we recall usefully that 1m2 gives an equivalent of 1L for 1mm of precipitations.
We can then do the calculus of mean precipitations previously estimated and mean consumption previously measured
Example for 1m2: yearly (L) 739 daily max (L) 55 quarterly min (L) 29 quarterly max (L) 350 minimum quarterly mean (L) 125 Needs: Max rainless 44d solo (L) 1735 Max rainless 44 d duo (L) 4727 quarterly solo consumption 3549 quarterly duo consumption 9669
Gross estimate:
quarterly consumption/minimum quarterly mean precipitations=
solo : 3588/125=29
duo: 9776/125=78
=> We need 29m2 to satisfy the solo needs with stage 1 hypothesis
=> We need 78m2 to satisfy duo needs with hypothesis stage 1
The strong precipitations are usually regrouped (high standard deviation to the mean),
and we will consequently take a minimum storage sized two times and a half
what is necessary for daily maximum precipitation
Important precipitation constraints:
We need a minimum storage of 3987L in solo (2.5*max daily precipitations*29)
and 10725L in duo (2.5*max precipitations *78)
But we also need a minimum for dry periods;
1735L in solo (44 maximum consecutive rainless days) of storage with stage 1 hypothesis
4727L in duo (44 maximum consecutive rainless days) of storage with stage 1 hypothesis
Which is satisfying with the previous constraint.
We will now use these minimum surface and minimum storage results
as basic hypothesis and add a "data-test" with iterations (50% of minimum surface
and 100% of minimum volume as starting points for the iteration) on the harvesting surface
and storage to verify we dont have drying up
(we make the hypothesis there is an overflow management and we dont
have storage overlows problems) and we statisfy the consumption needs.
Étape 5 - Storage optimisation and extra water use in summer season
The improved piece of puthon code is this one (the comments explain each stages)
To explain a bit the iteration stage: We start at volume0 storage capcity and surface0 harvesting surface precalculated in the previous stage. We do iteration loops on the precipitations data and each day we do a substract haversted water-daily consumption+summer consumption when summer En case of drying up: We have a first iteration loop 6 times of +33% of the sruface, and for each surface iteration, we have a secon iteration loop 40 times +50% of volume. We stop the iteration loops each time the sizing fits and we register the result. We display the result at the end of the iterations.
import math
import os
import pandas as pd
import time
# Watch out if you use this piece of code in other countries, you have to add adhoc meteorological stations
# data processing
print("\nprocessing des data\n")
files=os.listdir('.')
csv=[a for a in files if a[-3:]=='csv']
combined_df = pd.concat((pd.read_csv(f,sep=';') for f in csv), ignore_index=True)
#07510 bordeaux
#07535 gourdon
#"hard coded" meteorological stations
stations=[{'ID': '07005', 'Nom': 'ABBEVILLE', 'Latitude': '50.136000', 'Longitude': '1.834000', 'Altitude': '69'}, {'ID': '07015', 'Nom': 'LILLE-LESQUIN', 'Latitude': '50.570000', 'Longitude': '3.097500', 'Altitude': '47'}, {'ID': '07020', 'Nom': 'PTE DE LA HAGUE', 'Latitude': '49.725167', 'Longitude': '-1.939833', 'Altitude': '6'}, {'ID': '07027', 'Nom': 'CAEN-CARPIQUET', 'Latitude': '49.180000', 'Longitude': '-0.456167', 'Altitude': '67'}, {'ID': '07037', 'Nom': 'ROUEN-BOOS', 'Latitude': '49.383000', 'Longitude': '1.181667', 'Altitude': '151'}, {'ID': '07072', 'Nom': 'REIMS-PRUNAY', 'Latitude': '49.209667', 'Longitude': '4.155333', 'Altitude': '95'}, {'ID': '07110', 'Nom': 'BREST-GUIPAVAS', 'Latitude': '48.444167', 'Longitude': '-4.412000', 'Altitude': '94'}, {'ID': '07117', 'Nom': "PLOUMANAC'H", 'Latitude': '48.825833', 'Longitude': '-3.473167', 'Altitude': '55'}, {'ID': '07130', 'Nom': 'RENNES-ST JACQUES', 'Latitude': '48.068833', 'Longitude': '-1.734000', 'Altitude': '36'}, {'ID': '07139', 'Nom': 'ALENCON', 'Latitude': '48.445500', 'Longitude': '0.110167', 'Altitude': '143'}, {'ID': '07149', 'Nom': 'ORLY', 'Latitude': '48.716833', 'Longitude': '2.384333', 'Altitude': '89'}, {'ID': '07168', 'Nom': 'TROYES-BARBEREY', 'Latitude': '48.324667', 'Longitude': '4.020000', 'Altitude': '112'}, {'ID': '07181', 'Nom': 'NANCY-OCHEY', 'Latitude': '48.581000', 'Longitude': '5.959833', 'Altitude': '336'}, {'ID': '07190', 'Nom': 'STRASBOURG-ENTZHEIM', 'Latitude': '48.549500', 'Longitude': '7.640333', 'Altitude': '150'}, {'ID': '07207', 'Nom': 'BELLE ILE-LE TALUT', 'Latitude': '47.294333', 'Longitude': '-3.218333', 'Altitude': '34'}, {'ID': '07222', 'Nom': 'NANTES-BOUGUENAIS', 'Latitude': '47.150000', 'Longitude': '-1.608833', 'Altitude': '26'}, {'ID': '07240', 'Nom': 'TOURS', 'Latitude': '47.444500', 'Longitude': '0.727333', 'Altitude': '108'}, {'ID': '07255', 'Nom': 'BOURGES', 'Latitude': '47.059167', 'Longitude': '2.359833', 'Altitude': '161'}, {'ID': '07280', 'Nom': 'DIJON-LONGVIC', 'Latitude': '47.267833', 'Longitude': '5.088333', 'Altitude': '219'}, {'ID': '07299', 'Nom': 'BALE-MULHOUSE', 'Latitude': '47.614333', 'Longitude': '7.510000', 'Altitude': '263'}, {'ID': '07314', 'Nom': 'PTE DE CHASSIRON', 'Latitude': '46.046833', 'Longitude': '-1.411500', 'Altitude': '11'}, {'ID': '07335', 'Nom': 'POITIERS-BIARD', 'Latitude': '46.593833', 'Longitude': '0.314333', 'Altitude': '123'}, {'ID': '07434', 'Nom': 'LIMOGES-BELLEGARDE', 'Latitude': '45.861167', 'Longitude': '1.175000', 'Altitude': '402'}, {'ID': '07460', 'Nom': 'CLERMONT-FD', 'Latitude': '45.786833', 'Longitude': '3.149333', 'Altitude': '331'}, {'ID': '07471', 'Nom': 'LE PUY-LOUDES', 'Latitude': '45.074500', 'Longitude': '3.764000', 'Altitude': '833'}, {'ID': '07481', 'Nom': 'LYON-ST EXUPERY', 'Latitude': '45.726500', 'Longitude': '5.077833', 'Altitude': '235'}, {'ID': '07510', 'Nom': 'BORDEAUX-MERIGNAC', 'Latitude': '44.830667', 'Longitude': '-0.691333', 'Altitude': '47'}, {'ID': '07535', 'Nom': 'GOURDON', 'Latitude': '44.745000', 'Longitude': '1.396667', 'Altitude': '260'}, {'ID': '07558', 'Nom': 'MILLAU', 'Latitude': '44.118500', 'Longitude': '3.019500', 'Altitude': '712'}, {'ID': '07577', 'Nom': 'MONTELIMAR', 'Latitude': '44.581167', 'Longitude': '4.733000', 'Altitude': '73'}, {'ID': '07591', 'Nom': 'EMBRUN', 'Latitude': '44.565667', 'Longitude': '6.502333', 'Altitude': '871'}, {'ID': '07607', 'Nom': 'MONT-DE-MARSAN', 'Latitude': '43.909833', 'Longitude': '-0.500167', 'Altitude': '59'}, {'ID': '07621', 'Nom': 'TARBES-OSSUN', 'Latitude': '43.188000', 'Longitude': '0.000000', 'Altitude': '360'}, {'ID': '07627', 'Nom': 'ST GIRONS', 'Latitude': '43.005333', 'Longitude': '1.106833', 'Altitude': '414'}, {'ID': '07630', 'Nom': 'TOULOUSE-BLAGNAC', 'Latitude': '43.621000', 'Longitude': '1.378833', 'Altitude': '151'}, {'ID': '07643', 'Nom': 'MONTPELLIER', 'Latitude': '43.577000', 'Longitude': '3.963167', 'Altitude': '2'}, {'ID': '07650', 'Nom': 'MARIGNANE', 'Latitude': '43.437667', 'Longitude': '5.216000', 'Altitude': '9'}, {'ID': '07661', 'Nom': 'CAP CEPET', 'Latitude': '43.079333', 'Longitude': '5.940833', 'Altitude': '115'}, {'ID': '07690', 'Nom': 'NICE', 'Latitude': '43.648833', 'Longitude': '7.209000', 'Altitude': '2'}, {'ID': '07747', 'Nom': 'PERPIGNAN', 'Latitude': '42.737167', 'Longitude': '2.872833', 'Altitude': '42'}, {'ID': '07761', 'Nom': 'AJACCIO', 'Latitude': '41.918000', 'Longitude': '8.792667', 'Altitude': '5'}, {'ID': '07790', 'Nom': 'BASTIA', 'Latitude': '42.540667', 'Longitude': '9.485167', 'Altitude': '10'}, {'ID': '61968', 'Nom': 'GLORIEUSES', 'Latitude': '-11.582667', 'Longitude': '47.289667', 'Altitude': '3'}, {'ID': '61970', 'Nom': 'JUAN DE NOVA', 'Latitude': '-17.054667', 'Longitude': '42.712000', 'Altitude': '9'}, {'ID': '61972', 'Nom': 'EUROPA', 'Latitude': '-22.344167', 'Longitude': '40.340667', 'Altitude': '6'}, {'ID': '61976', 'Nom': 'TROMELIN', 'Latitude': '-15.887667', 'Longitude': '54.520667', 'Altitude': '7'}, {'ID': '61980', 'Nom': 'GILLOT-AEROPORT', 'Latitude': '-20.892500', 'Longitude': '55.528667', 'Altitude': '8'}, {'ID': '61996', 'Nom': 'NOUVELLE AMSTERDAM', 'Latitude': '-37.795167', 'Longitude': '77.569167', 'Altitude': '27'}, {'ID': '61997', 'Nom': 'CROZET', 'Latitude': '-46.432500', 'Longitude': '51.856667', 'Altitude': '146'}, {'ID': '61998', 'Nom': 'KERGUELEN', 'Latitude': '-49.352333', 'Longitude': '70.243333', 'Altitude': '29'}, {'ID': '67005', 'Nom': 'PAMANDZI', 'Latitude': '-12.805500', 'Longitude': '45.282833', 'Altitude': '7'}, {'ID': '71805', 'Nom': 'ST-PIERRE', 'Latitude': '46.766333', 'Longitude': '-56.179167', 'Altitude': '21'}, {'ID': '78890', 'Nom': 'LA DESIRADE METEO', 'Latitude': '16.335000', 'Longitude': '-61.004000', 'Altitude': '27'}, {'ID': '78894', 'Nom': 'ST-BARTHELEMY METEO', 'Latitude': '17.901500', 'Longitude': '-62.852167', 'Altitude': '44'}, {'ID': '78897', 'Nom': 'LE RAIZET AERO', 'Latitude': '16.264000', 'Longitude': '-61.516333', 'Altitude': '11'}, {'ID': '78922', 'Nom': 'TRINITE-CARAVEL', 'Latitude': '14.774500', 'Longitude': '-60.875333', 'Altitude': '26'}, {'ID': '78925', 'Nom': 'LAMENTIN-AERO', 'Latitude': '14.595333', 'Longitude': '-60.995667', 'Altitude': '3'}, {'ID': '81401', 'Nom': 'SAINT LAURENT', 'Latitude': '5.485500', 'Longitude': '-54.031667', 'Altitude': '5'}, {'ID': '81405', 'Nom': 'CAYENNE-MATOURY', 'Latitude': '4.822333', 'Longitude': '-52.365333', 'Altitude': '4'}, {'ID': '81408', 'Nom': 'SAINT GEORGES', 'Latitude': '3.890667', 'Longitude': '-51.804667', 'Altitude': '6'}, {'ID': '81415', 'Nom': 'MARIPASOULA', 'Latitude': '3.640167', 'Longitude': '-54.028333', 'Altitude': '106'}, {'ID': '89642', 'Nom': "DUMONT D'URVILLE", 'Latitude': '-66.663167', 'Longitude': '140.001000', 'Altitude': '43'}]
def distance(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2):
"""
distance computing between two geographic points using euclidian distance formula.
"""
return math.sqrt((lat2 - lat1)**2 + (lon2 - lon1)**2)
def station_la_plus_proche(x, y, stations):
"""
Find closest meteorological station using x and y coordinates (latitude and longitude).
"""
distance_min = float('inf')
station_proche = None
for station in stations:
lat_station = float(station['Latitude'])
lon_station = float(station['Longitude'])
d = distance(x, y, lat_station, lon_station)
if d < distance_min:
distance_min = d
station_proche = station
return station_proche
# Ask user to enter latitude and longitude
x_input = input("Enter your latitude: ")
y_input = input("Enter your longitude: ")
# Replace comma with points
x_input = float(x_input.replace(',', '.'))
y_input = float(y_input.replace(',', '.'))
# Use values entered by user as x and y variables to find the closest meteorological station
station_proche = station_la_plus_proche(x_input, y_input, stations)
print("\nThe closest meteorological station is:", station_proche['Nom'])
# Ask user to enter his/her weekly water consumption
waterconsohebdo = input("Entrez la consommation d'eau hebdomadaire constante(L): ")
# Replace comma with points
waterconsohebdo = float(waterconsohebdo.replace(',', '.'))
# Mean daily consumption calculus
waterconsojour = waterconsohebdo/7
# Ask a user to enter the starting month of the summer periodmoisdebutete = input("Enter the starting mont for the weekly extra use of water in summer (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12): ")
try:
_=int(moisdebutete)
moisdebutete=_
except Exception as err:
moisdebutete=5
print(f"\ntype error or empty user value, continuing with moisdebutete={moisdebutete}")
# Ask user to enter the final month of the summer period
moisfinete = input("Enter the ending month for the extra water consumption of summer period (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12): ")
try:
_=int(moisfinete)
moisfinete=_
except Exception as err:
moisfinete=9
print(f"\ntype error or empty user value, continuing with moisfinete={moisfinete}")
# Ask user to enter extra water consumption in summer period
waterconsohebdoete = input("Enter extra weekly water consumption in summer (L) - 0 L by default: ")
try:
_=float(waterconsohebdoete.replace(',', '.')) # Replace commas with points
waterconsohebdoete=_
except Exception as err:
waterconsohebdoete=0
print(f"\ntype error or empty user value, continuing with waterconsohebdoete={waterconsohebdoete}L")
# Mean daily consumption calculus
waterconsojourete = waterconsohebdoete/7
result=combined_df[combined_df['numer_sta']==int(station_proche['ID'])]
# Convertir la colonne 'date_column' dans un format datetime et la mettre en index trié
result['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(result['date'], format='%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
result.set_index('datetime', inplace=True)
result = result.sort_index()
# Replace missing values with 0
result['rr3']=result['rr3'].replace('mq','0')
result['rr3']=result['rr3'].astype('float')
# Only keep precipitations of last 3 hours
result=result['rr3']
# Calculate daily precipitation sums
resultday=result.resample('D').sum()
resultdaymonthindex=resultday.copy()
resultdaymonthindex.index=resultdaymonthindex.index.month
print("\Daily mean (mm):\n", resultday.mean())
print("Daily minimum (mm):\n", resultday.min())
print("Daily maximum (mm):\n", resultday.max())
# Calculate weekly precipitation sums
resultweek=result.resample('W').sum()
# Calculate monthly precipitation sums
resultmonth=result.resample('ME').sum()
# Calculate quarterly precipitation sums
resulttrim=result.resample('QE').sum()
resulttrim=resulttrim.rename_axis('trimestre')
print(resulttrim)
# Calculate yearly precipitation sums
resultyear=result.resample('YE').sum()
print("\nPrécipitations annuelles moyennes (mm):\n",resultyear.mean())
# Calculate maximum consecutive rainless days
max_streak = 0
current_streak = 0
for value in resultday:
if value == 0:
current_streak += 1
max_streak = max(max_streak, current_streak)
else:
current_streak = 0 # Reset the streak if the value is not zero
print(f"\nMaximum consecutive rainless days: {max_streak}")
# Quarterly mean for each quarter
moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre = resulttrim.groupby(resulttrim.index.quarter).mean()
# Quarterly minimum for each quarter
min_trimestrielle_par_trimestre = resulttrim.groupby(resulttrim.index.quarter).min()
# Quarterly maximum for each quarter
max_trimestrielle_par_trimestre = resulttrim.groupby(resulttrim.index.quarter).max()
# Print results
print("\nQuarterly mean for each quarter (mm):\n", moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre)
print("\nQuarterly minimum for each quarter(mm):\n", min_trimestrielle_par_trimestre)
print("\nQuarterly maximum for each quarter (mm):\n", max_trimestrielle_par_trimestre)
#Climate change consideration (conservative hypothesis from multimodels drias precipitations modelisations):
# Define impacts on seasonal precipitation volumes
adjustments = {0: -15, 1: -10, 2: -50, 3: -15} # Adjust quarter 1 by -15%, quarter 2 by -10%, quarter 3 by -50%, quarter 4 by -15%
# Impacts on quarterly mean precipitations:
cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre=moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre.copy()
for line, adjustment in adjustments.items():
cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre.iloc[line] = cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre.iloc[line]+cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre.iloc[line]*adjustment/100
print("\nQuarterly mean for each quarter with consideration for climate change (mm):\n", cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre)
# Daily mean for each quarter
min_par_jour_par_trimestre = resultday.groupby(resultday.index.quarter).min()
min_par_jour_par_trimestre=min_par_jour_par_trimestre.rename_axis('trimestre')
# Daily maximum for each quarter
max_par_jour_par_trimestre = resultday.groupby(resultday.index.quarter).max()
max_par_jour_par_trimestre=max_par_jour_par_trimestre.rename_axis('trimestre')
# Moyenne par jour pour chaque trimestre
moyenne_par_jour_par_trimestre = resultday.groupby(resultday.index.quarter).mean()
moyenne_par_jour_par_trimestre=moyenne_par_jour_par_trimestre.rename_axis('trimestre')
# Imprimer les résultats
print("\nMinimum par jour pour chaque trimestre (mm):\n", min_par_jour_par_trimestre)
print("\nMaximum par jour pour chaque trimestre (mm):\n", max_par_jour_par_trimestre)
print("\nMoyenne par jour pour chaque trimestre (mm):\n", moyenne_par_jour_par_trimestre)
#Calcul seuil mini surface de recuperation:
surf0=(1/2)*math.ceil((13*waterconsohebdo)/min(moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre))
print(f"""Seuil surface recuperation avec hypothèse entrée et données fournies par l'utilisateur (m2)
hypothese:(conso trimestre / precipitations moyenne min trimestre)
{int(math.ceil(surf0))} m2""")
#Calcul seuil mini reservoir:
contraintejourmax=(resultday.max())*surf0
contraintejourszero=max_streak*waterconsojour
volume0=math.ceil(max(2.5*contraintejourmax,contraintejourszero))
print(f"""\nSeuil volume avec hypothèse entrée et données fournies par l'utilisateur (L)
hypothèse: max((2.5*précipitations journaliere maxi*Seuil surface recuperation),(44j consécutifs max sans pluie*conso journaliere))
{int(math.ceil(volume0))} L""")
surf0_input = input("\n\nSi vous souhaitez corriger la valeur initiale de surface (m2) pour les itérations, entrer votre valeur, sinon appuyer sur entree")
try:
_=float(surf0_input)
surf0=_
except Exception as err:
print(f"\nerreur de type ou valeur utilisateur vide, poursuite avec utilisation de surf0={surf0}m2")
volume0_input = input("\n\nSi vous souhaitez corriger la valeur initiale de volume (L) pour les itérations, entrer votre valeur, sinon appuyer sur entree")
try:
_=float(volume0_input)
volume0=_
except Exception as err:
print(f"\nerreur de type ou valeur utilisateur vide, poursuite avec utilisation de volume0={volume0}L")
# Itérations algorithmiques stockage&consommation
#hypothèse récupérateur 2/3 plein à t0
water=(2/3)*volume0
resultsurfvolume=(volume0,surf0)
#boucle iteration
listsurf0=[surf0*(1+i*0.33) for i in range(0,999)]
listvolume0=[volume0*(1+i*0.5) for i in range(0,999)]
listeday=list(resultday)
listemonth=list(resultdaymonthindex.index)
listresult=[]
#fonction check surface volume
def iterv(data, v0,s0):
"fonction check surface volume"
water=(2/3)*v0
for k in range(0,len(data)):
recupday=data[k]*s0
#print(f'recupday:{recupday}')
if listemonth[k] in range(moisdebutete, moisfinete + 1):
consoday = waterconsojour + waterconsojourete
else:
consoday = waterconsojour
water=water+recupday-consoday
#print(f'water:{water}')
if water>v0:
print("récupérateur plein")
water=v0 #hypothese gestion du trop plein ok
continue
if water<0:
print("récupérateur vide")
#time.sleep(1)
return (0,0)
print("les surfaces et volumes permettent de subvenir à la consommation d'eau sur le dataset")
return (v0,s0)
for i in range(0,6): #boucle iteration surface
for k in range(0,len(listeday)):
recupday=listeday[k]*listsurf0[i]
print(f'recupday:{recupday}')
if listemonth[k] in range(moisdebutete,moisfinete+1):
consoday=waterconsojour+waterconsojourete
else:
consoday = waterconsojour
water=water+recupday-consoday
print(f'water:{water}')
if water>volume0:
print("récupérateur plein")
water=volume0 #hypothese gestion du trop plein ok
continue
if water<0:
print("récupérateur vide, iteration avec hypothèse volume de récupération plus grand")
#time.sleep(1)
for j in range (1,i+40):
resultsurfvolume=iterv(listeday,listvolume0[j],listsurf0[i])
if resultsurfvolume!=(0,0):
listresult.append(resultsurfvolume)
break
else:
continue
break
for k in listresult:
print(f"""avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et
un volume de {int(k[0])}L et
une surface de {int(k[1])}m2,
on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs ({waterconsohebdo}L/semaine constant)
et {waterconsohebdoete}L/semaine en periode estivale (du mois {moisdebutete} au mois {moisfinete})
entrées en hypothèse\n""")
On fait le test avec les hypothèses ci dessus (latitude 44.2, longitude 0.6, solo 276L semaine, duo 752L semaine)
On obtient les résultats suivants:
solo:
avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 7976L et une surface de 19m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 5982L et une surface de 24m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 4985L et une surface de 28m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 3988L et une surface de 33m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 3988L et une surface de 38m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse
solo avec 600L/semaine en periode estivale:
avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 15642L et une surface de 45m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 15642L et une surface de 60m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 12514L et une surface de 75m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 12514L et une surface de 90m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 12514L et une surface de 105m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 12514L et une surface de 120m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (276.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse
duo:
avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 24133L et une surface de 51m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 16089L et une surface de 64m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 13407L et une surface de 77m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 10726L et une surface de 90m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 10726L et une surface de 103m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse
duo avec 600L/semaine en periode estivale: :
avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 33687L et une surface de 70m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 24062L et une surface de 93m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 19250L et une surface de 116m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 19250L et une surface de 139m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 19250L et une surface de 162m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse avec les données fournies par l'utilisateur, et un volume de 19250L et une surface de 185m2, on satisfait aux besoins utilisateurs (752.0L/semaine constant) et 600.0L/semaine supplémentaire en periode estivale (du mois 5 au mois 9) entrées en hypothèse
Étape 6 - Utiliser des data du changement climatique
Comme très bien expliqué dans cet autre tuto : Estimer la quantité d'eau de pluie récupérable grâce à une toiture, dimensionner son stockage en prenant en compte les changements climatiques, le changement climatique va perturber les précipitations en termes de quantités mais surtout de fréquences.
Pour de la récupération/stockage, c'est particulièrement important notamment pour les périodes de sécheresses qui risques de s'accentuer.
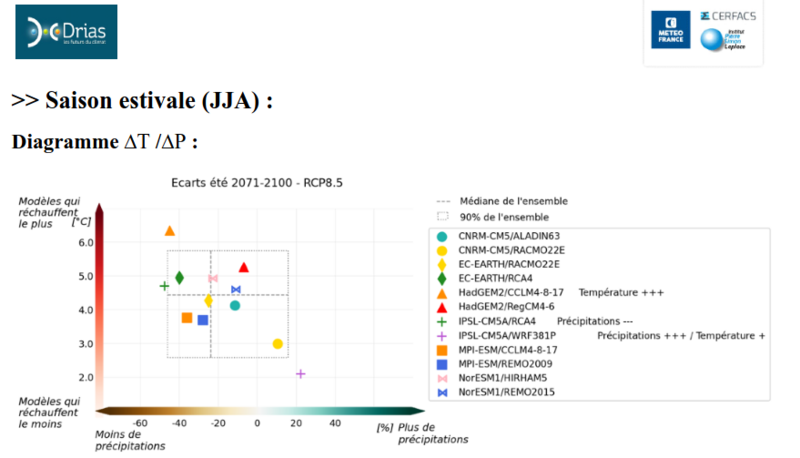
Techniquement, on peut "data-tester" au jour le jour avec les données de prévisions du portail drias (https://drias-climat.fr/). Cependant, il faudrait d'une part data tester avec plusieurs set de données car les modèles sont tres différents les uns des autres, et d'autres part il s'agit de modèles climatiques et pas météorologiques, ce qui limite la pertinence d'utiliser des résultats comme input meteo.
En attendant que les scientifiques affinent leurs modèles pour la prospective à échelle plus fine (spatiale et temporelle), on peut reprendre les estimations d'impact sur les volumes de précipitations par saisons à partir des modèles drias 2070-2100 rcp 8.5 (+10% à -10% selon modèles au printemps, -50% à +20% en été,-15% à +5% en automne, -15% à +30% en hiver)
En étant prudent pour chaque saison, c'est à dire en prenant l'hypothèse la plus conservatrice pour chaque saison, on obtient des volumes réduits de :
-10% au printemps
-50% en été
-15% en automne
-15% en hiver
On peut alors mettre à jour l'algorithme :
Vous noterez qu'on a déjà ajouté les lignes suivantes dans le code de l'etape 5 juste avant le calcul de # Moyenne par trimestre pour chaque trimestre:
#Prise en comptes changement climatiques (hypothèses conservatrices multimodeles drias precipitations):
# Definir les impacts sur les volumes de précipitations par saison
adjustments = {0: -15, 1: -10, 2: -50, 3: -15} # Adjust line 1 by -15%, line 2 by -10%, line 3 by -50%, line 4 by -15%
# Appliquer les impacts sur les précipitations moyennes par trimestres:
cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre=moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre.copy()
for line, adjustment in adjustments.items():
cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre.iloc[line] = cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre.iloc[line]+cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre.iloc[line]*adjustment/100
print("\nMoyenne par trimestre pour chaque trimestre avec prise en compte du changement climatique (mm):\n", cc_moyenne_trimestrielle_par_trimestre)
Ce qui affiche:
Moyenne par trimestre pour chaque trimestre avec prise en compte du changement climatique (mm): trimestre 1 165.719091 2 202.630909 3 62.836364 4 164.158182 Name: rr3, dtype: float64
On n'effectue pas le data-test au jour le jour compte tenu des biais trop importants induits par le choix d'un seul modèle de prévision.
En première approximation l'impact sur les résultats est de doubler la surface de récupération nécessaire à partir de la méthode décrite dans les étapes précédentes.
Published

 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português