Description
The objective of this tutorial is to make a manual pump which can be used for getting water out of a tank.
Introduction
Matériaux
- The parts for the pump mentioned here are all made of PVC:
- 3 adapters 50mm-25mm
- 2 couplings 50mm diameter
- 1 tee 50mm-25mm
- 1 or 2 elbows 25mm (in accordance with requirements for water outlet)
- 1 - 2 metres of 25mm diameter tubing (in accordance with requirements for water outlet)
- 1 - 2 metres tubing 50mm diameter
- 2 (glass) marbles with a diameter greater than 25mm,
- 2 screws 50mm long (minimum)
For the piston:
- 1 - 2 metres of tubing 40mm,
- 1 Tee XXmm-40mm
- 1 x tube cap 40mm (or preferably slightly larger)
- acetone (or similar solvent)
Outils
- Saw
- Electric Drill
- Screwdriver
- PVC glue
- Sandpaper
- Cloth
Étape 1 - Concept
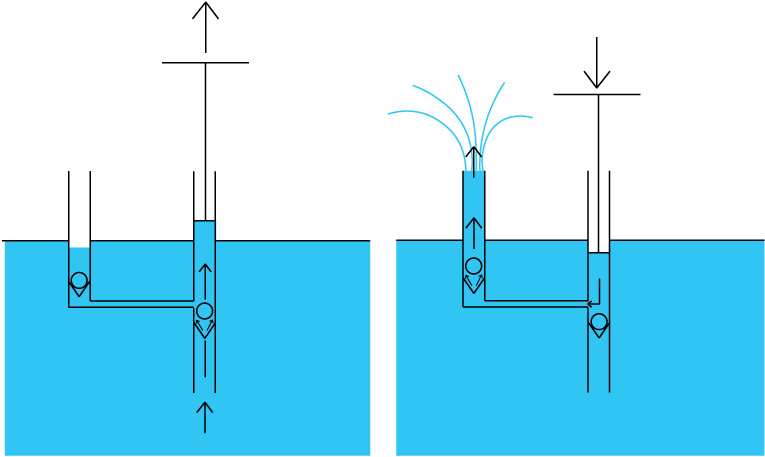
The pump works on a very simple concept.
A vacuum is created when the piston is raised.The other valve is the opposite way round so the water from the outlet is not sucked in.
Pressure is created when the piston is lowered which then closes the non-return valve at the bottom and opens up the other valve. This allows the water is to flow out.
This type of pump is called a ‘displacement pump’.
Étape 2 - Preparation
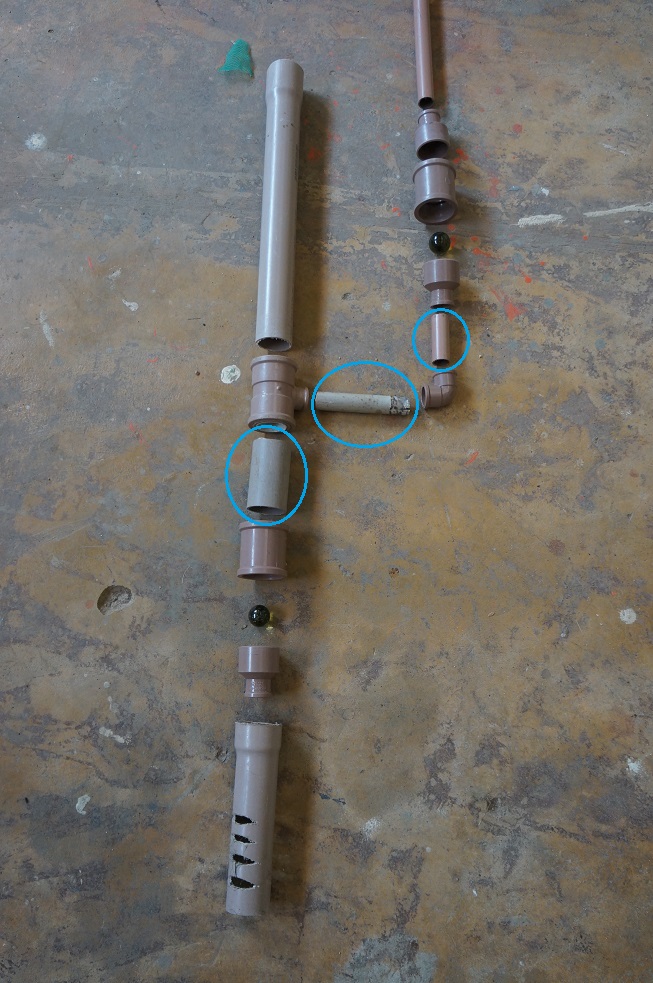
The aim of this step is to check the equipment is in order without gluing the components together.
Slot the components together as per the following diagram:
You can even check if it is working or not.
For best results: the areas circled in blue must be as short as possible.
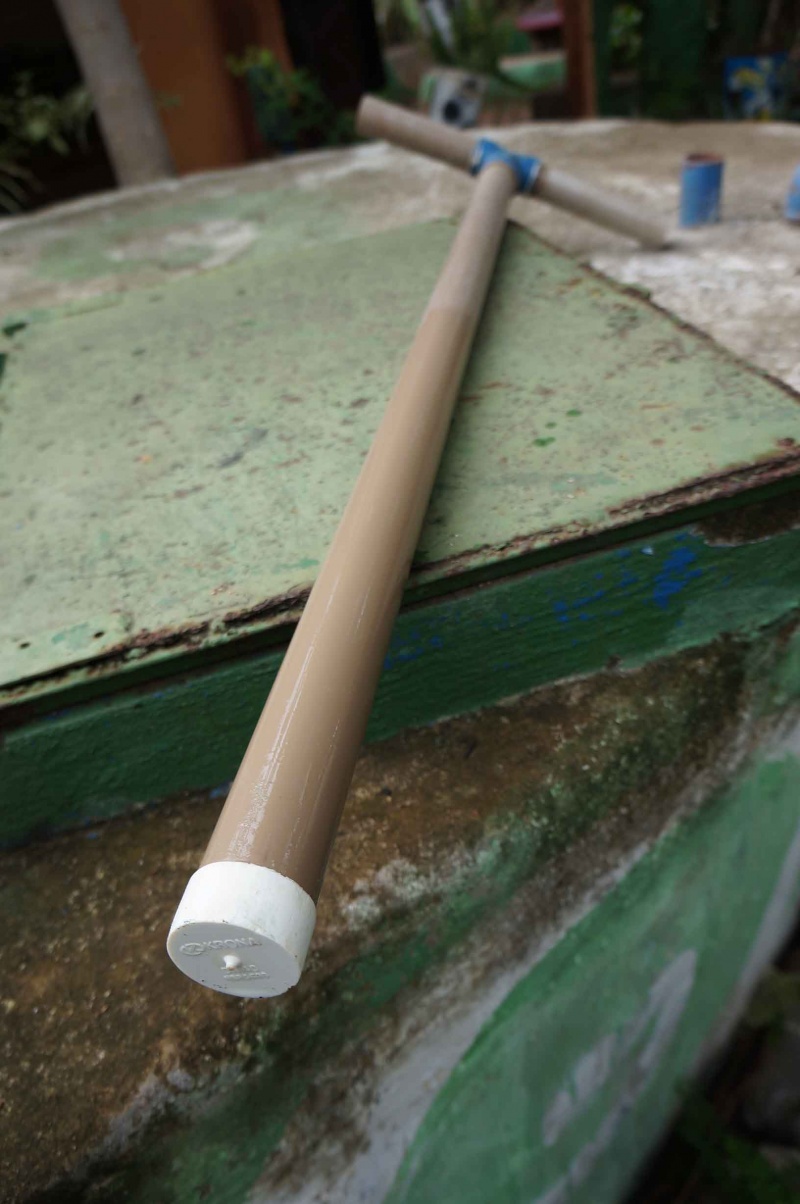
Étape 3 - Assembling the Handle
Once all checks have been completed, you can now start to assemble the components.
All that needs to be done is to glue the parts together using PVC glue and to check if the connections are watertight .
- Gluing instructions:
- Using fine sandpaper, rub down the connecting areas.
- Wipe with cloth soaked in the solvent to clean the area.
- Apply the glue inside of the opening of the female part and all over the male part.
- Immediately slot the two parts into each other without twisting.
- Wipe off any excess glue.
It will take about 1 hour to dry. However, if the water is intended for consumption, it is then advised to wait between 12 and 24 hours for any toxic solvents to disperse.
Étape 4 - Assembling the Pump Body
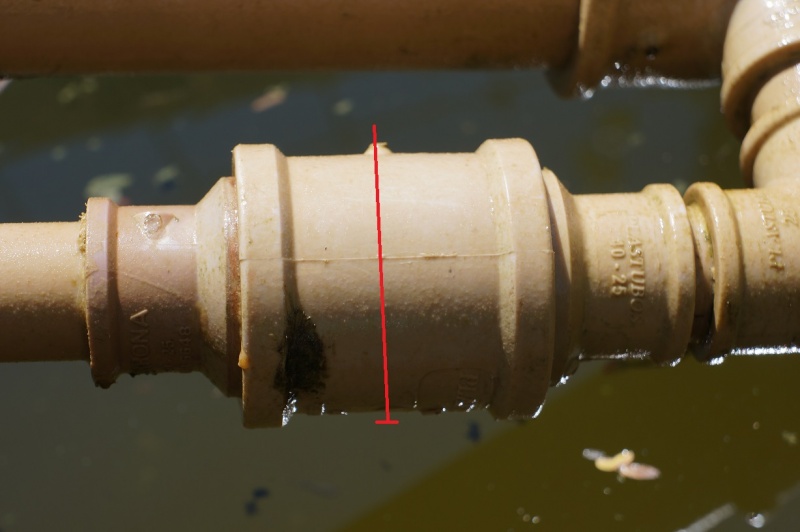
Collez tous les morceaux puis une fois sec, percez et vissez au milieu des raccord 50mm-50mm.
On peut aussi très bien clouer (voir image) en perçant avec un diamètre plus petit.
Ceci permet à la bille de se soulever suffisamment pour laisser passer l'eau, tout en l’empêchant d'aller obstruer l'autre extrémité.
/!\ Faire bien attention à ce que la bille soit du bon côté !
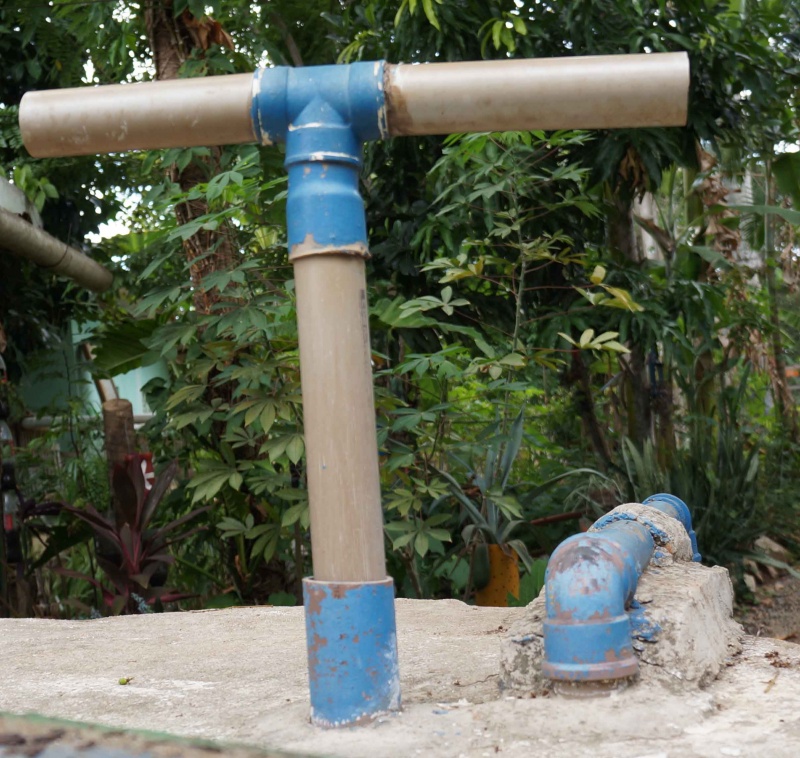
Étape 5 - Mise en place
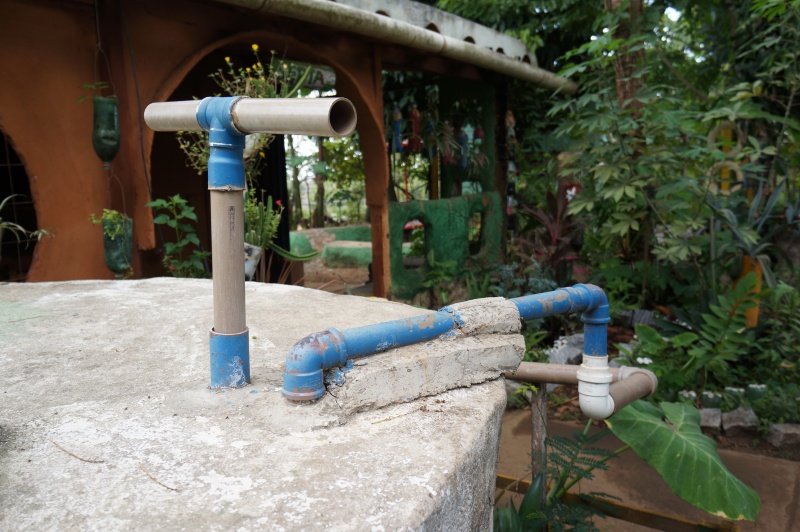
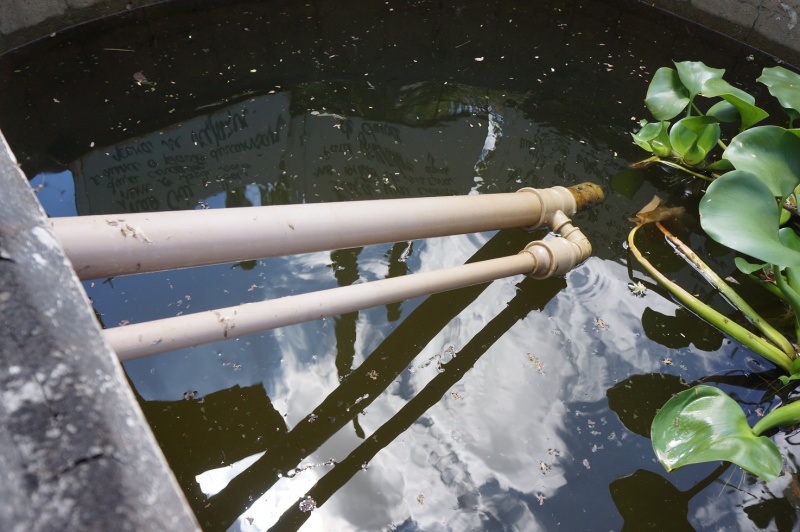
Pour une efficacité maximum, l'idéal est de sceller les tuyaux. Au SERTA, la partie non mobile est coulée dans le béton qui constitue le couvercle du réservoir.
L'important est que l'allonge, par où l'eau entrera dans le circuit, ne touche pas le fond du réservoir, mais en soit cependant assez proche pour pouvoir puiser au plus profond du bassin, et que l'ensemble du système soit assez rigide pour faciliter le pompage.
Il est conseillé de positionner l'ensemble du système avant de le fixer.
Notes et références
Système installé au SERTA (Serviço de Tecnologia Alternativa) au Brésil
Améliorations : lier la pompe à une éolienne pour un pompage continu, à un vélo pour une grosse quantité.
Yes







 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português