(Mise à jour pour être en accord avec la nouvelle version de la source de la page) |
|||
| (98 révisions intermédiaires par 3 utilisateurs non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 10 : | Ligne 10 : | ||
|Cost=6500 | |Cost=6500 | ||
|Currency=EUR (€) | |Currency=EUR (€) | ||
| − | |Tags=assainissement, eaux grises, eaux noires, plantes, filtre plantés, phyto épuration, épuration, fosse septique | + | |Tags=assainissement, eaux grises, eaux noires, plantes, filtre plantés, phyto épuration, épuration, fosse septique, écologie, infiltration, eutrophisation, Low-tech Tour France |
|SourceLanguage=fr | |SourceLanguage=fr | ||
|Language=en | |Language=en | ||
| Ligne 16 : | Ligne 16 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Introduction | {{Introduction | ||
| − | |Introduction=The purpose of water sanitation is to transform water that has been polluted by human activity (domestic, agricultural, industrial) into water that can be assimilated into the natural environment. There are numerous water sanitation | + | |Introduction=The purpose of water sanitation is to transform water that has been polluted by human activity (domestic, agricultural, industrial) into water that can be assimilated into the natural environment. There are numerous water sanitation solutions from the collective level that exist as individual solutions, referred to as "autonomous." All of these are based on bacteriological activity to clean up contaminated water. Likewise, each system, at its output, returns the water to the natural environment by infiltration or by leach field. The output of this water sanitation is not potable. It is highly rich in minerals that the sun and plants may assimilate, comparable to a fertilizer. Returning it to the aquatic environment is prohibited in most cases, except when infiltration or leaching is not possible. As the aquatic environment is more sensitive than the soil, the input of nutrient-laden water involves a high risk of disrupting the natural environment, or even causing asphyxiation or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eutrophication eutrophication]. |
| − | === | + | ===Les types de pollutions et l’assainissement=== |
Water pollution is grouped into four families: | Water pollution is grouped into four families: | ||
| − | *Organic pollution (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus) mainly comes from substances of biological origin (excrement, urine, manure, slurry | + | *Organic pollution (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus) mainly comes from substances of biological origin (excrement, urine, manure, slurry...). These particles are oxidizable, that is to say, that in the presence of oxygen, bacteria are able to degrade them and transform them into minerals. |
*Microbiological pollution is linked to organic pollution. Full of excrement, wastewater is rich in pathogenic microorganisms: viruses, bacteria, etc. which are harmful to health and the environment. High bacterial competition inhibits the development and proliferation of these parasites. | *Microbiological pollution is linked to organic pollution. Full of excrement, wastewater is rich in pathogenic microorganisms: viruses, bacteria, etc. which are harmful to health and the environment. High bacterial competition inhibits the development and proliferation of these parasites. | ||
| − | *Chemical pollution is comprised of all the major pollutants resulting from human activity such as medicines, pesticides, hydrocarbons, metals and heavy metals. These chemicals are dangerous for the environment | + | *Chemical pollution is comprised of all the major pollutants resulting from human activity such as medicines, pesticides, hydrocarbons, metals and heavy metals. These chemicals are dangerous for the environment, causing long-lasting pollution with their high toxicity and low biodegradability. Current sanitation systems (collective or not) are very inefficient in the face of this complex and varied pollution. Pollutants therefore end up in the natural environment and are bio-accumulated. In this way, they move up the food chain and increase their concentration at each new level. |
| − | *Suspended solids (SS) are insoluble solid particles. | + | *Suspended solids (SS) are insoluble solid particles. Over time, they clog filtration systems. |
| − | === | + | ===La phytoépuration – les filtres plantés=== |
| − | Like all the other sanitation systems (water treatment plants, septic systems, | + | Like all the other sanitation systems (water treatment plants, septic systems, all-water treatment systems...) phyto-purification is based on the principle of separating solids from liquids as well as the bacterial degradation of particles. Phyto-purification (or the planted filter) is based on three actors: |
- Bacteria. It degrades the organic particles to render them assimilable to the natural environment. | - Bacteria. It degrades the organic particles to render them assimilable to the natural environment. | ||
| − | - The substrate, comprised of gravel or aggregate, creates a habitat for the bacteria, which settle upon the surface of each material. It plays an equally important role | + | - The substrate, comprised of gravel or aggregate, creates a habitat for the bacteria, which settle upon the surface of each material. It plays an equally important role in the root systems of the plants. With granule size going from finer to coarser, the substrate is also a filter, permitting the passage of water while blocking the bigger materials. |
- The plants, with the development of their roots and the movement of of their overground parts, clean the filter which, contrary to all the other solutions, self-maintains it. | - The plants, with the development of their roots and the movement of of their overground parts, clean the filter which, contrary to all the other solutions, self-maintains it. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Intérêts et inconvénients de la phytoépuration=== |
| − | Phyto-purification is an effective solution | + | Phyto-purification is an effective solution to wastewater sanitation quality. Contrary to the other systems, a plant-based filter consumes no electrical energy (brewing, foaming, pumping...) and requires no complex maintenance such as sludge drainage or re-direction to treatment plants. Self-sufficient energetically and logistically, phyto-purification is the most ecological solution for wastewater sanitation. |
| − | Phyto-purification is an extensive solution which takes up | + | Phyto-purification is an extensive solution which takes up between 2 and 4m²/population equivalent (PE) -- more space than a compact filter, but less space than a sand filter. The filters are sized by the accommodation capacity of the related housing, not by the number of inhabitants, with one main room = 1 PE. For example, a house with 3 bedrooms, 1 kitchen-dining room, and 1 living room has 5 main rooms. The sanitation system must then have a capacity of 5 PE. Individual sanitation, being means-based and not end-based, would require at minimum 10m² of planted filters. |
| − | Filters that are installed | + | Filters that are installed as such, thanks to the diversity of the filtering plants, play a part in the aesthetic appeal of gardens. What's more, they replicate wetlands, a necessary element in the development of natural life. Numerous helpers (insects, birds, amphibeans...) return--it's a great step toward biodiversity. Phyto-purification is different from lagoon-based systems in that there is no water on the surface of the filters, but instead gravel--therefore, no risk of the proliferation of mosquitos. |
| − | However, the installation of planted filters remains a greater investment than that of | + | However, the installation of planted filters remains a greater initial investment than that of conventional solutions (For 5 PE: approximately 10,000 € for planted filters, versus 7,000 € for an all-water septic system). The system becomes profitable at around 15 years, as it demands neither management by a professional workforce, tank drainage (there is no tank), nor energy (apart from cases requiring a sewage pump station for powering the filters, but this costs only a few euros per year where necessary). |
| − | If your housing is part of collective or public sanitation (all to the sewer), you cannot run an autonomous sanitation system. But don't lose hope, phyto-purification is the dominant sanitation system in France for towns of less than 1000 inhabitants. Your wastewater may already be in the roots of plants! | + | If your housing is part of collective or public sanitation (all to the sewer), you cannot run an autonomous sanitation system [depending on country]. But don't lose hope, phyto-purification is the dominant sanitation system in France for towns of less than 1000 inhabitants. Your wastewater may already be in the roots of plants! |
| − | === | + | ===Autoconstruction et agréments=== |
To limit pollution in the natural environment, sanitation systems are subject to regulation. A performance requirement is requested by the sanitation collective (>20 PE). Individual sanitation must meet an obligation of means. | To limit pollution in the natural environment, sanitation systems are subject to regulation. A performance requirement is requested by the sanitation collective (>20 PE). Individual sanitation must meet an obligation of means. | ||
| Ligne 64 : | Ligne 64 : | ||
The system presented was produced with Kévin Quentric, self-building guide affiliated with the network Aquatiris. This tutorial retraces the key milestones of an installation, providing an evaluation of the capacity of self-building and the value of the planted filters. To act in compliance with French law, it would be beneficial to connect with a company whose solutions are authorized. | The system presented was produced with Kévin Quentric, self-building guide affiliated with the network Aquatiris. This tutorial retraces the key milestones of an installation, providing an evaluation of the capacity of self-building and the value of the planted filters. To act in compliance with French law, it would be beneficial to connect with a company whose solutions are authorized. | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
}} | }} | ||
{{TutoVideo | {{TutoVideo | ||
| Ligne 92 : | Ligne 92 : | ||
* Utility Knife | * Utility Knife | ||
* Drill-Screwdriver | * Drill-Screwdriver | ||
| + | |Tuto_Attachments={{Tuto Attachments | ||
| + | |Attachment=Phyto_puration_eaux_us_es_10_ForumClimat_Phytoepuration_VF_2_.pdf | ||
| + | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
|Step_Title=Filter Sizing | |Step_Title=Filter Sizing | ||
| − | |Step_Content=While many planted filter solutions | + | |Step_Content=While many planted filter solutions exist, the filter proposed in this tutorial is the solution most used in collective water sanitation, customized to an "individual format." It is composed of two filters having two different roles: first a vertical filter, then a horizontal filter. |
| − | === | + | === Filtre vertical === |
The vertical-flow filter (VF), which receives the polluted wastewater, is made up of two parallel beds, utilized alternately. The sand on the surface of the filter facilitates the passage of water while blocking the larger particles. | The vertical-flow filter (VF), which receives the polluted wastewater, is made up of two parallel beds, utilized alternately. The sand on the surface of the filter facilitates the passage of water while blocking the larger particles. | ||
| − | The water percolates across the gravel and is collected by a drain at the bottom of the filter, spending between 4 and 8 hours in this first stage. The environment not being | + | The water percolates across the gravel and is collected by a drain at the bottom of the filter, spending between 4 and 8 hours in this first stage. The environment not being flooded with water makes it rich in oxygen, which stimulates the aerobic bacterial activity necessary for the mineralization of the organic particles. Mineralization is a result of complex chemical reactions based on the principle of oxidation of organic compounds. It is this mineralization process that allows the transformation of an element from being non-assimilable by plants to assimilable. The simplification of of the reactions looks like: Norg => NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup> => NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup> => NO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>. |
The vertical filter measures 60 to 80 cm deep and has a surface area of 2m²/PE. | The vertical filter measures 60 to 80 cm deep and has a surface area of 2m²/PE. | ||
| − | === | + | === Filtre horizontal === |
The horizontal-flow filter (HF) collects the filtered wastewater following the vertical filter. The horizontal filter works "loaded up," meaning, the substrate is nearly always saturated in water. In absence of oxygen, anaerobic bacteria denitrify, or remove the nitrogen, from the water: they collect the oxygen they need from the molecules of nitrates, which then go on to transform into dinitrogen: N0<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> => N<sub>2</sub>O => N<sub>2</sub> | The horizontal-flow filter (HF) collects the filtered wastewater following the vertical filter. The horizontal filter works "loaded up," meaning, the substrate is nearly always saturated in water. In absence of oxygen, anaerobic bacteria denitrify, or remove the nitrogen, from the water: they collect the oxygen they need from the molecules of nitrates, which then go on to transform into dinitrogen: N0<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> => N<sub>2</sub>O => N<sub>2</sub> | ||
| Ligne 125 : | Ligne 128 : | ||
* Cover lightly with sand to create a flat floor with a slight slope (≈1%) in the direction of the second filter. | * Cover lightly with sand to create a flat floor with a slight slope (≈1%) in the direction of the second filter. | ||
| − | * For construction dug into the ground, | + | * For construction dug into the ground, set a root-resistant barrier down. |
|Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Terrassement_FV-min.JPG | |Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Terrassement_FV-min.JPG | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_TerrassementFV_FH-en-contrebas-min.JPG | |Step_Picture_01=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_TerrassementFV_FH-en-contrebas-min.JPG | ||
| Ligne 143 : | Ligne 146 : | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
|Step_Title=VF - Waterproofing | |Step_Title=VF - Waterproofing | ||
| − | |Step_Content=* Lay | + | |Step_Content=* Lay down a geotextile |
* Install an EPDM lining which will achieve watertightness. | * Install an EPDM lining which will achieve watertightness. | ||
| Ligne 149 : | Ligne 152 : | ||
* Lay down a geotextile | * Lay down a geotextile | ||
| − | * Install a pass-through fitting on the EPDM lining in the | + | * Install a pass-through fitting on the EPDM lining in the lower end of the filter |
|Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_D_roulement_g_osynth_tiques-min.jpg | |Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_D_roulement_g_osynth_tiques-min.jpg | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Travers_e_de_paroi_FH_pos_e_avant_d_coupe-min.jpg | |Step_Picture_01=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Travers_e_de_paroi_FH_pos_e_avant_d_coupe-min.jpg | ||
| Ligne 155 : | Ligne 158 : | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
|Step_Title=VF - Drainage | |Step_Title=VF - Drainage | ||
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=Install a slotted drainpipe at the bottom of the filter with a T leading to the pass-through fitting. |
* Install a ventilation shaft on the top end of the drain and a plug on the other. | * Install a ventilation shaft on the top end of the drain and a plug on the other. | ||
| Ligne 181 : | Ligne 184 : | ||
|Step_Content=The plants present in the vertical filter need to be very hardy and resistant to great variances in temperature between the summer and winter and times of overflow and times of stillness; equally, it must withstand contact with water full of organic matter. | |Step_Content=The plants present in the vertical filter need to be very hardy and resistant to great variances in temperature between the summer and winter and times of overflow and times of stillness; equally, it must withstand contact with water full of organic matter. | ||
| − | + | The common reed (Phragmites australis), not to be confused with the cattail, is the plant most commonly used in the vertical filter. The density of planting should be 6 plants/m². | |
| − | + | One could just as well plant Sweet flag, Marsh Marigold, Pickerel Weed, Brooklime, Lakeshore Bulrush, Broadleaf Cattail. | |
|Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_800px-Phragmites_australis_inflorescences_-min.jpg | |Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_800px-Phragmites_australis_inflorescences_-min.jpg | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Plantation_FH_1-min.JPG | |Step_Picture_01=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Plantation_FH_1-min.JPG | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=HF - Excavation |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=As the top of the horizontal filter must be lower than the floor of the vertical filter, this filter is carved into the earth. |
| − | * | + | * Dig out the horizontal filter to 60cm x 2m x PE in meters. |
| − | * | + | * Cover lightly with sand to create a flat floor with a slight slope (≈1%) in the direction of the infiltration zone. |
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=HF - Plumbing |
| − | |Step_Content=* | + | |Step_Content=* Install a manhole at the bottom of the filter that collects the drained water. |
| − | * | + | * Install in the manhole a stop-start system (overflow) to keep the basin full of water. The water level needs to come to a few centimeters lower than the gravel. You will need to dig into the gravel to have access to the water. |
|Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Travers_e_terre_FH_1.JPG | |Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Travers_e_terre_FH_1.JPG | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=HF - Waterproofing |
| − | |Step_Content=* | + | |Step_Content=* Lay down a geotextile |
| − | * | + | * Install an EPDM lining which will achieve watertightness. |
| − | * | + | * Lay down a geotextile |
| − | * | + | * Install a pass-through fitting on the EPDM lining in the bottom of the filter |
|Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Remplissage_FH-min.JPG | |Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Remplissage_FH-min.JPG | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=HF - Drainage |
| − | |Step_Content=* | + | |Step_Content=?? > * Install a drain split toward the bottom in the base of the filter with a T toward the pass-through fitting. |
| − | * | + | * Fill with 40cm of gravel (granule size 4/8mm). |
|Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_FH_-_Drain_6-min.JPG | |Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_FH_-_Drain_6-min.JPG | ||
|Step_Picture_01=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_FH_-_Drain_5-min.JPG | |Step_Picture_01=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_FH_-_Drain_5-min.JPG | ||
| Ligne 225 : | Ligne 228 : | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=HF - Planting |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=As the water in the horizontal flow filter has already been separated from some of the organic material, the purifying plants can be a bit less durable than the reeds, while remaining hardy and adapted to an aquatic environment. Generally, the benefit of the filter is that it increases biodiversity and introduces plants that flower during different periods of the year. The planting density should be 6 plants/m² |
| − | + | The following plants are beneficial in these planted filters: | |
| − | * | + | * Broadleaf Cattail (Typha Latifolia) |
| − | * | + | *Branched Bur-Reed (Sparganium erectum) |
| − | * Plantain | + | * Common Water Plantain (Alisma plantago) |
| − | * | + | * Lakeshore Bulrush (Schoenoplectus lacustris) |
| − | * | + | * Water Mint (Mentha Aquatica) |
* Iris (Iris pseudocorus) | * Iris (Iris pseudocorus) | ||
| − | * | + | * Purple Loosestrife ( Lythrum salicaria) |
|Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Nikon_-_2018.07.17_-_58-min.JPG | |Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Nikon_-_2018.07.17_-_58-min.JPG | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Outlet |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=At the exit of the horizontal flow filter, the water is assimilable by the natural environment. The ability of the soil to purify and absorb the water is very important to its surface layer: the topsoil. The objective is for the water to slowly enter the aquatic environment (the water table or streams). The infiltration must therefore be made on the surface. |
| − | |||
| − | * | + | * Install a drain connected to the outlet of the horizontal filter. |
| − | * | + | * Fill with gravel |
| − | + | If the soil does not permit infiltration because it is too clayey or compact, the outlet may be a dry well or go directly into a stream. These solutions remain, however, to be used very occasionally and with great precaution since the aquatic environment is particularly sensitive to disruptions generated by the introduction of water concentrated with minerals. | |
|Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Infiltration-min.JPG | |Step_Picture_00=Phytoépuration_eaux_usées_Infiltration-min.JPG | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Maintenance and Use |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=Planted filters require very minimal maintenance, and, if there is any, most commonly calls for gardening. |
| − | + | During the winter, the overground part of the plants is going to dry out, but this doesn't stop the root system and its associated bacteria from functioning properly. For aesthetic purposes and to encourage vegetative recovery, it is necessary to cut these dry parts at the start of springtime. These materials are ideal for compost or making mulch. In the past, reeds were also used to cover thatched cottage roofs. | |
| − | + | With water toilets, wastewater is full of a lot more organic matter than in dry or composting toilets, in which wastewater is nearly non-existent. This material will compost on the vertical filter and accumulate with time. Every 10 to 20 years, a few centimeters of settled organic matter should be collected, which will make a very good amendment for the soil. It is recommended to undertake a supplementary compost cycle for this material because it will be overrun with reed rhizomes. The rise in temperature provoked by the degradation of the manure will destroy the germs. | |
| − | + | During the first months of use of the planted filters, it is recommended to introduce compost to the vertical filter, which kicks off the bacterial activity and covers up the "first travelers" through the filter. Down the road, the plants will entirely mask the polluted wastewater inlet and no odor will be able to escape the plant wall. | |
| − | + | For good decontamination and to avoid fermentation, alternate the usage of the vertical filter beds from one week to the next. After each week of use, change the filtration bed using the valve set. | |
=== Produits d’entretiens et toxicité phytosanitaire === | === Produits d’entretiens et toxicité phytosanitaire === | ||
| − | + | Sanitation via planted filters encourages the use of products that are respectful to the environment, and that's a good thing. Many simplified products exist for house cleaning and hygiene. The simpler the molecules, the easier they are degraded by bacteria. The inverse, "8-in-1," complex products are extremely difficult to reduce, and they pollute the environment. | |
| − | + | Whether collective sanitation or not, it is important to reaffirm that discarded sink water and the flush of the toilet are not to be the trash of the natural habitat. Whether used oils, paints, solvents, hydrocarbons (petroleum products), medicine, cleaning products...all involve serious risks for the environment, as they are addressed very little or not at all by major sanitation systems, whatever they may be. We must take responsibility for these products, specifically concerning the waste they leave and the risk of finding them in nature. Sanitation is not a waste bin! | |
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
| − | |Step_Title= | + | |Step_Title=Dry Toilets and Phyto-purificaton |
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=The ministerial approvals do not differentiate dry and wet types of toilets, so the filters are of the same dimensions regardless of the toilet system being used. |
| − | {{Info| | + | {{Info|The high concentration of organic material in water toilets stimulates bacterial activity in the filters. This high concentration of bacteria promotes microbiological and chemical decontamination of the wastewater. With dry toilets, the volume of organic material in the water would be ridiculously low. To compensate for this deficit, one may introduce compost to the vertical filter from time to time. }} |
| − | + | Evidently, water that is free of excrement contains considerably fewer parasites. Likewise, using simplified cleaning and hygiene products that don't impact the environment is within all of our reach. The use of dry or composting toilets can significantly decrease the consumption of potable water and significantly increase the production of compost, if there is an identified need for it. | |
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Tuto Step | ||
| + | |Step_Title=Educational content to download | ||
| + | |Step_Content=You can download an educational sheet created by the Low-tech Lab for the exhibition "In Search of a Sustainable Habitat" in the "Files" part of the tutorial (tab in the "Tools-Materials" section) | ||
| + | |Step_Picture_00=Phyto_puration_eaux_us_es_Phyto.JPG | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Step | {{Tuto Step | ||
|Step_Title= | |Step_Title= | ||
| − | |Step_Content=''' | + | |Step_Content='''Do you have a minute? Interested in doing this tutorial or not, your response to [https://framaforms.org/votre-avis-sur-ce-tutoriel-du-low-tech-lab-1589450161 this survey] helps us improve our tutorials. Thank you in advance for your help!''' |
| − | + | Like all the work at Low-tech Lab, ''this tutorial is collaborative.'' Don't hesitate to add modifications that seem important, and share your results in the comments. | |
}} | }} | ||
{{Notes | {{Notes | ||
| − | |Notes= | + | |Notes=This tutorial has been produced by Clément CHABOT with the assistance of Camille DUBAND and Thibaud LANCIEN out of the work of Kevin QUENTRIC. |
| + | |||
| − | + | English traduction by: Katia Krussel | |
| − | + | To take this futher, we recommend reading the book "La Phytoépuration" by Aymeric and Guillaume LAZARIN | |
| − | + | References | |
| − | https:// | + | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eutrophication |
| + | |||
| + | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phragmites_australis | ||
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phyto%C3%A9puration | https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phyto%C3%A9puration | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phytoremediation | ||
http://www.assainissement-non-collectif.developpement-durable.gouv.fr/les-filtres-plantes-agrees-a749.html | http://www.assainissement-non-collectif.developpement-durable.gouv.fr/les-filtres-plantes-agrees-a749.html | ||
| − | Impact | + | Impact of chemical pollution on life: |
| − | Widespread Sexual Disruption in Wild Fish - Susan Jobling - https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ | + | Widespread Sexual Disruption in Wild Fish - Susan Jobling - https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/es9710870 |
[https://www.futura-sciences.com/planete/actualites/zoologie-feminisation-poissons-rivieres-nouveaux-produits-cause-18015/ https://www.futura-sciences.com/planete/actualites/zoologie-feminisation-poissons-rivieres-nouveaux-produits-cause-1] | [https://www.futura-sciences.com/planete/actualites/zoologie-feminisation-poissons-rivieres-nouveaux-produits-cause-18015/ https://www.futura-sciences.com/planete/actualites/zoologie-feminisation-poissons-rivieres-nouveaux-produits-cause-1] | ||
Version du 14 mai 2021 à 16:37
Description
Ecological Sanitation of Wastewater
Sommaire
Sommaire
- 1 Description
- 2 Sommaire
- 3 Introduction
- 4 Video d'introduction
- 5 Étape 1 - Filter Sizing
- 6 Étape 2 - VF - Excavation
- 7 Étape 3 - VF - Plumbing
- 8 Étape 4 - VF - Waterproofing
- 9 Étape 5 - VF - Drainage
- 10 Étape 6 - VF - Planting
- 11 Étape 7 - HF - Excavation
- 12 Étape 8 - HF - Plumbing
- 13 Étape 9 - HF - Waterproofing
- 14 Étape 10 - HF - Drainage
- 15 Étape 11 - HF - Planting
- 16 Étape 12 - Outlet
- 17 Étape 13 - Maintenance and Use
- 18 Étape 14 - Dry Toilets and Phyto-purificaton
- 19 Étape 15 - Educational content to download
- 20 Étape 16 -
- 21 Notes et références
- 22 Commentaires
Introduction
The purpose of water sanitation is to transform water that has been polluted by human activity (domestic, agricultural, industrial) into water that can be assimilated into the natural environment. There are numerous water sanitation solutions from the collective level that exist as individual solutions, referred to as "autonomous." All of these are based on bacteriological activity to clean up contaminated water. Likewise, each system, at its output, returns the water to the natural environment by infiltration or by leach field. The output of this water sanitation is not potable. It is highly rich in minerals that the sun and plants may assimilate, comparable to a fertilizer. Returning it to the aquatic environment is prohibited in most cases, except when infiltration or leaching is not possible. As the aquatic environment is more sensitive than the soil, the input of nutrient-laden water involves a high risk of disrupting the natural environment, or even causing asphyxiation or eutrophication.
Les types de pollutions et l’assainissement
Water pollution is grouped into four families:
- Organic pollution (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus) mainly comes from substances of biological origin (excrement, urine, manure, slurry...). These particles are oxidizable, that is to say, that in the presence of oxygen, bacteria are able to degrade them and transform them into minerals.
- Microbiological pollution is linked to organic pollution. Full of excrement, wastewater is rich in pathogenic microorganisms: viruses, bacteria, etc. which are harmful to health and the environment. High bacterial competition inhibits the development and proliferation of these parasites.
- Chemical pollution is comprised of all the major pollutants resulting from human activity such as medicines, pesticides, hydrocarbons, metals and heavy metals. These chemicals are dangerous for the environment, causing long-lasting pollution with their high toxicity and low biodegradability. Current sanitation systems (collective or not) are very inefficient in the face of this complex and varied pollution. Pollutants therefore end up in the natural environment and are bio-accumulated. In this way, they move up the food chain and increase their concentration at each new level.
- Suspended solids (SS) are insoluble solid particles. Over time, they clog filtration systems.
La phytoépuration – les filtres plantés
Like all the other sanitation systems (water treatment plants, septic systems, all-water treatment systems...) phyto-purification is based on the principle of separating solids from liquids as well as the bacterial degradation of particles. Phyto-purification (or the planted filter) is based on three actors:
- Bacteria. It degrades the organic particles to render them assimilable to the natural environment.
- The substrate, comprised of gravel or aggregate, creates a habitat for the bacteria, which settle upon the surface of each material. It plays an equally important role in the root systems of the plants. With granule size going from finer to coarser, the substrate is also a filter, permitting the passage of water while blocking the bigger materials.
- The plants, with the development of their roots and the movement of of their overground parts, clean the filter which, contrary to all the other solutions, self-maintains it.
Intérêts et inconvénients de la phytoépuration
Phyto-purification is an effective solution to wastewater sanitation quality. Contrary to the other systems, a plant-based filter consumes no electrical energy (brewing, foaming, pumping...) and requires no complex maintenance such as sludge drainage or re-direction to treatment plants. Self-sufficient energetically and logistically, phyto-purification is the most ecological solution for wastewater sanitation.
Phyto-purification is an extensive solution which takes up between 2 and 4m²/population equivalent (PE) -- more space than a compact filter, but less space than a sand filter. The filters are sized by the accommodation capacity of the related housing, not by the number of inhabitants, with one main room = 1 PE. For example, a house with 3 bedrooms, 1 kitchen-dining room, and 1 living room has 5 main rooms. The sanitation system must then have a capacity of 5 PE. Individual sanitation, being means-based and not end-based, would require at minimum 10m² of planted filters.
Filters that are installed as such, thanks to the diversity of the filtering plants, play a part in the aesthetic appeal of gardens. What's more, they replicate wetlands, a necessary element in the development of natural life. Numerous helpers (insects, birds, amphibeans...) return--it's a great step toward biodiversity. Phyto-purification is different from lagoon-based systems in that there is no water on the surface of the filters, but instead gravel--therefore, no risk of the proliferation of mosquitos.
However, the installation of planted filters remains a greater initial investment than that of conventional solutions (For 5 PE: approximately 10,000 € for planted filters, versus 7,000 € for an all-water septic system). The system becomes profitable at around 15 years, as it demands neither management by a professional workforce, tank drainage (there is no tank), nor energy (apart from cases requiring a sewage pump station for powering the filters, but this costs only a few euros per year where necessary).
If your housing is part of collective or public sanitation (all to the sewer), you cannot run an autonomous sanitation system [depending on country]. But don't lose hope, phyto-purification is the dominant sanitation system in France for towns of less than 1000 inhabitants. Your wastewater may already be in the roots of plants!
Autoconstruction et agréments
To limit pollution in the natural environment, sanitation systems are subject to regulation. A performance requirement is requested by the sanitation collective (>20 PE). Individual sanitation must meet an obligation of means.
Individual phyto-purification must therefore be approved to be set up, which is to say, if one wishes to go ahead with planted filters at their home, it is necessary to commission a study and installation by a company that insures the system has received a ministerial approval.
In France, the Service Public d'Assainissement Non Collectif (SPANC) or Public Service of Non-Collective Sanitation is charged with the regulation of all the domestic wastewater sanitation systems not linked to collective networks of water sanitation.
Be that as it may, doing one's own construction is possible by calling on a certified guide who will administer soil studies and measurements and who will provide materials and all guidance necessary for a long-lasting and effective result. Self-built systems save at least 30% of costs on the global system and take the individual further in terms of control and knowledge of one's habitat.
The system presented was produced with Kévin Quentric, self-building guide affiliated with the network Aquatiris. This tutorial retraces the key milestones of an installation, providing an evaluation of the capacity of self-building and the value of the planted filters. To act in compliance with French law, it would be beneficial to connect with a company whose solutions are authorized.
Youtube
Matériaux
- Gravel (granule size 12/20 or 20/40mm)
- Gravel (granule size 4/8, 4/12, or 6/10 mm)
- Washed silica sand
- Puncture-resistant geotextile
- EPDM sheeting
- PVC pipes
- 2 PVC T-connectors
- Drains
- PVC Glue
- 2 manholes
- 2 valves
- 2 pass-through fittings
Outils
- Shovels and some good friends, or an excavator
- Shovel
- Pick
- Rake
- Level
- Saw
- Utility Knife
- Drill-Screwdriver
Étape 1 - Filter Sizing
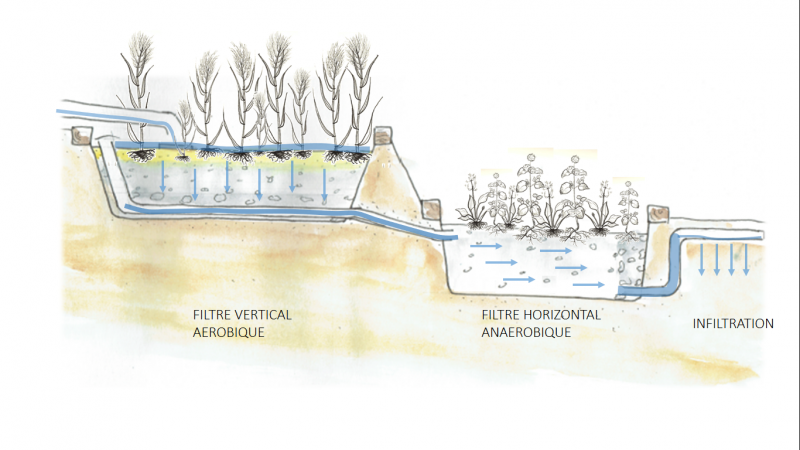
While many planted filter solutions exist, the filter proposed in this tutorial is the solution most used in collective water sanitation, customized to an "individual format." It is composed of two filters having two different roles: first a vertical filter, then a horizontal filter.
Filtre vertical
The vertical-flow filter (VF), which receives the polluted wastewater, is made up of two parallel beds, utilized alternately. The sand on the surface of the filter facilitates the passage of water while blocking the larger particles.
The water percolates across the gravel and is collected by a drain at the bottom of the filter, spending between 4 and 8 hours in this first stage. The environment not being flooded with water makes it rich in oxygen, which stimulates the aerobic bacterial activity necessary for the mineralization of the organic particles. Mineralization is a result of complex chemical reactions based on the principle of oxidation of organic compounds. It is this mineralization process that allows the transformation of an element from being non-assimilable by plants to assimilable. The simplification of of the reactions looks like: Norg => NH4+ => NO2- => NO3-.
The vertical filter measures 60 to 80 cm deep and has a surface area of 2m²/PE.
Filtre horizontal
The horizontal-flow filter (HF) collects the filtered wastewater following the vertical filter. The horizontal filter works "loaded up," meaning, the substrate is nearly always saturated in water. In absence of oxygen, anaerobic bacteria denitrify, or remove the nitrogen, from the water: they collect the oxygen they need from the molecules of nitrates, which then go on to transform into dinitrogen: N03- => N2O => N2
The horizontal-flow filter measures 2m²/PE for a depth of 60cm.
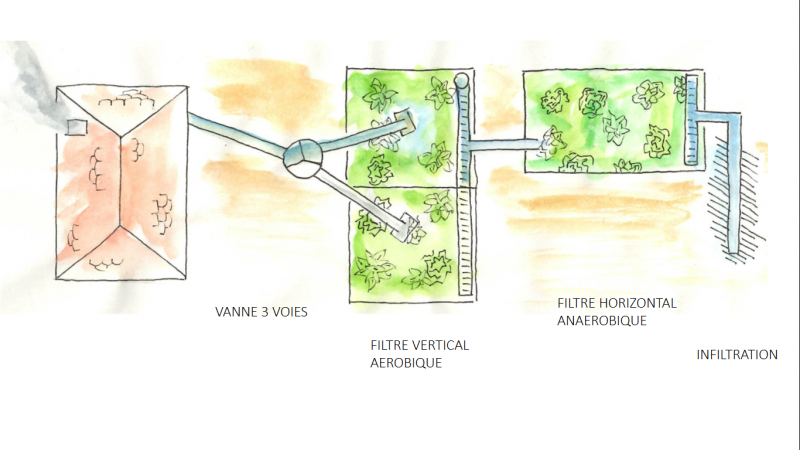
In order for the sanitation to be entirely self-sufficient and to consume no energy, we use gravity to power the two filters. The top of the vertical filter, then, must be lower than the point of collection of wastewater from the house. Likewise, the top of the horizontal filter must be lower than the bottom of the vertical filter. The installation will therefore probably take place on the lowest part of the garden. If this is not possible due to flat terrain, a condensate pump can be installed between the point of collection and the vertical filter, the latter being above ground and the horizontal filter respectively being underground.
The filters must be installed at least 3 meters away from trees, as their roots may risk puncturing the waterproof linings.
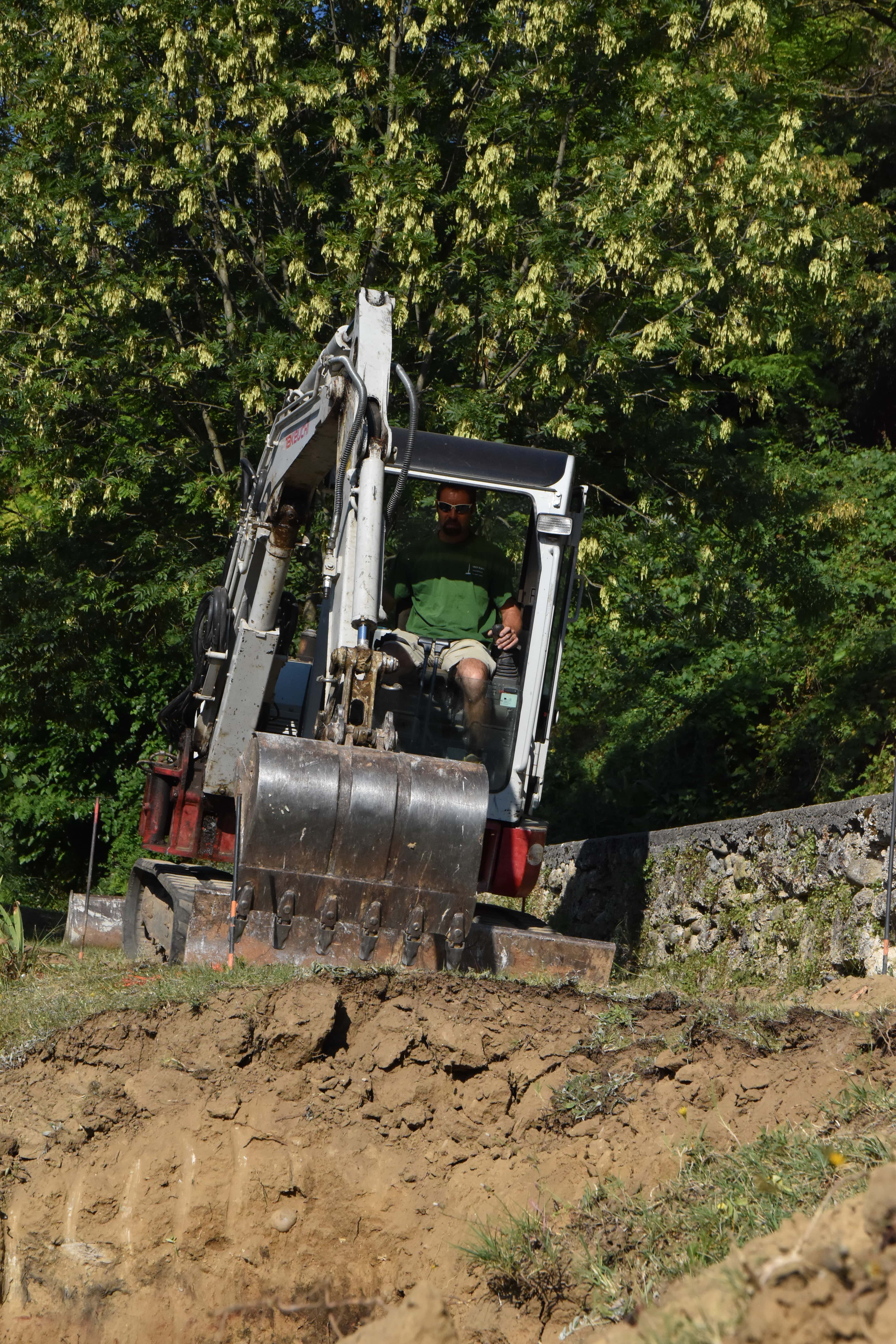
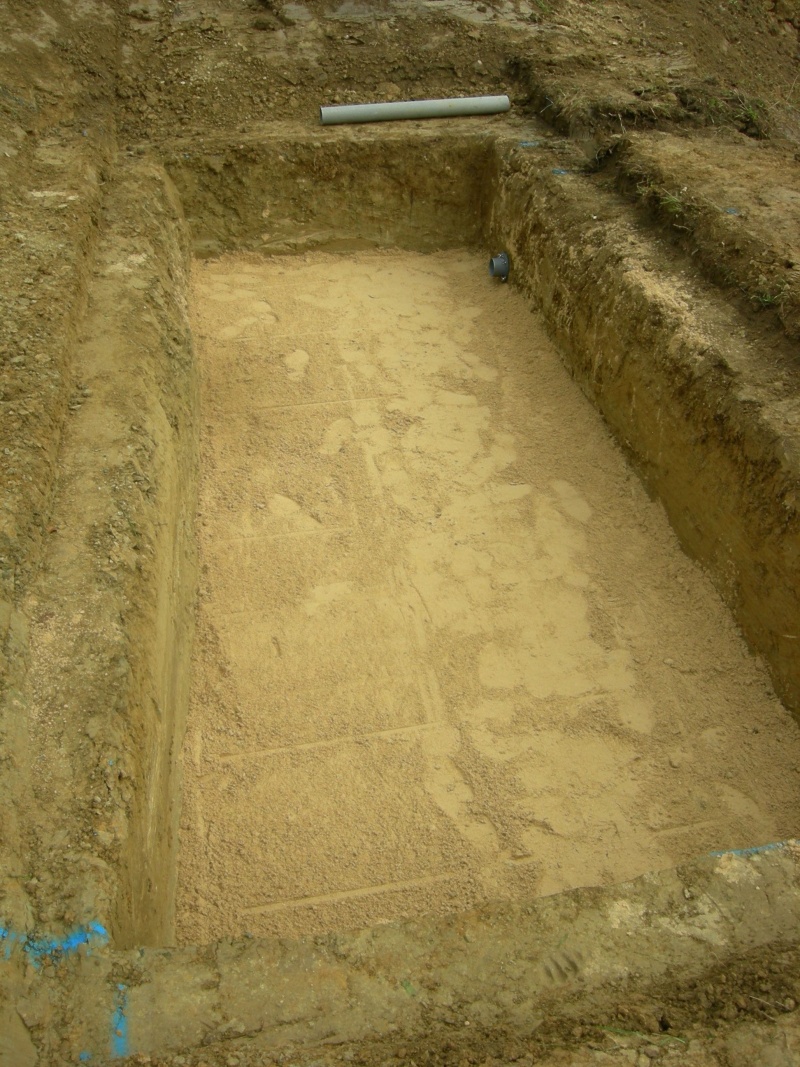
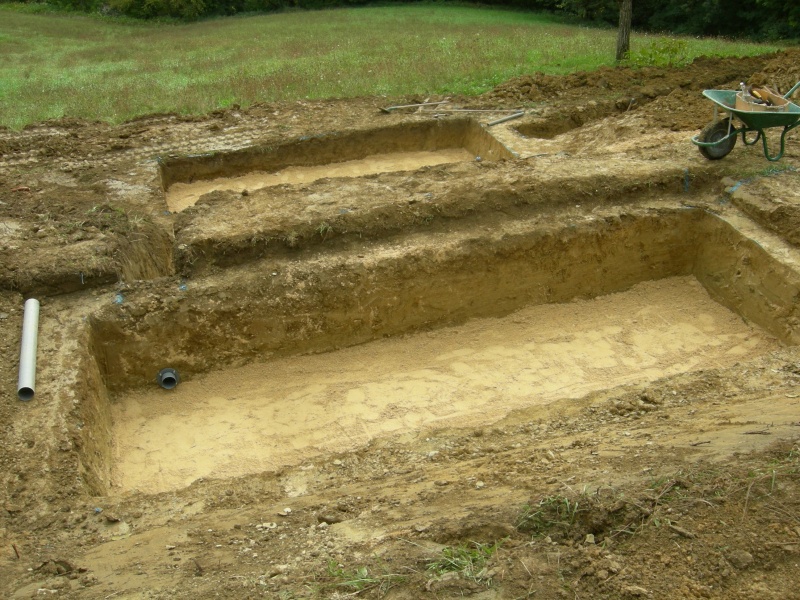
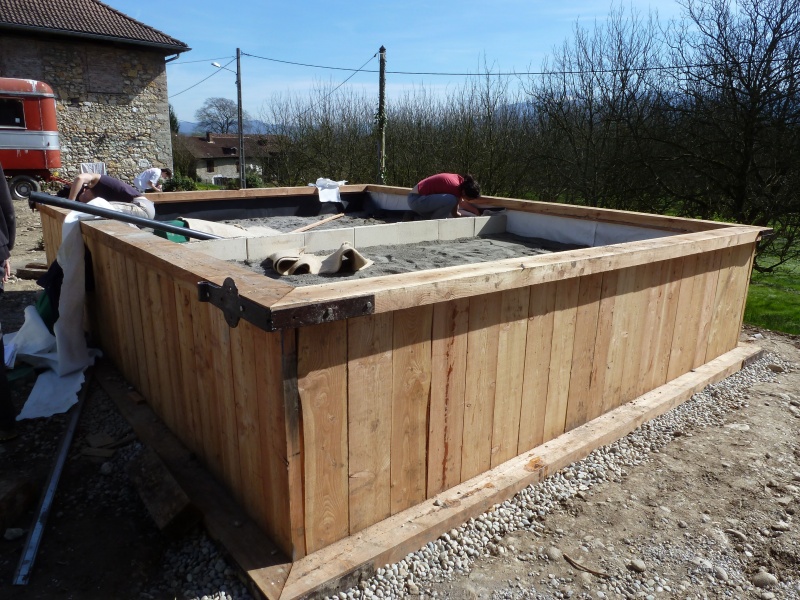
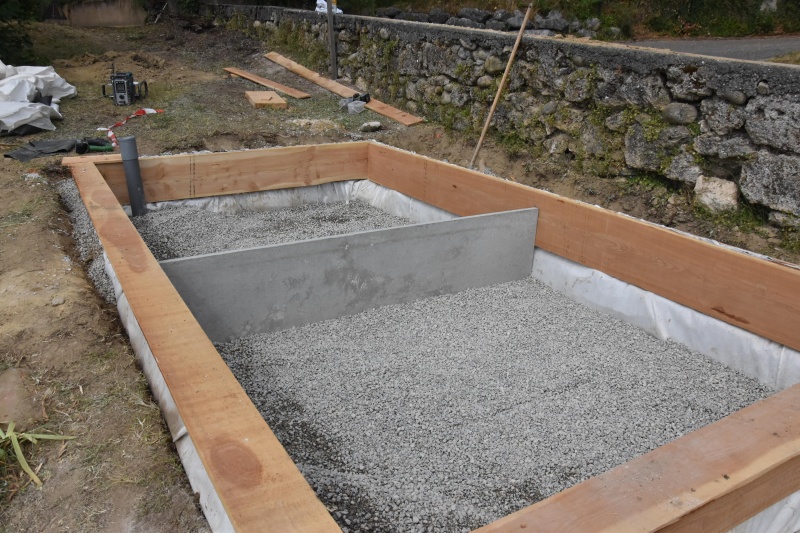
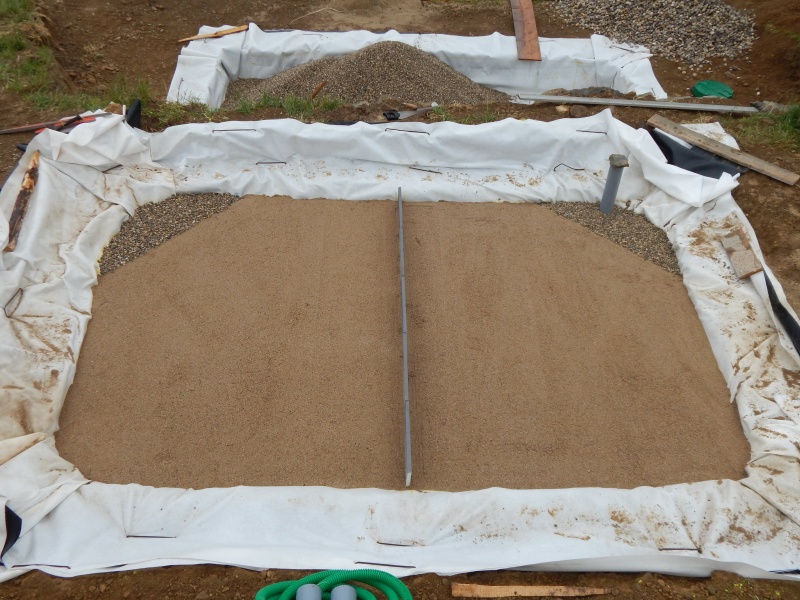
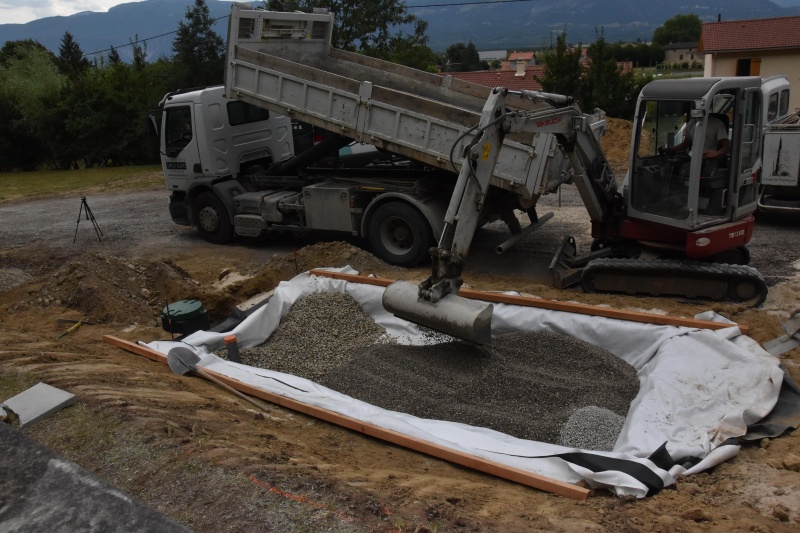
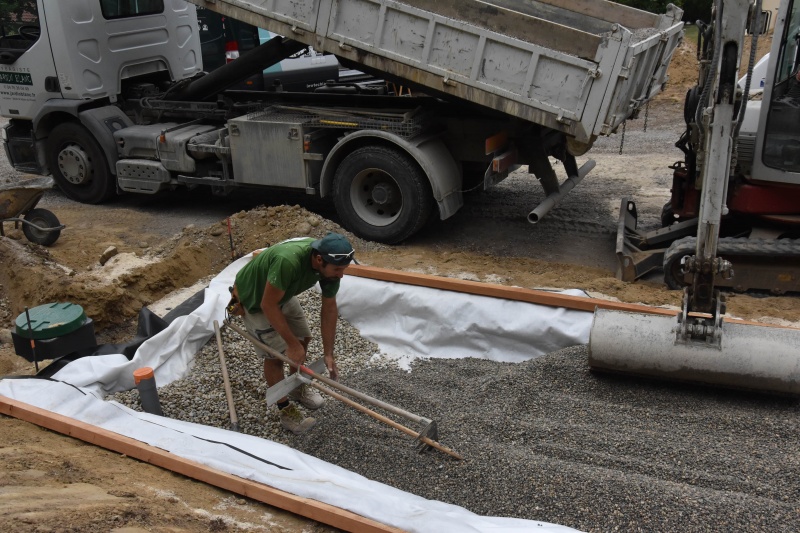
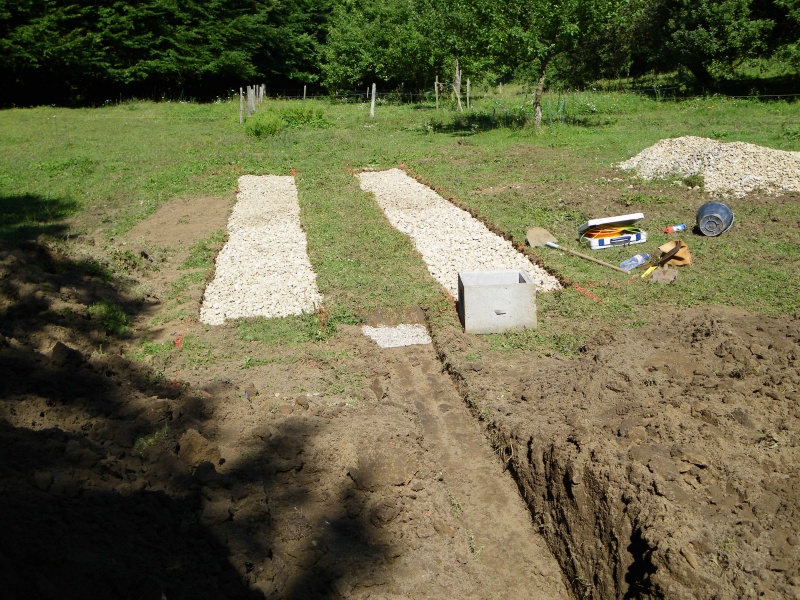
Étape 2 - VF - Excavation
Depending on the characteristics of the terrain
- Dig, build, or construct from wood the structure of the vertical filter at 90cm x 2m x [PE number in meters]
- Cover lightly with sand to create a flat floor with a slight slope (≈1%) in the direction of the second filter.
- For construction dug into the ground, set a root-resistant barrier down.
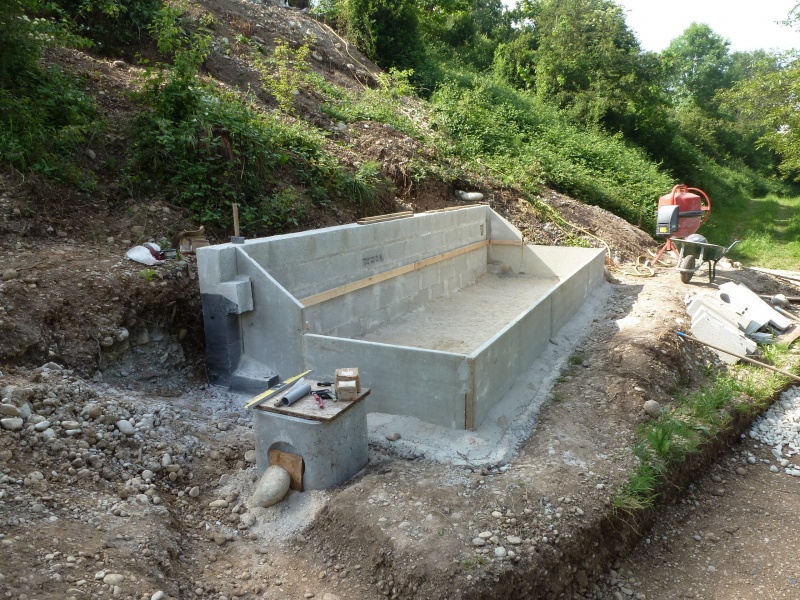
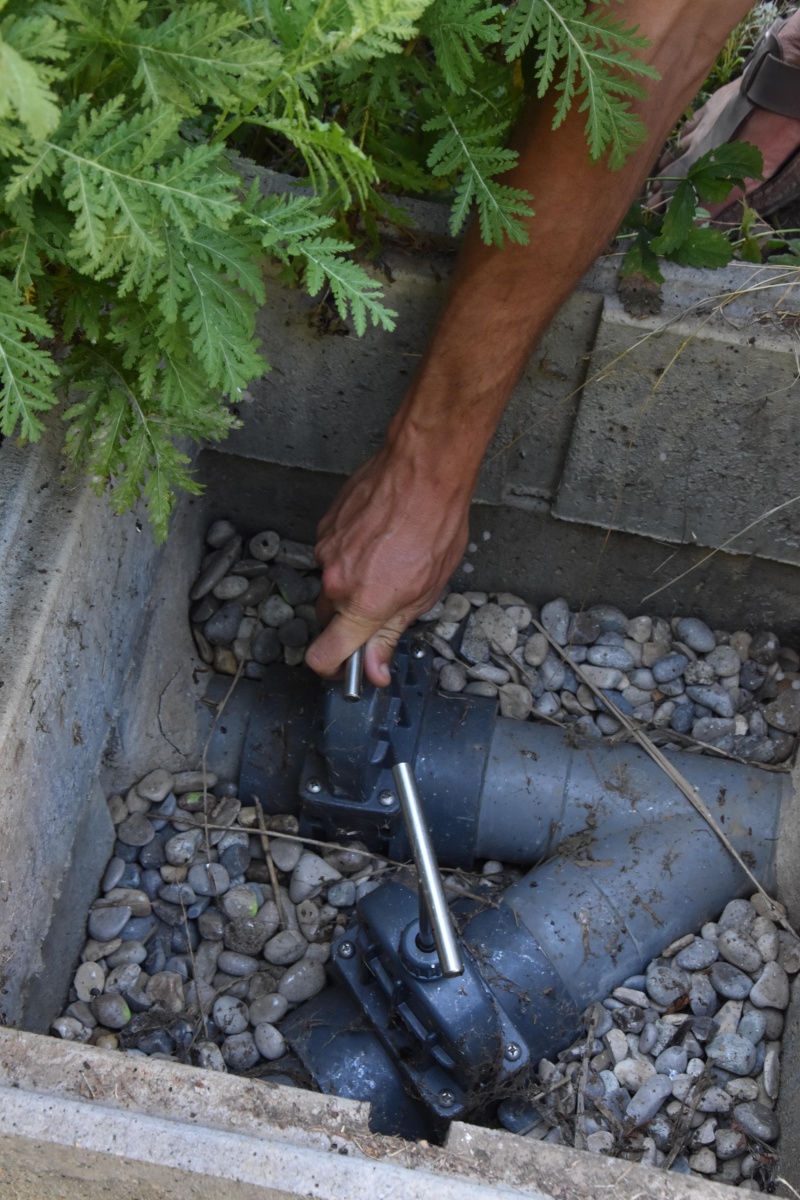
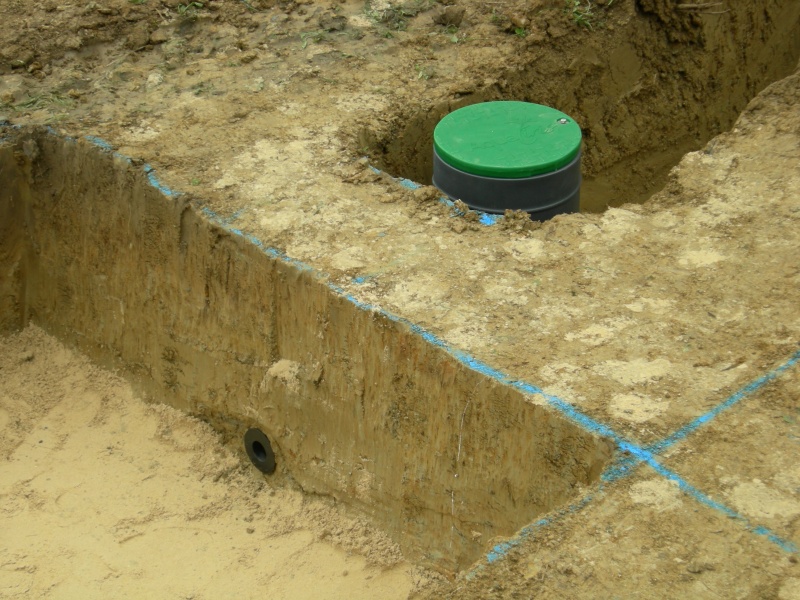
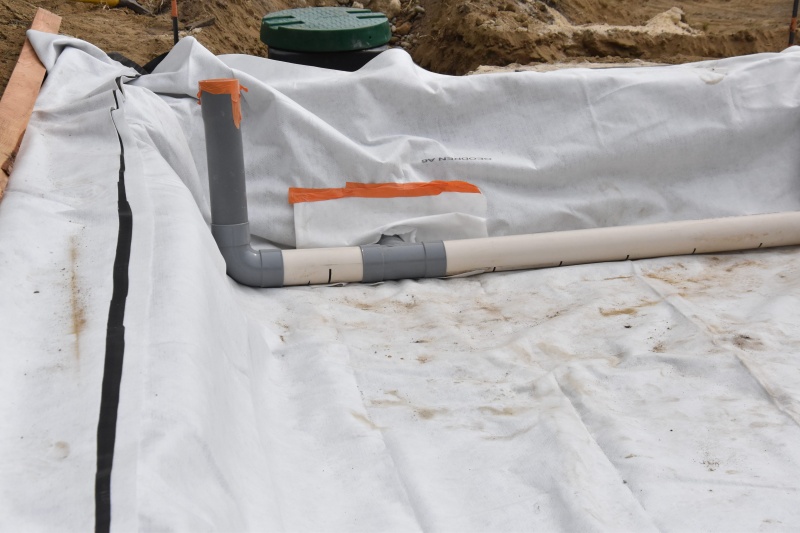
Étape 3 - VF - Plumbing
- Install a manhole at the top of the filter as an inlet for the polluted wastewater.
- Inside the manhole, install a 3-way valve to distribute the water between the two beds.
- Install a manhole at the bottom of the filter that collects the drained water.
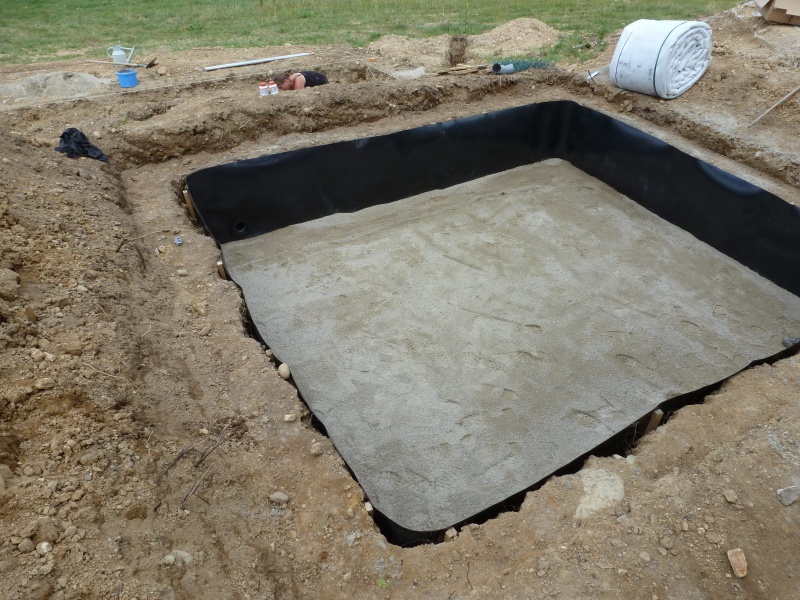
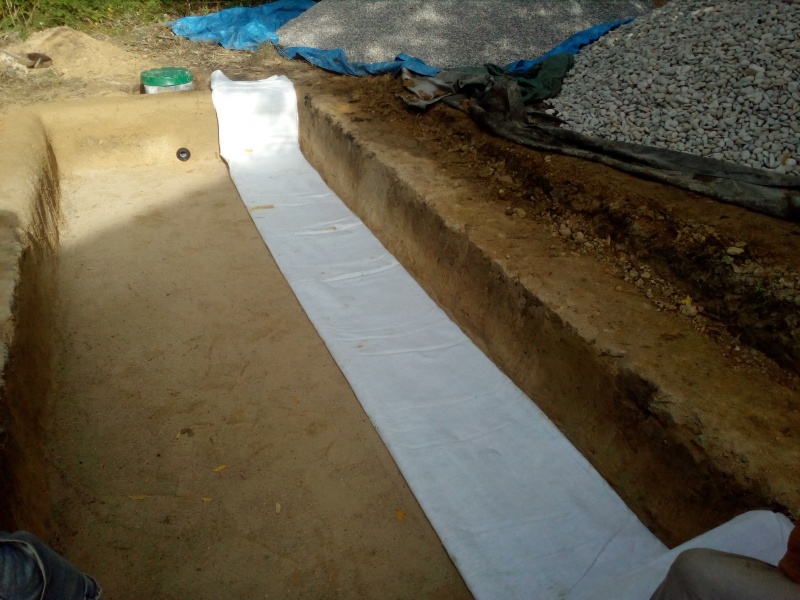
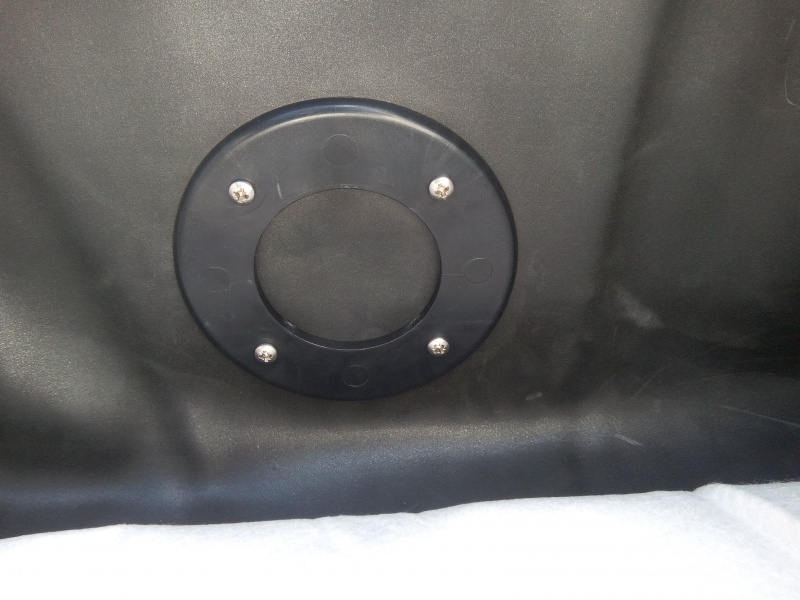
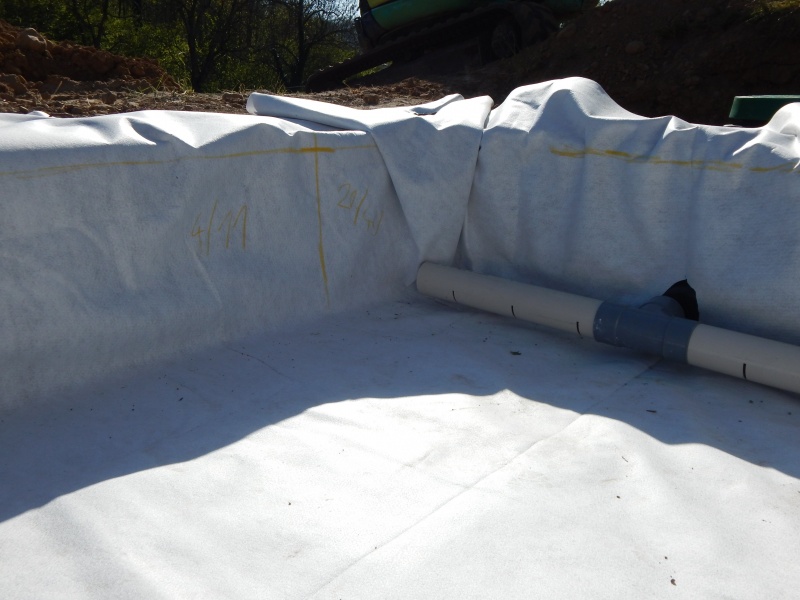
Étape 4 - VF - Waterproofing
- Lay down a geotextile
- Install an EPDM lining which will achieve watertightness.
- Lay down a geotextile
- Install a pass-through fitting on the EPDM lining in the lower end of the filter
Étape 5 - VF - Drainage
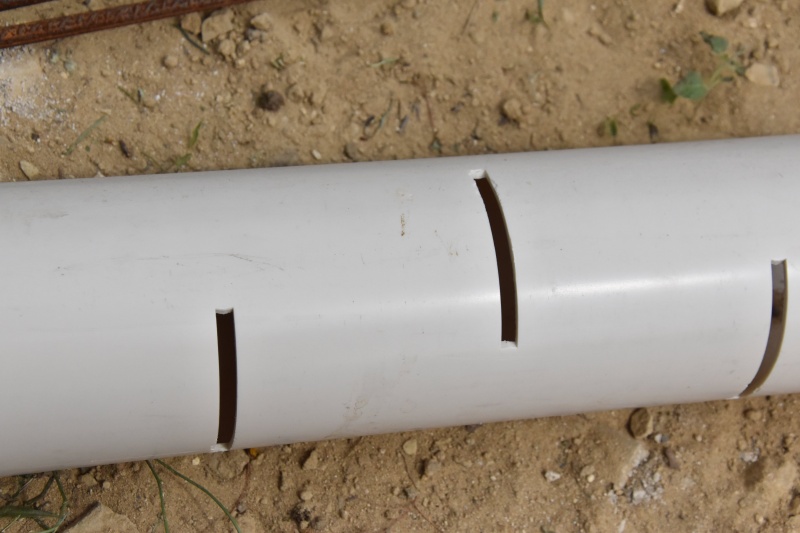
Install a slotted drainpipe at the bottom of the filter with a T leading to the pass-through fitting.
- Install a ventilation shaft on the top end of the drain and a plug on the other.
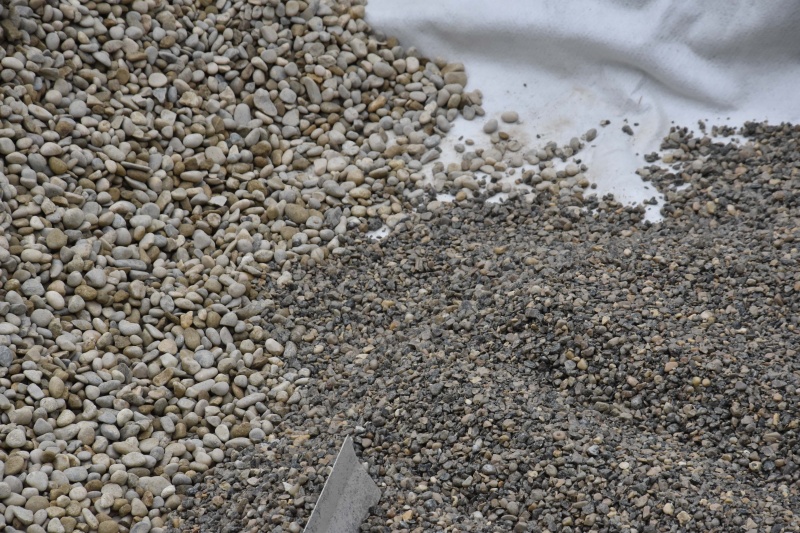
- Fill with 20cm of gravel (granule size 10/20 mm).
- Separate the two beds by installing a dividing wall 60cm high along the width of the VF.
- Fill with 30cm of gravel (granule size 4/8mm).
- Fill with 20cm of washed silica sand (granule size 0/2 mm).
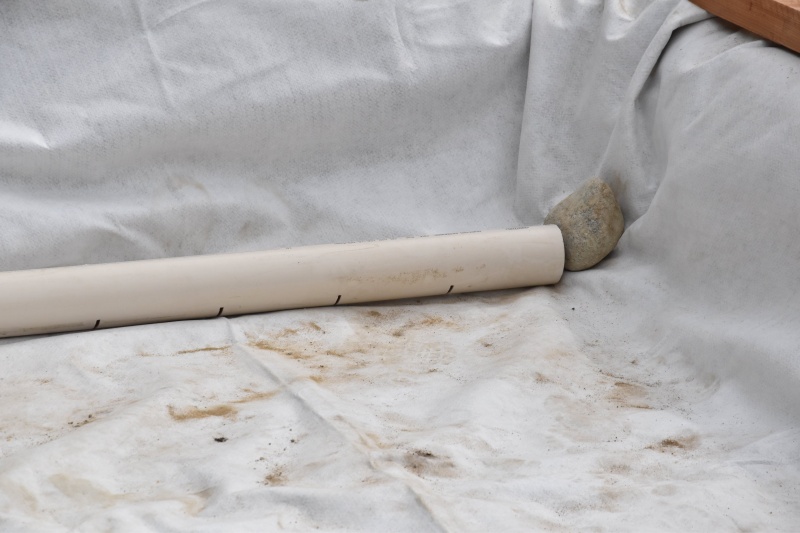
- Install the supply pipes at the outlet of the 3-way valve, one for each bed.
- Under the outlet of the supply pipes, place a stone or a tile to ensure that the inflow of water does not carve into the substrate.
Étape 6 - VF - Planting
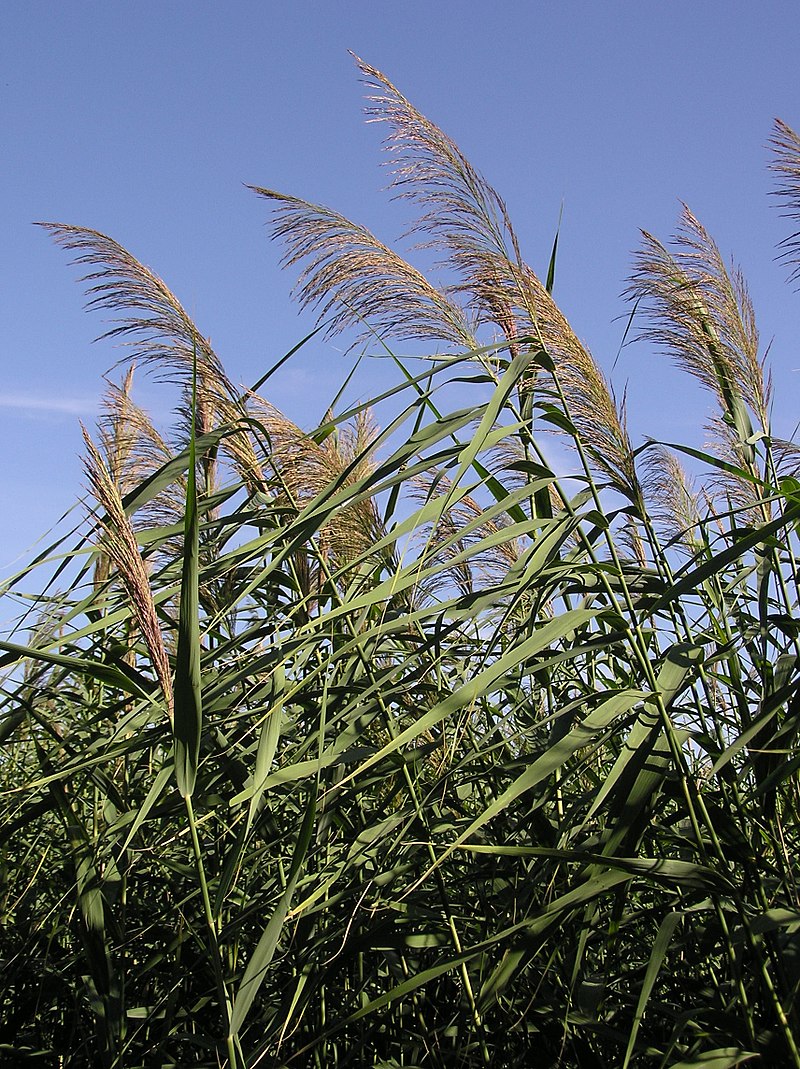
The plants present in the vertical filter need to be very hardy and resistant to great variances in temperature between the summer and winter and times of overflow and times of stillness; equally, it must withstand contact with water full of organic matter.
The common reed (Phragmites australis), not to be confused with the cattail, is the plant most commonly used in the vertical filter. The density of planting should be 6 plants/m².
One could just as well plant Sweet flag, Marsh Marigold, Pickerel Weed, Brooklime, Lakeshore Bulrush, Broadleaf Cattail.
Étape 7 - HF - Excavation
As the top of the horizontal filter must be lower than the floor of the vertical filter, this filter is carved into the earth.
- Dig out the horizontal filter to 60cm x 2m x PE in meters.
- Cover lightly with sand to create a flat floor with a slight slope (≈1%) in the direction of the infiltration zone.
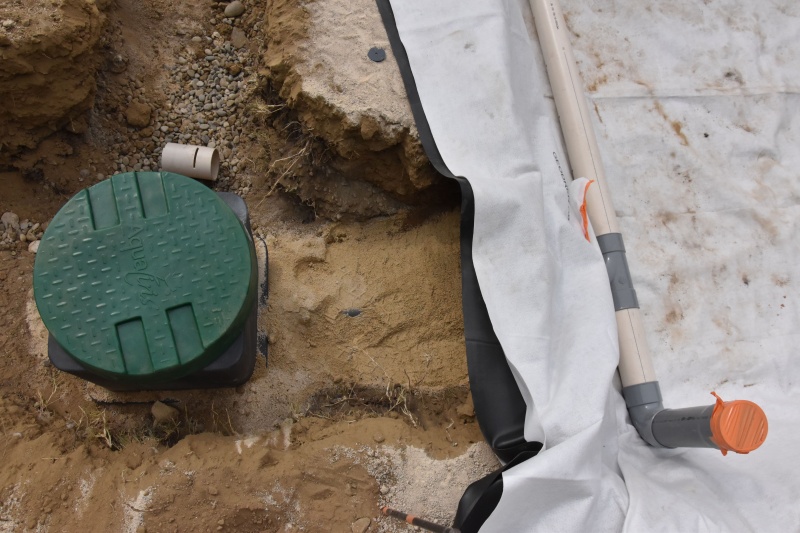
Étape 8 - HF - Plumbing
- Install a manhole at the bottom of the filter that collects the drained water.
- Install in the manhole a stop-start system (overflow) to keep the basin full of water. The water level needs to come to a few centimeters lower than the gravel. You will need to dig into the gravel to have access to the water.
Étape 9 - HF - Waterproofing
- Lay down a geotextile
- Install an EPDM lining which will achieve watertightness.
- Lay down a geotextile
- Install a pass-through fitting on the EPDM lining in the bottom of the filter
Étape 10 - HF - Drainage
?? > * Install a drain split toward the bottom in the base of the filter with a T toward the pass-through fitting.
- Fill with 40cm of gravel (granule size 4/8mm).
Étape 11 - HF - Planting
As the water in the horizontal flow filter has already been separated from some of the organic material, the purifying plants can be a bit less durable than the reeds, while remaining hardy and adapted to an aquatic environment. Generally, the benefit of the filter is that it increases biodiversity and introduces plants that flower during different periods of the year. The planting density should be 6 plants/m²
The following plants are beneficial in these planted filters:
- Broadleaf Cattail (Typha Latifolia)
- Branched Bur-Reed (Sparganium erectum)
- Common Water Plantain (Alisma plantago)
- Lakeshore Bulrush (Schoenoplectus lacustris)
- Water Mint (Mentha Aquatica)
- Iris (Iris pseudocorus)
- Purple Loosestrife ( Lythrum salicaria)
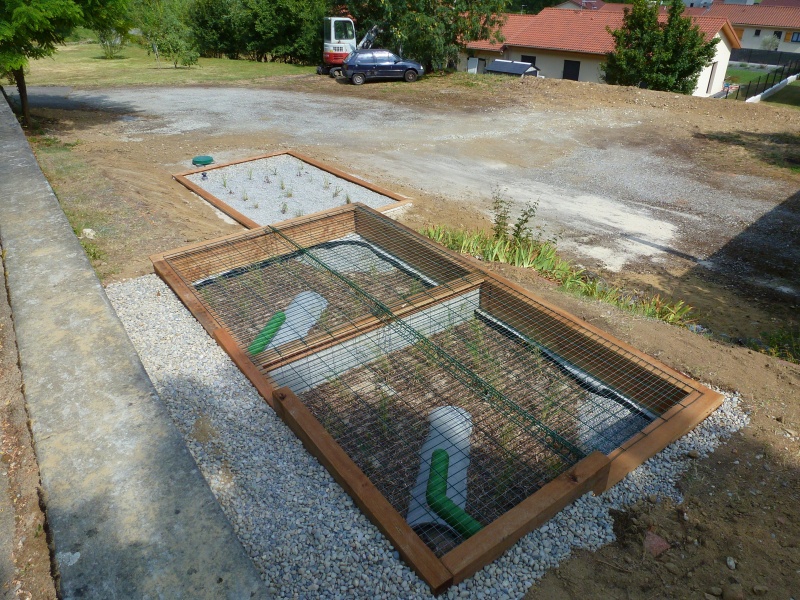
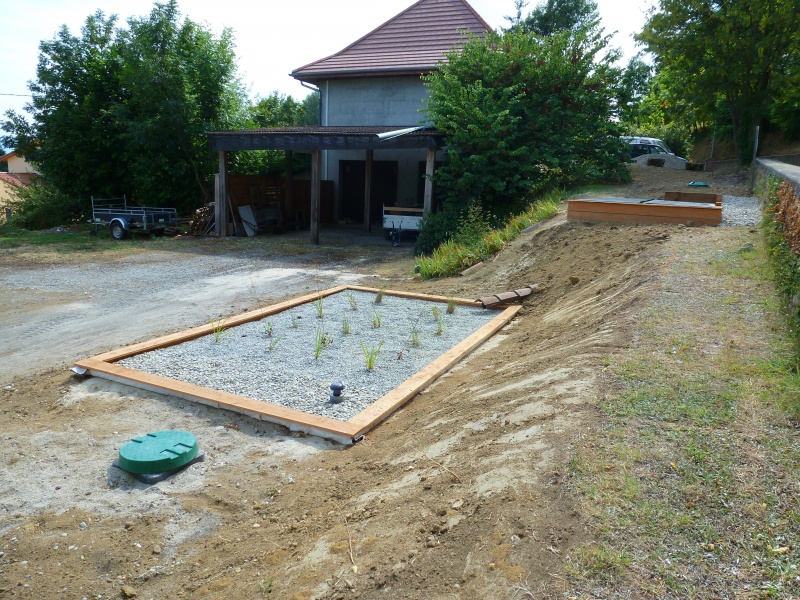
Étape 12 - Outlet
At the exit of the horizontal flow filter, the water is assimilable by the natural environment. The ability of the soil to purify and absorb the water is very important to its surface layer: the topsoil. The objective is for the water to slowly enter the aquatic environment (the water table or streams). The infiltration must therefore be made on the surface.
- Install a drain connected to the outlet of the horizontal filter.
- Fill with gravel
If the soil does not permit infiltration because it is too clayey or compact, the outlet may be a dry well or go directly into a stream. These solutions remain, however, to be used very occasionally and with great precaution since the aquatic environment is particularly sensitive to disruptions generated by the introduction of water concentrated with minerals.
Étape 13 - Maintenance and Use
Planted filters require very minimal maintenance, and, if there is any, most commonly calls for gardening.
During the winter, the overground part of the plants is going to dry out, but this doesn't stop the root system and its associated bacteria from functioning properly. For aesthetic purposes and to encourage vegetative recovery, it is necessary to cut these dry parts at the start of springtime. These materials are ideal for compost or making mulch. In the past, reeds were also used to cover thatched cottage roofs.
With water toilets, wastewater is full of a lot more organic matter than in dry or composting toilets, in which wastewater is nearly non-existent. This material will compost on the vertical filter and accumulate with time. Every 10 to 20 years, a few centimeters of settled organic matter should be collected, which will make a very good amendment for the soil. It is recommended to undertake a supplementary compost cycle for this material because it will be overrun with reed rhizomes. The rise in temperature provoked by the degradation of the manure will destroy the germs.
During the first months of use of the planted filters, it is recommended to introduce compost to the vertical filter, which kicks off the bacterial activity and covers up the "first travelers" through the filter. Down the road, the plants will entirely mask the polluted wastewater inlet and no odor will be able to escape the plant wall.
For good decontamination and to avoid fermentation, alternate the usage of the vertical filter beds from one week to the next. After each week of use, change the filtration bed using the valve set.
Produits d’entretiens et toxicité phytosanitaire
Sanitation via planted filters encourages the use of products that are respectful to the environment, and that's a good thing. Many simplified products exist for house cleaning and hygiene. The simpler the molecules, the easier they are degraded by bacteria. The inverse, "8-in-1," complex products are extremely difficult to reduce, and they pollute the environment.
Whether collective sanitation or not, it is important to reaffirm that discarded sink water and the flush of the toilet are not to be the trash of the natural habitat. Whether used oils, paints, solvents, hydrocarbons (petroleum products), medicine, cleaning products...all involve serious risks for the environment, as they are addressed very little or not at all by major sanitation systems, whatever they may be. We must take responsibility for these products, specifically concerning the waste they leave and the risk of finding them in nature. Sanitation is not a waste bin!
Étape 14 - Dry Toilets and Phyto-purificaton
The ministerial approvals do not differentiate dry and wet types of toilets, so the filters are of the same dimensions regardless of the toilet system being used.
Evidently, water that is free of excrement contains considerably fewer parasites. Likewise, using simplified cleaning and hygiene products that don't impact the environment is within all of our reach. The use of dry or composting toilets can significantly decrease the consumption of potable water and significantly increase the production of compost, if there is an identified need for it.
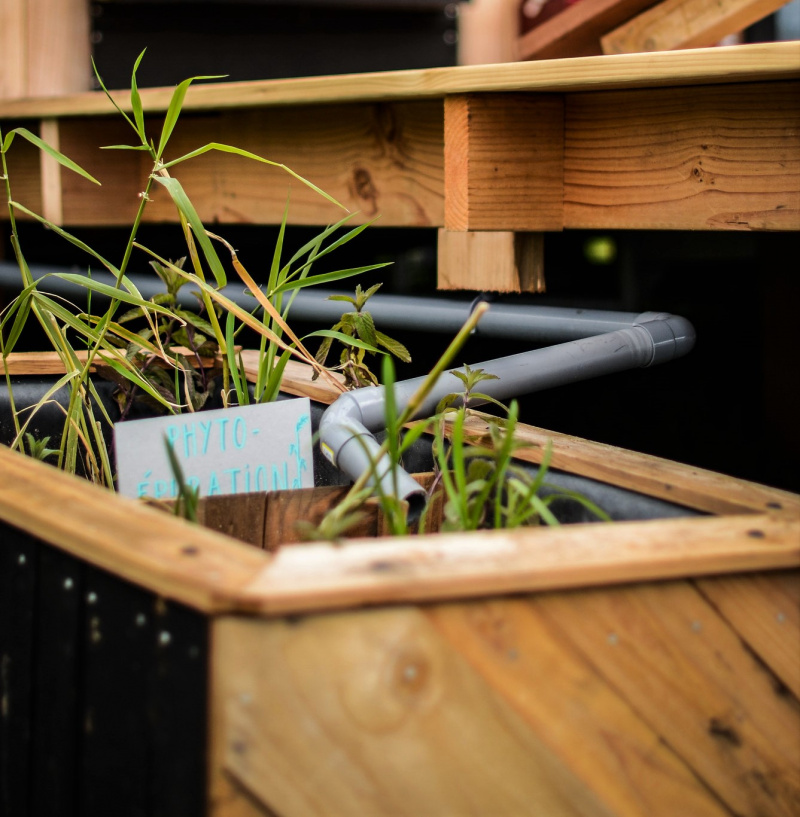
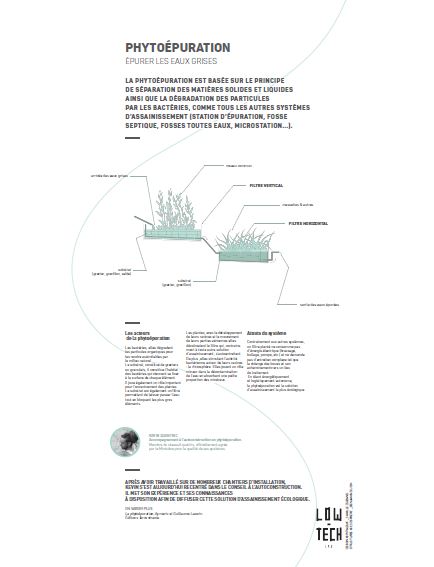
Étape 15 - Educational content to download
You can download an educational sheet created by the Low-tech Lab for the exhibition "In Search of a Sustainable Habitat" in the "Files" part of the tutorial (tab in the "Tools-Materials" section)
Étape 16 -
Do you have a minute? Interested in doing this tutorial or not, your response to this survey helps us improve our tutorials. Thank you in advance for your help!
Like all the work at Low-tech Lab, this tutorial is collaborative. Don't hesitate to add modifications that seem important, and share your results in the comments.
Notes et références
This tutorial has been produced by Clément CHABOT with the assistance of Camille DUBAND and Thibaud LANCIEN out of the work of Kevin QUENTRIC.
English traduction by: Katia Krussel
To take this futher, we recommend reading the book "La Phytoépuration" by Aymeric and Guillaume LAZARIN
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eutrophication
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phragmites_australis
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phyto%C3%A9puration
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phytoremediation
Impact of chemical pollution on life:
Widespread Sexual Disruption in Wild Fish - Susan Jobling - https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/es9710870
Published





























 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português