(Page créée avec « Drilling the evacuation of fresh water. ») |
(Page créée avec « Choose a lower corner of the frames to drill through the tarpaulin and wood a hole of diameter slightly smaller than the diameter of the tube you have. This tube will be f... ») |
||
| Ligne 49 : | Ligne 49 : | ||
|Step_Picture_00=D_salinisateur_solaire_IMG_6683.JPG | |Step_Picture_00=D_salinisateur_solaire_IMG_6683.JPG | ||
|Step_Title=Drilling the evacuation of fresh water. | |Step_Title=Drilling the evacuation of fresh water. | ||
| − | |Step_Content= | + | |Step_Content=Choose a lower corner of the frames to drill through the tarpaulin and wood a hole of diameter slightly smaller than the diameter of the tube you have. This tube will be forced into the hole and through a patch in air chamber which has the role of making a tight connection between the pipe and the cover (the hole drilled in the air chamber is much smaller than the tube, that is forced back into the air chamber). The patch will be glued to the tarpaulin with neoprene glue. The two pipes thus fixed to the frame will open into the freshwater recovery bottle. We will take care to make a hole in the cap of this bottle to allow a good flow. Both pipes pass through the cap. Plan to secure the two tubes to avoid pulling on the inner tube patches while handling the desalinator. |
}} | }} | ||
{{ {{tntn|Tuto Step}} | {{ {{tntn|Tuto Step}} | ||
Version du 15 janvier 2018 à 17:30
Description
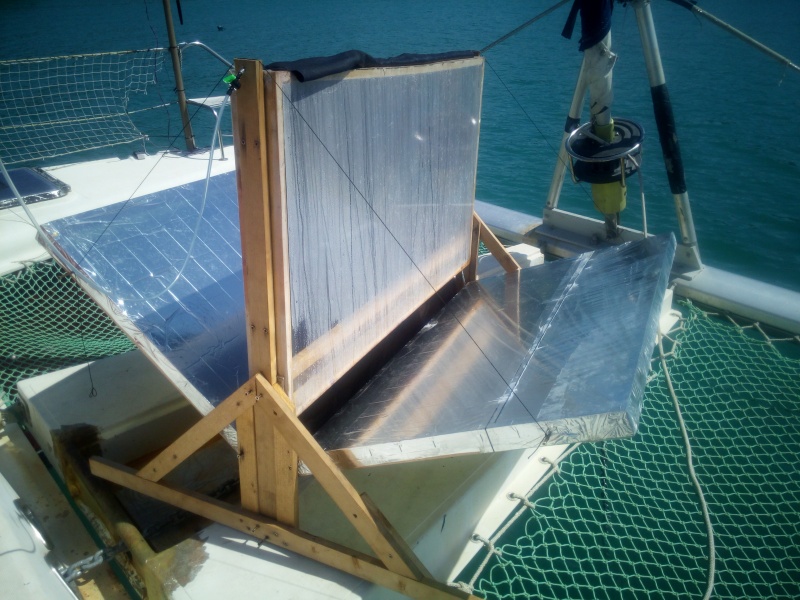
A cloth impregnated with seawater is wedged between two frames on which transparent sheets have been stretched. Thanks to the sun and two reflectors made with a cover of survival, the water of the fabric will evaporate then come to trickle on the baches, while the salt will remain trapped by the fabric. The desalinated water flows down the frames and is collected in a can with two pipes. At the bottom of the frames, waterproofness is essential to the proper functioning of the desalinator.
Sommaire
Sommaire
- 1 Description
- 2 Sommaire
- 3 Étape 1 - Manufacture of freshwater recovery frames
- 4 Étape 2 - Laying the tarpaulin on the freshwater recovery frames.
- 5 Étape 3 - Drilling the evacuation of fresh water.
- 6 Étape 4 - Fabrication des réflecteurs solaires
- 7 Étape 5 - Assemblage
- 8 Étape 6 - Utilisation
- 9 Étape 7 - Remarques
- 10 Notes et références
- 11 Commentaires
Matériaux
- Wooden cleats (used in this tutorial: 44 * 22mm)
- Small plastic tube diameter 5 or 6 mm
- Two bottles of 5 or 6 liters
- Strong and transparent plastic tarpaulin
- Cotton fabric
- Blanket
- Wood screws
- Inner tube
Outils
- Screwdriver or screwdriver
- Drill and drills
- Handsaw
- Tapestry stapler
- Neoprene glue
Étape 1 - Manufacture of freshwater recovery frames
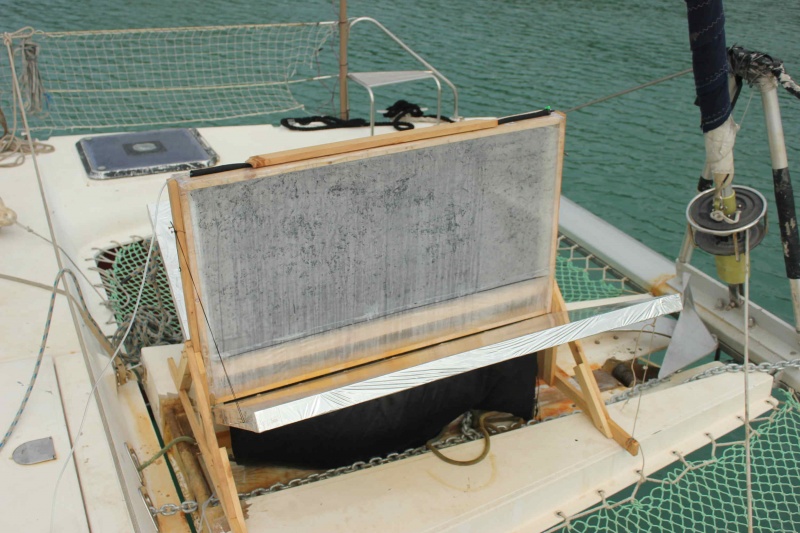
For this model, the chosen floor area is 110 cm horizontal by 66 cm vertical. The wooden battens used have a section of 44 mm by 22 mm. The thickness of the frame is 44 mm. The frame is assembled with screws. At about 10 centimeters from the bottom of the frame, a cleat is added, as can be seen in the picture. It makes it possible to stiffen the frame, to stretch the sheet and to separate the freshwater and seawater parts (no risk of salt contamination).
Étape 2 - Laying the tarpaulin on the freshwater recovery frames.
The tarpaulin should extend about 10 centimeters on each side of the frame, to ensure effective stapling and tension. Begin by stapling the tarpaulin on the separation strip as shown in the diagram (diagram to be added). The tarpaulin should then surround the lower part of the frame and go up, without any staple less than 7 or 8 centimeters from the bottom, at the risk of having water leaks. It will bend the overflowing plastic and staple so as to ensure a tight tank at the bottom of the frame. Finally, cover the panel of the whole tarpaulin and stretch it as much as possible by stapling it inside the frame. Repeat these operations for the second frame.
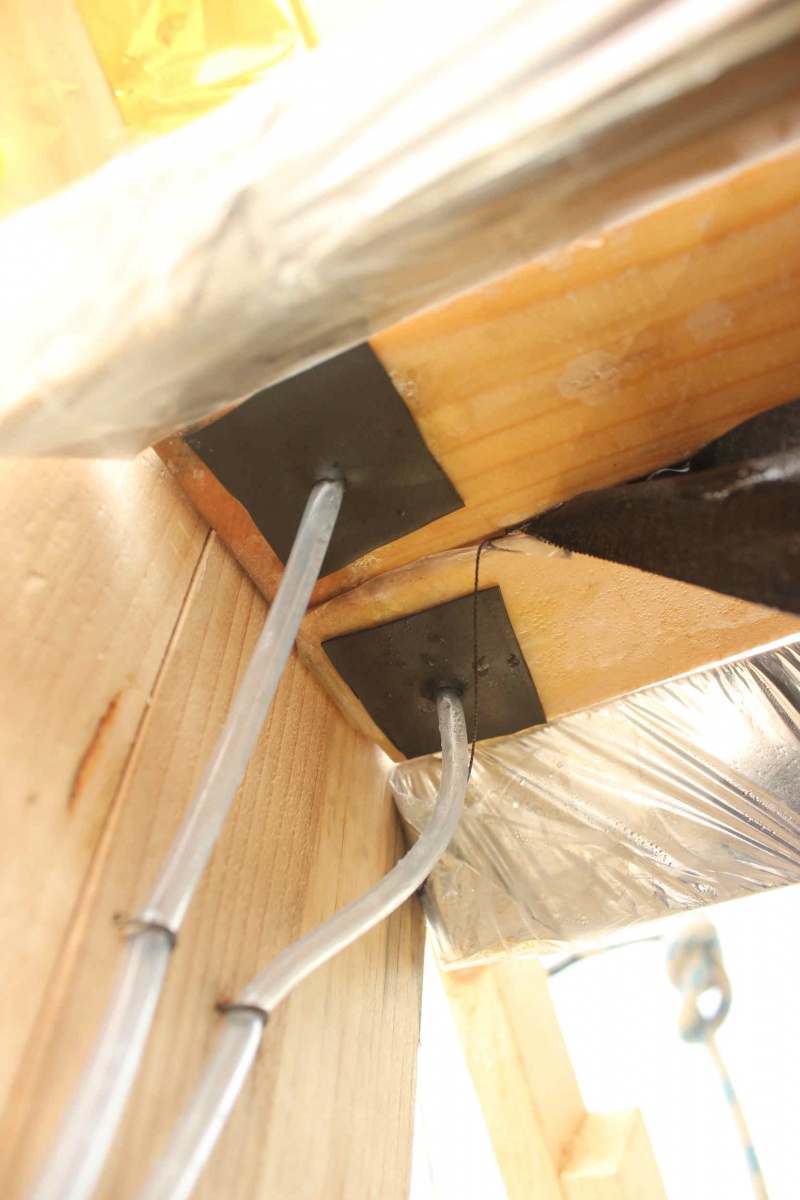
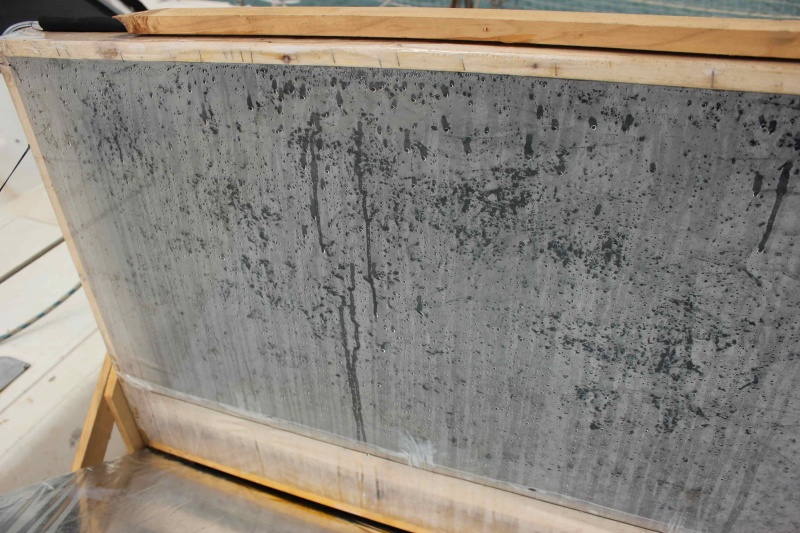
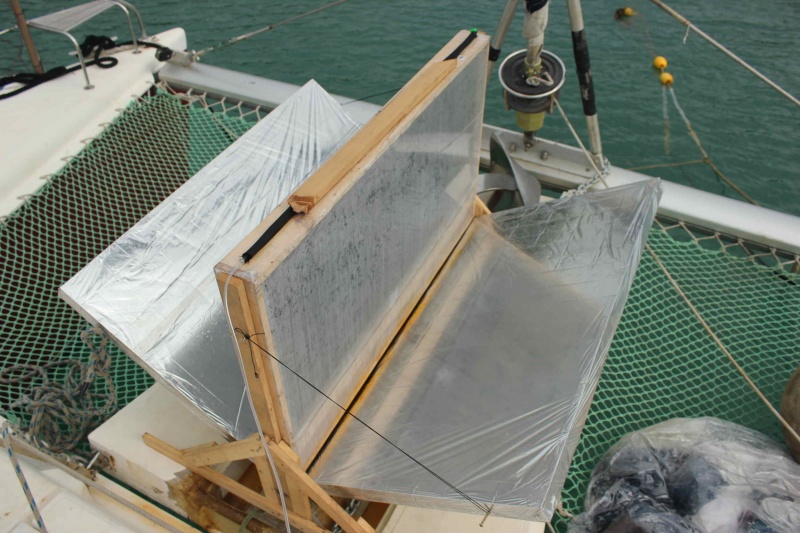
Étape 3 - Drilling the evacuation of fresh water.
Choose a lower corner of the frames to drill through the tarpaulin and wood a hole of diameter slightly smaller than the diameter of the tube you have. This tube will be forced into the hole and through a patch in air chamber which has the role of making a tight connection between the pipe and the cover (the hole drilled in the air chamber is much smaller than the tube, that is forced back into the air chamber). The patch will be glued to the tarpaulin with neoprene glue. The two pipes thus fixed to the frame will open into the freshwater recovery bottle. We will take care to make a hole in the cap of this bottle to allow a good flow. Both pipes pass through the cap. Plan to secure the two tubes to avoid pulling on the inner tube patches while handling the desalinator.
Étape 4 - Fabrication des réflecteurs solaires
Fabriquer deux cadres de mêmes dimensions que les précédents, mais sans le tasseau de renfort. Tendre et agrafer la couverture de survie et la bâche sur le cadre. La bâche sert à protéger la couverture de survie, qui est fragile. C'est le côté argenté de la couverture qui fera face au soleil !
Étape 5 - Assemblage
Agrafer le tissu tendu sur un des deux cadres de récupération d'eau douce, sans que les côtés ne touchent les bords verticaux du cadre. Le tissu est agrafé entre le tasseau du haut du cadre et le tasseau de renfort ! Attention à ne pas faire de trou dans le bas du cadre! Fixer les deux cadres l'un face à l'autre en enfermant le tissu entre les deux. Prévoir 10 centimètres de tissu dépassant en bas et en haut des cadres. Prévoir des pieds pour maintenir le désalinisateur en hauteur. Enfin, fixer les réflecteurs à l'ensemble de manière à pouvoir les inclinez selon la hauteur du soleil. Il seront maintenus en position à l'aide de ficelle.
Étape 6 - Utilisation
Percer un tuyau tous les 4 centimètres à l'aide d'une aiguille à coudre sur toute la longueur du désalinisateur. Au bout de ce tuyau, prévoir un robinet qui permettra de siphonner l'arrivée d'eau de mer. A l'autre extremité, ce tuyau est noyé jusqu'au fond dans une bouteille d'eau de mer, située plus haut que le désalinisateur pour que l'écoulement puisse se faire. Prévoir un robinet en sortie de bouteille d'eau de mer pour régler le débit. La partie percée du tube d'arrivée d'eau de mer est enroulée dans le tissu dépassant en haut des cadres, ainsi, toute l'eau de mer sera captée par le tissu. Poser le désalinisateur face au soleil, ouvrez les réflecteurs, siphonnez l'eau de mer, et observez la condensation à l'intérieur des bâches ! Assez vite, de l'eau douce devrait couler en bas des cadres et remplir la bouteille ! Penché légèrement le désalinisateur à l'aide de cales pour que l'eau douce s'écoule doucement vers les évacuations.
Étape 7 - Remarques
Cette low-tech est actuellement en plein test. Les points testés sont les suivants : - position optimale du désalinisateur et des réflecteurs par rapport au soleil - collecte efficace de l'eau douce - réglage du débit d'eau de mer
Notes et références
- Réalisé par Thomas Piboum et Karel Janik pour Nomade des Mers.
Yes





 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português